Maria Wilińska 1, Thomas E. Bachman 2, Janusz Świetliński Developmental Period Medicine, 2015;XIX,3(I)
|
|
|
- Aleksander Maciejewski
- 7 lat temu
- Przeglądów:
Transkrypt
1 254 Developmental Period Medicine, 2015;XIX,3(I) IMiD, Wydawnictwo Aluna Maria Wilińska 1, Thomas E. Bachman 2, Janusz Świetliński 3 THE CONSEQUENCES OF FAILING ELECTIVE NONINVASIVE RESPIRATORY SUPPORT AS COMPARED TO IMMEDIATE INTUBATION: A POPULATION STUDY OF VERY LOW BIRTH WEIGHT NEONATES NIEPOWODZENIE WENTYLACJI NIEINWAZYJNEJ VS ELEKTYWNA INTUBACJA OD URODZENIA PORÓWNANIE WYNIKÓW LECZENIA; BADANIE POPULACYJNE U NOWORODKÓW Z BARDZO MAŁĄ URODZENIOWĄ MASĄ CIAŁA 1 Department of Neonatology, The Medical Centre of Postgraduate Education, Warsaw, Poland 2 Czech Technical University, Prague 3 Silesia Institute of Mother and Newborn, Chorzow, Poland Abstract Introduction: Elective noninvasive respiratory support has become common. However, many neonates fail this procedure and they may require intubation. The aim of this study was to determine the relative outcome of very low birth weight neonates who failed noninvasive respiratory support compared to those that were initially intubated and mechanically ventilated. Material and methods: We accessed the database of every neonate who received respiratory support in 18 hospitals in the central region of Poland and examined the records for a 7-year period. The evaluation encompassed 1667 neonates with very low birth weight who were potential candidates for elective noninvasive respiratory support. Three prospective primary outcome measures were assessed using logistic regression to control for differences in baseline risk. We also examined the length of respiratory support corrected for EGA. Results: After controlling for significant baseline factors, we found that there was no statistically significant difference in mortality, severe retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) or severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) between infants failing noninvasive respiratory support and those electively intubated. However, their mortality and severe ROP were significantly higher than in those successfully treated with noninvasive respiratory support. Additionally, there was no difference in the length of mechanical ventilation or the length of all respiratory support between those that failed noninvasive support and those that were electively intubated. Conclusion: Our study suggests that in those preterm infants who are at a higher risk of failing noninvasive ventilation there is no compelling reason to administer elective intubation and mechanical ventilation immediately after birth. It seems that efforts should rather be made towards the implementation of the optimal non-invasive respiratory support. Key words: noninvasive ventilation, preterm infants, treatment outcome, retrospective study Streszczenie Wstęp: Nieinwazyjna wentylacja stała się powszechną metodą wspomagania oddychania u nowo-rodków. Jednakże nie u wszystkich pacjentów jest ona skuteczna i konieczne jest jednak ich zaintubowanie.
2 The consequences of failing elective noninvasive respiratory support as compared to immediate intubation 255 Cel: Celem naszych badań było porównanie wyników leczenia grupy noworodków z bardzo małą urodzeniową masą ciała (very low birth weight VLBW), u których wentylacja nieinwazyjna była nieskuteczna z grupą noworodków VLBW intubowanych bezpośrednio po urodzeniu i wentylowanych mechanicznie. Materiał i metody: W 18 szpitalach centralnego regionu Polski zebrano dane o każdym dziecku, które w okresie 7 lat otrzymało wsparcie oddychania. Analizie poddano 1667 noworodków z bardzo małą urodzeniową masą ciała, u których po urodzeniu istniała konieczność zastosowania wsparcia oddechowego. Metodą regresji logistycznej oceniano trzy pierwotne punkty końcowe. Dodatkowo analizowano długotrwałość stosowanego wsparcia oddechowego. Wyniki: Nie było różnic istotnych statystycznie w długości stosowanego wsparcia oddechowego między grupą noworodków intubowanych po nieskutecznym wsparciu nieinwazyjnym a intubowanymi elektywnie bezpośrednio po urodzeniu i wentylowanymi mechanicznie. Wykazano, po skontrolowaniu istotnych czynników wyjściowych, brak różnic w śmiertelności oraz występowaniu ciężkiej retinopatii wcześniaczej i ciężkiej dysplazji oskrzelowo-płucnej między obiema grupami. W obu powyższych grupach śmiertelność i występowanie ROP było istotnie wyższe niż w grupie skutecznie leczonej od urodzenia wsparciem nieinwazyjnym. Wnioski: Nasze badanie wykazuje, że w grupie noworodków przedwcześnie urodzonych z podwyższonym ryzykiem niepowodzenia wentylacji nieinwazyjnej nie ma istotnych powodów do planowej intubacji i wentylacji mechanicznej bezpośrednio po urodzeniu. Dla poprawy wyników leczenia należy optymalizować nieinwazyjne wspomaganie oddychania. Słowa kluczowe: wentylacja nieinwazyjna, noworodki przedwcześnie urodzone, wyniki leczenia, badanie retrospektywne. DEV PERIOD MED. 2015;XIX,3,I: BACKGROUND Noninvasive respiratory support of neonates was first reported in 1971 [1]. The use of elective noninvasive respiratory support had become quite common by the last decade [2, 3] and encompassed both continuous and biphasic positive airway pressure. The aggregate of related randomized controlled trials has now confirmed the safety and effectiveness of noninvasive respiratory support and rescue surfactant as a more useful method in comparison to elective surfactant and mechanical ventilation [4]. We also reported that the increased use of noninvasive ventilation in Poland led to decreased neonatal mortality [5]. Some focus has been placed on the selection of appropriate candidates for elective noninvasive respiratory support [6-9], though no general guidelines have evolved. There is a consensus that infants that fail elective noninvasive respiratory support and are subsequently intubated have poorer outcomes. While a few studies support this [8, 10], there is a paucity of evidence to suggest that these infants would have been better off having been initially intubated and managed with invasive ventilation. We previously developed a database of the baseline parameters, the course of treatment and outcome for every infant requiring respiratory support in the central region of Poland over a 7-year period [5]. AIM To determine the relative outcome of very low birth weight (VLBW) neonates who failed noninvasive respiratory support compared to those that were electively intubated and mechanically ventilated. MATERIAL AND METHODS In collaboration with the Noninvasive Respiratory Support Group of the Polish Neonatal Society, a program was developed to capture the course of treatment and outcomes of all the neonates requiring respiratory support in 18 hospitals in the central region of Poland [5]. The project, including a publication of its analyses, was approved by the Ethics Committee of each of the participating centers. The database collected over a 7- year period includes the demographics, respiratory care and neonatal outcomes of every neonate requiring respiratory support in the region. It straddles the adoption of new guidelines calling for expanded use of noninvasive ventilation. Our definition of respiratory support did not include supplemental oxygen or high-flow nasal support, but rather only invasive or noninvasive ventilation. The latter included nasal continuous and biphasic continuous airway pressure [NCPAP] delivered either with Infant Flow (CareFusion, Yorba Linda California) or ventilator based NCPAP. The median year of this study was The data were collected by means of careful chart reviews conducted by clinicians at each hospital. Once submitted to the coordinating center, data were carefully reviewed for completeness and illogical responses. This was accomplished through rule-based data flagging and also by manual review. Clinical monitors adjudicated apparent problems in addition to conducting site visits to clarify and audit the data.
3 256 Maria Wilińska et al. Of the 5551 infants requiring respiratory support in our database, 2002 had birth weights of 1500 grams or less. Of these, 335 were excluded from the analysis, because they were felt to be poor candidates for elective noninvasive respiratory support based on low Apgar scores. Of the 335 infants who were excluded, nearly all, i.e. 285, had been electively intubated. Thus, the population that was analyzed comprised 1667 VLBW infants. Of these 55% were electively intubated and invasively ventilated and the rest were electively managed with noninvasive respiratory support. Noninvasive respiratory support failure and subsequent intubation occurred in 21%. The population analyzed thus comprised three groups: noninvasive respiratory support successes (589), noninvasive respiratory support failures (161) and elective intubations (917). To select the population to be analyzed for this study, the cases of all the neonates with a birth weight of 1500 grams or less were identified. Clearly, neonates that were not spontaneously breathing or were moribund were not appropriate candidates for elective noninvasive ventilation. To address this, we excluded neonates that had a 1-minute Apgar score of 1 or less or a 5-minute Apgar score of 3 or less. Infants that were initially intubated for the administration of surfactant and extubated within 2 hours of birth and then managed noninvasively were categorized as elective noninvasive support. Noninvasive failure was defined as subsequent intubation and mechanical ventilation. We prospectively identified three primary outcome measures. The first was mortality at discharge. The other two were severe BPD (bronchopulmonary dysplasia) and severe ROP (retinopathy of prematurity) among survivors. Severe ROP was defined as the need for laser therapy. Severe BPD was defined as the need for 0.30 inspired oxygen, or continued respiratory support at 36 weeks post conceptual age. Severe BPD was selected due to its being associated with significant long-term morbidity. We hypothesized that the outcomes of infants who failed noninvasive respiratory support would be no worse than those electively intubated, after controlling for baseline risk factors. We developed a separate logistic regression model to control for baseline risk for each of the three outcomes. Twelve baseline parameters were evaluated as risk factors (estimated gestational age (EGA), birth weight, small for gestational age), elective surfactant (first two hours of life), gender, outborn delivery, Apgar 1, Apgar 5, C-Section, singleton birth, gestational diabetes, and antenatal steroids). Each model was constructed using backward stepwise logistic regression of these 12 potential risk factors. The only risk factors that were statistically significantly related to the dependent variable (primary outcome) were retained in each of the three models. Following the development of the risk model, the tricotomous respiratory support category variable was added, with its p-value indicating significance among the 3 categories. Differences between pairs of the three were then evaluated with the risk model. When the differences were significant, the Relative Risk (RR) was calculated based on the Odds Ratio (OR) and nominal incidence rates for the two in order to help interpretation. The Pearson chi-square test was used to evaluate differences in categorical variables for treatment groups. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) was used to evaluate differences among continuous variables for the three treatment groups. Differences between two of the three were evaluated using the post hoc Least Squares Difference test. For all the statistical analyses a p<0.05 was considered statistically significant. RESULTS Table I presents a summary of the baseline status for each of the three categories. There were marked differences among the three groups. What is of note is a slight, but statistically significant difference in the birth-weight and maturity. Of more clinical relevance, and likely associated with the selection of the mode of elective support, were statistically significant differences in such factors as the use of prenatal steroids, outborn delivery, Apgar scores and use of surfactant within 2 hours of birth. The outcomes for each of the 3 treatment categories are summarized in table II. There were marked, clinically relevant, statistically significant differences among the groups for most of these parameters. While the statistics is not shown in the table, the infants who successfully managed with noninvasive respiratory support experienced significantly decreased severe BPD (p<0.001), severe ROP and shorter respiratory support. There were no differences in the length of mechanical ventilation or total length of respiratory support between those electively intubated and those failing noninvasive respiratory support. Table III identifies the baseline risk factors that were found to be statistically significantly related to the three clinical outcomes: mortality, severe retinopathy of prematurity and severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Birth weight and EGA were significant risk factors for all the three outcomes. In addition, five other risk factors were statistically significant for mortality (SGA, Apgar 5, elective surfactant, antenatal steroids, and outborn status). For severe ROP in survivors one other risk factor, i.e. C-section, was statistically significant. For severe BPD among survivors, two other risk factors were statistically significant, i.e. antenatal steroids, and being outborn. After controlling for these significant baseline variables, the difference in mortality persisted among the three groups. However, the difference in mortality between noninvasive respiratory support failures and elective intubation did not persist. In contrast, patients with noninvasive respiratory support success had a markedly lower risk of mortality than patients with failures (p<0.001, RR=0.27) and than those initially intubated (p<0.001 RR=0.32). After controlling for significant baseline variables, the difference in the incidence of severe ROP among the 3 groups was diminished. The difference in risk between noninvasive respiratory support
4 The consequences of failing elective noninvasive respiratory support as compared to immediate intubation 257 Table I. Characteris cs of neonates in the study groups regarding selected clinical and demographic parameters. Tabela I. Charakterystyka noworodków w badanych grupach pod względem wybranych parametrów demograficznych i klinicznych. NRS Success (NIW powodzenie) NRS Failure (NIW niepowodzenie) Elec ve MV (Elektywna MW) p-value:nrs Success vs. NRS Failure (p-value NIW powodzenie vs. NIW niepowodzenie) p-value:nrs Success vs. MV (p-value NIW powodzenie vs. MW) p-value:nrs Failure vs. MV (p-value: NIW niepowodzenie vs. MW) [A] [B] [C] [p value: A vs. B] [p value: A vs. C] [p value: B vs. C] n Weight (kg) Masa ciała (kg) EGA [hbd] Wiek płodowy [tydzień ciąży] SGA (%) Hipotrofia wewnątrzłonowa (%) Gender (% female) Płeć (%żeńskiej) Singleton (%) Ciąża pojedyncza (%) C-Sec on Cięcie cesarskie Gesta onal Diabetes (%) Cukrzyca ciężarnej (%) Antenatal steroids (%) Sterydy prenatalne (%) Outborn (%) Urodzone poza ośrodkiem (%) 1.19 (.25) 1.11 (.26) 1.04 (.27) =0.001 <0.001 = (2.6) 28.7 (2.6) 28.0 (2.6) <0.001 <0.001 = ns ns ns ns ns Ns ns ns Ns ns ns ns ns ns ns =0.002 ns = <0.001 <0.001 ns Apgar 1 min 5.9 (2.6) 6.0 (2.6) 4.6 (2.6) ns <0.001 <0.001 Apgar 5 min 7.1 (1.7) 7.0 (1.8) 5.9 (1.8) ns <0.001 <0.001 Early surfactant (%) Wczesna podaż surfaktantu (%) ns ns ns Abbrevia ons (skróty): NRS noninvasive respiratory support (NIW nieinwazyjne wsparcie oddechowe) MV elec ve intuba on and invasive ven la on (MW elektywna intubacja i wentylacja inwazyjna) Table descrip on (opis tabeli): Con nuous data are presented as mean (standard devia on). The p value reflects the difference among the 3 groups, determined by ANOVA or chi-squared, as appropriate. Dane ciągłe są prezentowane w postaci średniej (odchylenia standardowego). Wartość p przedstawiono jako wynik testu analizy wariancji lub chi-kwadrat.
5 258 Maria Wilińska et al. Table II. The clinical characteris cs of neonates in the study groups. Tabela II. Charakterystyka kliniczna noworodków w badanych grupach. NRS Success (NIW powodzenie) NRS Failure (NIW niepowodzenie) Elec ve MV (Elektywna MW) p-value: NRS Success vs. NRS Failure (p-value) (NIW powodzenie vs. NIW niepowodzenie) p-value: NRS Success vs. MV (p-value) (NIW powodzenie vs. MW) p-value: NRS Failure vs. MV (p-value): (NIW niepowodzenie vs. MW) [A] [B] [C] [p value: A vs. B] [p value: A vs. C] [p value: B vs. C] n Any surfactant (%) Podaż surfaktantu (%) PDA Treated (%) Leczenie przetrwałego przewodu tętniczego (%) <0.001 <0.001 < <0.001 ns ns All pa ents (wszyscy pacjenci) Pneumothorax (%) Odma opłucnowa(%) Death (%) Zgon (%) Length MV (weeks PCA) Długość MW (wiek postkoncepcyjny) Length RS (weeks PCA) Długość wsparcia oddechowego (wiek postkoncepcyjny) Severe BPD (%) Ciężka dysplazja oskrzelowo-płucna(%) <0.001 <0.001 ns <0.001 <0.001 = (2.4) 29.6(2.7) - - = (5.3) 40.4(10.4) 39.6(14.7) <0.001 <0.001 ns ns <0.001 ns Among survivors (tylko pacjenci, którzy przeżyli) Severe ROP (%) Ciężka re nopa a wcześniaków (%) <0.001 <0.001 ns Abbrevia ons (skróty): NRS noninvasive respiratory support (NIW nieinwazyjne wsparcie oddechowe) MV elec ve intuba on and invasive ven la on (MW elektywna intubacja i wentylacja inwazyjna) Severe ROP is defined as the need for laser treatment. (Ciężka e nopa a wcześniaków jest określana jako wymagajaca laseroterapii.) Severe BPD as the need for 0.30 FiO2 or respiratory support at 36 weeks PCA. (Ciężka dysplazja oskrzelowo-płucna jako konieczność stosowania biernej tlenoterapii co najmniej 30% lub jakiegokolwiek wsparcia oddechowego w 36 tygodniu wieku postkoncepcyjnego) Table descrip on (opis tabeli): Con nuous data are presented as mean (standard devia on). The p value reflects the difference among the 3 groups, determined by ANOVA or chi-squared, as appropriate. Dane ciągłe są prezentowane w postaci średniej (odchylenia standardowego). Wartość p przedstawiono jako wynik testu analizy wariancji lub chi-kwadrat.
6 The consequences of failing elective noninvasive respiratory support as compared to immediate intubation 259 Table III. Analysis of the prevalence of clinical failures. Tabela III. Analiza częstości występowania niepowodzeń klinicznych. EGA Wiek płodowy Birth weigh Urodzeniowa masa ciała Small for GA Za mały w stosunku do wieku płodowego Early surfactant Wczesna podaż surfaktantu Outborn Urodzony poza ośrodkiem Apgar 5 min Ocena wg skali Apgar Cesarean Sec on Cięcie cesarskie Antenatal steroids Sterydoterapia prenatalna Mortality Umieralność Severe ROP Ciężka re nopa a wcześniaków Severe BPD Ciężka dysplazja oskrzelowo-płucna <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 =0.030 <0.001 =0.006 ns ns =0.041 ns ns =0.037 ns <0.001 <0.001 ns ns ns =0.014 ns =0.010 ns =0.002 Small for GA body weight below 10 pc for age (Za mały w stosunku do wieku płodowego masa ciała poniżej 10 percentyla dla wieku GA gesta onal age (wiek płodowy) Early surfactant in the first two hours a er birth (Wczesna podaż surfaktantu w pierwszych dwóch godzinach po urodzeniu) Abbrevia ons (skróty): EGA es mated gesta onal age (szacowany wiek płodowy) Severe ROP is defined as the need for laser treatment (Ciężka e nopa a wcześniaków jest określana jako wymagająca laseroterapii.) Severe BPD as the need for 0.30 FiO2 or respiratory support at 36 weeks PCA (Ciężka dysplazja oskrzelowo-płucna jako konieczność stosowania biernej tlenoterapii co najmniej 30% lub jakiegokolwiek wsparcia oddechowego w 36 tygodniu wieku postkoncepcyjnego) failures and elective intubations was not statistically significant. Those neonates who were successfully treated with noninvasive respiratory support had less risk of severe-rop than those electively intubated (p=0.042, RR=0.66) and those that failed (p=0.012 RR=0.48). After controlling for significant baseline variables, the differences in the incidence of severe BPD among the 3 groups disappeared (tab. IV). DISCUSSION We evaluated a population of 1667 VLBW infants felt to have been candidates for elective noninvasive ventilation to determine if there were consequences of delayed intubation associated with noninvasive ventilation failure. It is our belief that the present report is the first one comparing infants failing elective noninvasive respiratory support with those electively intubated. We found that after controlling for baseline risk factors, there were no significant consequences of noninvasive failure and subsequent delayed intubation. We evaluated mortality and, for those who were survivors, severe ROP, severe BPD as well as length of support. Mortality, severe ROP and severe BPD, controlling for baseline risks, were comparable. The length of respiratory support and mechanical ventilation, and adjusting for EGA, were also nearly identical. Other authors have reported comparisons of noninvasive respiratory support success and failure. In line with our expectations, after controlling for baseline risks, we found that those neonates who successfully managed with noninvasive respiratory support, compared to the ones electively or subsequently intubated, had markedly lower mortality and also less severe ROP. We also found that the incidence of severe BPD seen among the three groups was fully explained by the baseline risk factors. In the population we analyzed this is not surprising. From an observational study of extremely preterm infants (32 weeks EGA or less), Dargaville et al. recently reported on the outcome of those who failed NCPAP, as compared to those that succeeded [10]. They found an increase in BPD, major morbidities and mortality associated with NCPAP failure, but only among those infants who were 28 weeks EGA or less. However, their analysis of mortality and morbidity did not control for baseline risk factors. A recent metaanalysis of randomized comparisons of NCPAP and elective intubation found a trend suggesting reduced mortality associated with elective NCPAP, reduced BPD and reduced severe ROP [4]. However, only the combined variable of death or BPD was lower in a statistically significant way. The trials in this metaanalysis all included only infants of lower maturity than those in our evaluation. We identified birth weight and
7 260 Maria Wilińska et al. Table IV. Evalua on of rela ve risk of clinical failure in three compared groups of respiratory support. Tabela IV. Ocena ryzyka względnego niepowodzeń klinicznych w trzech porównywanych grupach wsparcia oddechowego. p-value OR (95% CI) Iloraz szans (95% przedział ufności) RR Ryzyko względne Mortality Umieralność NRS Failure/MV NIW niepowodzenie/mw NRS Success/MV NIW powodzenie/mw NIV Success/Failure NIW powodzenie/niepowodzenie Severe ROP Ciężka re nopa a wcześniaków NRS Failure/MV NIW nieskuteczna/mw NRS Success/MV NIW powodzenie/mw NIV Success/Failure NIW powodzenie/niepowodzenie Severe BPD Ciężka dysplazja oskrzelowo-płucna NRS Failure/MV NIW niepowodzenie/mw NRS Success/MV NIW powodzenie/mw NIV Success/Failure NIW powodzenie/niepowodzenie < ( ) na < ( ).32 < ( ) ( ) na ( ) ( ) ( ) na ( ) na ( ) na Abbrevia ons (skróty): NRS noninvasive respiratory support (NIW nieinwazyjne wsparcie oddechowe) MV elec ve intuba on and invasive ven la on (MW elektywna intubacja i wentylacja inwazyjna) Severe ROP is defined as the need for laser treatment (Ciężka e nopa a wcześniaków jest określana jako wymagajaca laseroterapii.) Severe BPD as the need for 0.30 FiO2 or respiratory support at 36 weeks PCA (Ciężka dysplazja oskrzelowo-płucna jako konieczność stosowania biernej tlenoterapii co najmniej 30% lub jakiegokolwiek wsparcia oddechowego w 36 tygodniu wieku postkoncepcyjnego) Table descrip on (opis tabeli): OR is Odds Ra o and RR the Rela ve Risk. CI is confidence Interval. OR iloraz szans, RR ryzyko względne, CI przedział ufności EGA as significant risk factors in our risk model for each of the three outcomes, which is consistent with the findings of these two studies. It is not clear to what degree outcomes are driven by baseline risk rather than the success or failure of elective noninvasive respiratory support. Our data suggest that that failure has its consequences when compared to successful noninvasive respiratory support, but not to elective intubation. Timing the decision of when to intubate might also be an important factor. Whether morbidity is associated with the physiological perturbations of failure (e.g. pneumothorax, poorer gas exchange) or the consequences of eventual intubation and its inherent risks, is, however, uncertain. Several authors have reported that increasing FiO2 requirements in response to noninvasive respiratory support is a predictor of eventual noninvasive respiratory support failure [7, 10]. We believe more research is needed to identify the optimum criteria for failure of noninvasive respiratory support and the corresponding appropriate time for subsequent intubation. However, it should be remembered that adverse events associated with tracheal intubation are still common in neonatal intensive care units [11]. Some work suggests that differences in the effectiveness of noninvasive respiratory support are associated with elements of management. Buzzella et al. reported from a randomized trial that increased success was associated with a strategy of higher nominal NCPAP pressures [12]. Others have reported on the differences in the effectiveness associated with the type of device [9, 13, 14]. The mode of support is also believed to be important. Ramanathan et al. recently reported results from a randomized trial comparing
8 The consequences of failing elective noninvasive respiratory support as compared to immediate intubation 261 NCPAP and NIPPV, finding the latter more effective [15]. However, another larger trial of more diverse devices did not confirm this conclusion [16]. While all these variations are evident, we further suggest that optimizing noninvasive respiratory support management (mode, pressures and perhaps devices) and reducing treatment failure might result in better relative outcomes. However, much work needs to be done to evaluate optimum strategies, before careful comparisons of these factors can be undertaken. Our study has limitations. It is a population study and not data from a randomized comparison. A project of the latter kind would be needed to compare specific noninvasive respiratory support populations, strategies and failure criteria. To address the natural selection of our population, we controlled for relevant risks associated with 12 baseline parameters. Other factors not available to us might have yielded different results. We also used initial Apgar scores to exclude infants less appropriate for noninvasive respiratory support. A different threshold, and thus a different population, might yield different results. Finally, the conditions of prenatal practice in Poland 10 years ago, most notably the limited use of surfactant and also the lower utilization of antenatal steroids, might have an effect on the applicability of our findings. CONCLUSIONS There is nothing in this study to suggest outcomes could have been markedly improved if more neonates were intubated electively. This information is definitely directly projectable to healthcare systems which are in the process of developing prenatal practices. We also believe that it has important implications in areas with more developed practices. Most importantly, it highlights the importance of considering baseline risk when evaluating the outcomes associated with delayed intubation. In addition, we suggest that more emphasis, in both research and clinical practice, needs to be placed on improving the management of noninvasive respiratory support. This includes not only the refined use of support pressure and perhaps the expanded use of biphasic noninvasive respiratory support and noninvasive positive pressure ventilation, but also optimal noninvasive respiratory support failure criteria. Acknowledgement The creation of this database was funded by a generous grant from the Great Orchestra of Christmas Charity and support from The Medical Centre of Postgraduate Education. We would also like to acknowledge the supervision and guidance of the Noninvasive Respiratory Support Group of the Polish Neonatal Society and the leadership and vision of Professor Elżbieta Gajewska. REFERENCES 1. Gregory GA, Kitterman JA, Phibbs RH, Tooley WH, Hamilton WK. Treatment of the idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome with CPAP. NEJM 1971;284(24): Soll RF, Edwards EM, Badger GJ, Kenny MJ, Kate A. Morrow KA, et al. Obstetric and Neonatal Care Practices for Infants 501 to 1500 g From 2000 to Pediatrics. 2013;132; Bachman TE, Marks NE, Rimensberger PC. Factors effecting adoption of new neonatal and pediatric respiratory technologies. Intensive Care Med. 2008;Jan;34(1): Schmölzer GM, Kumar M, Pichler G, Aziz K, O Reilly M, Cheung PY. Non-invasive versus invasive respiratory support in preterm infants at birth: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2013;347:f Wilinska M, Bachman TE, Swietlinski J, Gajewska, E;Meller J, Helwich, et al. Impact of the Shift to Neonatal Noninvasive Ventilation in Poland: A Population Study. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2014;15: Swietlinski J, Bachman T, Gajewska E, Bober K, Helwich E, Lauterbach R, et al. Factors affecting outcomes in very low birth weight infants treated electively with nasal continuous positive airway pressure. J Perinatol. 2010;30(2): Fuchs H, Lindner W, Leiprecht A, Mendler MR, Hummler HD. Predictors of early nasal CPAP failure and effects of various intubation criteria on the rate of mechanical ventilation in preterm infants of <29 weeks gestational age. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2011;96:F343-F Ammari A, Suri M, Milisavljevic V, Sahni R, Bateman D, Sanocka U, et al. Variables associated with the early failure of nasal CPAP in very low birth weight infants. J Pediatr. 2005;147: Bober K, Swietlinski J, Zejda J, Kornacka K, Pawlik D, Behrendt J, et al. A multicenter randomized controlled trial comparing effectiveness of two nasal continuous positive airway pressure devices in very-low-birth-weight infants. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2012;13: Dargaville PA, Aiyappan A, De Paoli AG, Dalton RGB, Carl A. Kuschel CA, Kamlin O, et al. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Failure in Preterm Infants: Incidence, Predictors and Consequences. Neonatology. 2013;104: Foglia EE, Ades A, Napolitano N, Leffelman J, Nadkarni V, Nishisaki A. Factors Associated with Adverse Events during Tracheal Intubation in the NICU Neonatology 2015;108: Buzzella B, Claure N, D Ugard C, Bancalari E. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Two Nasal Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Levels after Extubation in Preterm Infants. J Pediatr. 2014;164(1); Courtney SE, Pyon KH, Saslow JG, Arnold GK, Pandit PB, Habib RH. Lung recruitment and breathing pattern during variable versus continuous flow nasal continuous positive airway pressure in premature infants: an evaluation of three devices. Pediatrics 2001 Feb;107(2): Supta S, Sinha SK, MD, Tin W, Donn SM. A randomized controlled trial of post-extubation bubble continuous positive airway pressure versus Infant Flow Driver continuous positive airway pressure in preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome. J Pediatr 2009;154(6): Ramanathan R, Sekar KC, Rasmussen M, Bhatia J, Soll RF. Nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation after
9 262 Maria Wilińska et al. surfactant treatment for respiratory distress syndrome in preterm infants <30 weeks gestation: a randomized, controlled trial. J Perinatol. 2012;32: Kirpalani H, Millar D, Lemyre B, Yoder BA, Chiu A, et al. A trial comparing noninvasive ventilation strategies in preterm infants. N Engl J Med Aug 15;369(7): Author s contributions/wkład Autorów According to the order of the Authorship/Według kolejności Conflicts of interest/konflikt interesu The Authors declare no conflict of interest. Autorzy pracy nie zgłaszają konfliktu interesów. Received/Nadesłano: r. Accepted/Zaakceptowano: r. Published online/dostępne online Address for correspondence: Maria Wilińska The Medical Centre of Postgraduate Education, Warsaw, Poland ul. Czerniakowska 231, Warszawa tel. (+48) wilinska.maria@gmail.com
Żywienie wyłącznie mlekiem własnej matki vs żywienie naturalne z udziałem mleka kobiecego pasteryzowanego
 Żywienie wyłącznie mlekiem własnej matki vs żywienie naturalne z udziałem mleka kobiecego pasteryzowanego porównanie w okresie 4 lat (2012-2016) Maria Wilińska, CMKP 1 Mleko Matki jest zawsze pierwszym
Żywienie wyłącznie mlekiem własnej matki vs żywienie naturalne z udziałem mleka kobiecego pasteryzowanego porównanie w okresie 4 lat (2012-2016) Maria Wilińska, CMKP 1 Mleko Matki jest zawsze pierwszym
 aforementioned device she also has to estimate the time when the patients need the infusion to be replaced and/or disconnected. Meanwhile, however, she must cope with many other tasks. If the department
aforementioned device she also has to estimate the time when the patients need the infusion to be replaced and/or disconnected. Meanwhile, however, she must cope with many other tasks. If the department
Ocena skuteczności preparatów miejscowo znieczulających skórę w redukcji bólu w trakcie pobierania krwi u dzieci badanie z randomizacją
 234 Ocena skuteczności preparatów miejscowo znieczulających skórę w redukcji bólu w trakcie pobierania krwi u dzieci badanie z randomizacją The effectiveness of local anesthetics in the reduction of needle
234 Ocena skuteczności preparatów miejscowo znieczulających skórę w redukcji bólu w trakcie pobierania krwi u dzieci badanie z randomizacją The effectiveness of local anesthetics in the reduction of needle
Warsztaty Ocena wiarygodności badania z randomizacją
 Warsztaty Ocena wiarygodności badania z randomizacją Ocena wiarygodności badania z randomizacją Każda grupa Wspólnie omawia odpowiedź na zadane pytanie Wybiera przedstawiciela, który w imieniu grupy przedstawia
Warsztaty Ocena wiarygodności badania z randomizacją Ocena wiarygodności badania z randomizacją Każda grupa Wspólnie omawia odpowiedź na zadane pytanie Wybiera przedstawiciela, który w imieniu grupy przedstawia
Rozpoznawanie twarzy metodą PCA Michał Bereta 1. Testowanie statystycznej istotności różnic między jakością klasyfikatorów
 Rozpoznawanie twarzy metodą PCA Michał Bereta www.michalbereta.pl 1. Testowanie statystycznej istotności różnic między jakością klasyfikatorów Wiemy, że możemy porównywad klasyfikatory np. za pomocą kroswalidacji.
Rozpoznawanie twarzy metodą PCA Michał Bereta www.michalbereta.pl 1. Testowanie statystycznej istotności różnic między jakością klasyfikatorów Wiemy, że możemy porównywad klasyfikatory np. za pomocą kroswalidacji.
Lek. med. Arkadiusz Soski. Streszczenie
 Lek. med. Arkadiusz Soski Streszczenie Wstęp Rozwojową dysplazję stawu biodrowego (DDH developmental dysplasia of the hip) uznaje się za najczęstszą wadę u noworodków i niemowląt. Wada ta powstać może
Lek. med. Arkadiusz Soski Streszczenie Wstęp Rozwojową dysplazję stawu biodrowego (DDH developmental dysplasia of the hip) uznaje się za najczęstszą wadę u noworodków i niemowląt. Wada ta powstać może
STRESZCZENIE Słowa kluczowe: Wstęp Cel pracy
 STRESZCZENIE Słowa kluczowe: Noworodek urodzony przedwcześnie, granulocyt obojętnochłonny, molekuły adhezji komórkowej CD11a, CD11b, CD11c, CD18, CD54, CD62L, wczesne zakażenie, posocznica. Wstęp W ostatnich
STRESZCZENIE Słowa kluczowe: Noworodek urodzony przedwcześnie, granulocyt obojętnochłonny, molekuły adhezji komórkowej CD11a, CD11b, CD11c, CD18, CD54, CD62L, wczesne zakażenie, posocznica. Wstęp W ostatnich
Współczesna rola surfaktantu na Sali porodowej
 Współczesna rola surfaktantu na Sali porodowej dr n. med. Anita Chudzik Historia surfaktantu 1. 1959r. -AveryiMeadniedobórsurfaktantu odgrywa kluczowa rolę w patogenezierds. 2. 1972 r. -Enhorningand Robertsonpierwszedotchawiczepodanie
Współczesna rola surfaktantu na Sali porodowej dr n. med. Anita Chudzik Historia surfaktantu 1. 1959r. -AveryiMeadniedobórsurfaktantu odgrywa kluczowa rolę w patogenezierds. 2. 1972 r. -Enhorningand Robertsonpierwszedotchawiczepodanie
SSW1.1, HFW Fry #20, Zeno #25 Benchmark: Qtr.1. Fry #65, Zeno #67. like
 SSW1.1, HFW Fry #20, Zeno #25 Benchmark: Qtr.1 I SSW1.1, HFW Fry #65, Zeno #67 Benchmark: Qtr.1 like SSW1.2, HFW Fry #47, Zeno #59 Benchmark: Qtr.1 do SSW1.2, HFW Fry #5, Zeno #4 Benchmark: Qtr.1 to SSW1.2,
SSW1.1, HFW Fry #20, Zeno #25 Benchmark: Qtr.1 I SSW1.1, HFW Fry #65, Zeno #67 Benchmark: Qtr.1 like SSW1.2, HFW Fry #47, Zeno #59 Benchmark: Qtr.1 do SSW1.2, HFW Fry #5, Zeno #4 Benchmark: Qtr.1 to SSW1.2,
Gdański Uniwersytet Medyczny Wydział Nauk o Zdrowiu z Oddziałem Pielęgniarstwa i Instytutem Medycyny Morskiej i Tropikalnej. Beata Wieczorek-Wójcik
 Gdański Uniwersytet Medyczny Wydział Nauk o Zdrowiu z Oddziałem Pielęgniarstwa i Instytutem Medycyny Morskiej i Tropikalnej Beata Wieczorek-Wójcik Poziom obsad pielęgniarskich a częstość i rodzaj zdarzeń
Gdański Uniwersytet Medyczny Wydział Nauk o Zdrowiu z Oddziałem Pielęgniarstwa i Instytutem Medycyny Morskiej i Tropikalnej Beata Wieczorek-Wójcik Poziom obsad pielęgniarskich a częstość i rodzaj zdarzeń
 www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
ERASMUS + : Trail of extinct and active volcanoes, earthquakes through Europe. SURVEY TO STUDENTS.
 ERASMUS + : Trail of extinct and active volcanoes, earthquakes through Europe. SURVEY TO STUDENTS. Strona 1 1. Please give one answer. I am: Students involved in project 69% 18 Student not involved in
ERASMUS + : Trail of extinct and active volcanoes, earthquakes through Europe. SURVEY TO STUDENTS. Strona 1 1. Please give one answer. I am: Students involved in project 69% 18 Student not involved in
Analysis of Movie Profitability STAT 469 IN CLASS ANALYSIS #2
 Analysis of Movie Profitability STAT 469 IN CLASS ANALYSIS #2 aaaklnictzzjb9tgfmcnadpg7oy0lxa9edva9kkapdarhyk2k7gourinlwsweyzikuyiigvyleiv/cv767fpf/5crc1xt9va5mx7w3m/ecuqw1kuztpx/rl3/70h73/w4cog9dhhn3z62d6jzy+yzj766txpoir9nzszisjynetqr+rvlfvyoozu5xbybpsxb1wahul8phczdt2v4zgchb7uecwphlyigrgkjcyiflfyci0kxnmr4z6kw0jsokvot8isntpa3gbknlcufiv/h+hh+eur4fomd417rvtfjoit5pfju6yxiab2fmwk0y/feuybobqk+axnke8xzjjhfyd8kkpl9zdoddkazd5j6bzpemjb64smjb6vb4xmehysu08lsrszopxftlzee130jcb0zjxy7r5wa2f1s2off2+dyatrughnrtpkuprlcpu55zlxpss/yqe2eamjkcf0jye8w8yas0paf6t0t2i9stmcua+inbi2rt01tz22tubbqwidypvgz6piynkpobirkxgu54ibzoti4pkw2i5ow9lnuaoabhuxfxqhvnrj6w15tb3furnbm+scyxobjhr5pmj5j/w5ix9wsa2tlwx9alpshlunzjgnrwvqbpwzjl9wes+ptyn+ypy/jgskavtl8j0hz1djdhzwtpjbbvpr1zj7jpg6ve7zxfngj75zee0vmp9qm2uvgu/9zdofq6r+g8l4xctvo+v+xdrfr8oxiwutycu0qgyf8icuyvp/sixfi9zxe11vp6mrjjovpmxm6acrtbia+wjr9bevlgjwlz5xd3rfna9g06qytaoofk8olxbxc7xby2evqjmmk6pjvvzxmpbnct6+036xp5vdbrnbdqph8brlfn/n/khnfumhf6z1v7h/80yieukkd5j0un82t9mynxzmk0s/bzn4tacdziszdhwrl8x5ako8qp1n1zn0k6w2em0km9zj1i4yt1pt3xiprw85jmc2m1ut2geum6y6es2fwx6c+wlrpykblopbuj5nnr2byygfy5opllv4+jmm7s6u+tvhywbnb0kv2lt5th4xipmiij+y1toiyo7bo0d+vzvovjkp6aoejsubhj3qrp3fjd/m23pay8h218ibvx3nicofvd1xi86+kh6nb/b+hgsjp5+qwpurzlir15np66vmdehh6tyazdm1k/5ejtuvurgcqux6yc+qw/sbsaj7lkt4x9qmtp7euk6zbdedyuzu6ptsu2eeu3rxcz06uf6g8wyuveznhkbzynajbb7r7cbmla+jbtrst0ow2v6ntkwv8svnwqnu5pa3oxfeexf93739p93chq/fv+jr8r0d9brhpcxr2w88bvqbr41j6wvrb+u5dzjpvx+veoaxwptzp/8cen+xbg==
Analysis of Movie Profitability STAT 469 IN CLASS ANALYSIS #2 aaaklnictzzjb9tgfmcnadpg7oy0lxa9edva9kkapdarhyk2k7gourinlwsweyzikuyiigvyleiv/cv767fpf/5crc1xt9va5mx7w3m/ecuqw1kuztpx/rl3/70h73/w4cog9dhhn3z62d6jzy+yzj766txpoir9nzszisjynetqr+rvlfvyoozu5xbybpsxb1wahul8phczdt2v4zgchb7uecwphlyigrgkjcyiflfyci0kxnmr4z6kw0jsokvot8isntpa3gbknlcufiv/h+hh+eur4fomd417rvtfjoit5pfju6yxiab2fmwk0y/feuybobqk+axnke8xzjjhfyd8kkpl9zdoddkazd5j6bzpemjb64smjb6vb4xmehysu08lsrszopxftlzee130jcb0zjxy7r5wa2f1s2off2+dyatrughnrtpkuprlcpu55zlxpss/yqe2eamjkcf0jye8w8yas0paf6t0t2i9stmcua+inbi2rt01tz22tubbqwidypvgz6piynkpobirkxgu54ibzoti4pkw2i5ow9lnuaoabhuxfxqhvnrj6w15tb3furnbm+scyxobjhr5pmj5j/w5ix9wsa2tlwx9alpshlunzjgnrwvqbpwzjl9wes+ptyn+ypy/jgskavtl8j0hz1djdhzwtpjbbvpr1zj7jpg6ve7zxfngj75zee0vmp9qm2uvgu/9zdofq6r+g8l4xctvo+v+xdrfr8oxiwutycu0qgyf8icuyvp/sixfi9zxe11vp6mrjjovpmxm6acrtbia+wjr9bevlgjwlz5xd3rfna9g06qytaoofk8olxbxc7xby2evqjmmk6pjvvzxmpbnct6+036xp5vdbrnbdqph8brlfn/n/khnfumhf6z1v7h/80yieukkd5j0un82t9mynxzmk0s/bzn4tacdziszdhwrl8x5ako8qp1n1zn0k6w2em0km9zj1i4yt1pt3xiprw85jmc2m1ut2geum6y6es2fwx6c+wlrpykblopbuj5nnr2byygfy5opllv4+jmm7s6u+tvhywbnb0kv2lt5th4xipmiij+y1toiyo7bo0d+vzvovjkp6aoejsubhj3qrp3fjd/m23pay8h218ibvx3nicofvd1xi86+kh6nb/b+hgsjp5+qwpurzlir15np66vmdehh6tyazdm1k/5ejtuvurgcqux6yc+qw/sbsaj7lkt4x9qmtp7euk6zbdedyuzu6ptsu2eeu3rxcz06uf6g8wyuveznhkbzynajbb7r7cbmla+jbtrst0ow2v6ntkwv8svnwqnu5pa3oxfeexf93739p93chq/fv+jr8r0d9brhpcxr2w88bvqbr41j6wvrb+u5dzjpvx+veoaxwptzp/8cen+xbg==
Zakopane, plan miasta: Skala ok. 1: = City map (Polish Edition)
 Zakopane, plan miasta: Skala ok. 1:15 000 = City map (Polish Edition) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Zakopane, plan miasta: Skala ok. 1:15 000 = City map (Polish Edition) Zakopane,
Zakopane, plan miasta: Skala ok. 1:15 000 = City map (Polish Edition) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Zakopane, plan miasta: Skala ok. 1:15 000 = City map (Polish Edition) Zakopane,
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition)
 Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
 www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
ARNOLD. EDUKACJA KULTURYSTY (POLSKA WERSJA JEZYKOWA) BY DOUGLAS KENT HALL
 Read Online and Download Ebook ARNOLD. EDUKACJA KULTURYSTY (POLSKA WERSJA JEZYKOWA) BY DOUGLAS KENT HALL DOWNLOAD EBOOK : ARNOLD. EDUKACJA KULTURYSTY (POLSKA WERSJA Click link bellow and free register
Read Online and Download Ebook ARNOLD. EDUKACJA KULTURYSTY (POLSKA WERSJA JEZYKOWA) BY DOUGLAS KENT HALL DOWNLOAD EBOOK : ARNOLD. EDUKACJA KULTURYSTY (POLSKA WERSJA Click link bellow and free register
Charakterystyka kliniczna chorych na raka jelita grubego
 Lek. Łukasz Głogowski Charakterystyka kliniczna chorych na raka jelita grubego Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych Opiekun naukowy: Dr hab. n. med. Ewa Nowakowska-Zajdel Zakład Profilaktyki Chorób
Lek. Łukasz Głogowski Charakterystyka kliniczna chorych na raka jelita grubego Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych Opiekun naukowy: Dr hab. n. med. Ewa Nowakowska-Zajdel Zakład Profilaktyki Chorób
Akademia Morska w Szczecinie. Wydział Mechaniczny
 Akademia Morska w Szczecinie Wydział Mechaniczny ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA mgr inż. Marcin Kołodziejski Analiza metody obsługiwania zarządzanego niezawodnością pędników azymutalnych platformy pływającej Promotor:
Akademia Morska w Szczecinie Wydział Mechaniczny ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA mgr inż. Marcin Kołodziejski Analiza metody obsługiwania zarządzanego niezawodnością pędników azymutalnych platformy pływającej Promotor:
Is there a relationship between age and side dominance of tubal ectopic pregnancies? A preliminary report
 Is there a relationship between age and side dominance of tubal ectopic pregnancies? A preliminary report Czy istnieje zależność pomiędzy wiekiem i stroną, po której umiejscawia się ciąża ektopowa jajowodowa?
Is there a relationship between age and side dominance of tubal ectopic pregnancies? A preliminary report Czy istnieje zależność pomiędzy wiekiem i stroną, po której umiejscawia się ciąża ektopowa jajowodowa?
Rozprawa na stopień naukowy doktora nauk medycznych w zakresie medycyny
 Lek. Maciej Jesionowski Efektywność stosowania budezonidu MMX u pacjentów z aktywną postacią łagodnego do umiarkowanego wrzodziejącego zapalenia jelita grubego w populacji polskiej. Rozprawa na stopień
Lek. Maciej Jesionowski Efektywność stosowania budezonidu MMX u pacjentów z aktywną postacią łagodnego do umiarkowanego wrzodziejącego zapalenia jelita grubego w populacji polskiej. Rozprawa na stopień
Metodyki projektowania i modelowania systemów Cyganek & Kasperek & Rajda 2013 Katedra Elektroniki AGH
 Kierunek Elektronika i Telekomunikacja, Studia II stopnia Specjalność: Systemy wbudowane Metodyki projektowania i modelowania systemów Cyganek & Kasperek & Rajda 2013 Katedra Elektroniki AGH Zagadnienia
Kierunek Elektronika i Telekomunikacja, Studia II stopnia Specjalność: Systemy wbudowane Metodyki projektowania i modelowania systemów Cyganek & Kasperek & Rajda 2013 Katedra Elektroniki AGH Zagadnienia
Formularz recenzji magazynu. Journal of Corporate Responsibility and Leadership Review Form
 Formularz recenzji magazynu Review Form Identyfikator magazynu/ Journal identification number: Tytuł artykułu/ Paper title: Recenzent/ Reviewer: (imię i nazwisko, stopień naukowy/name and surname, academic
Formularz recenzji magazynu Review Form Identyfikator magazynu/ Journal identification number: Tytuł artykułu/ Paper title: Recenzent/ Reviewer: (imię i nazwisko, stopień naukowy/name and surname, academic
Lek. Ewelina Anna Dziedzic. Wpływ niedoboru witaminy D3 na stopień zaawansowania miażdżycy tętnic wieńcowych.
 Lek. Ewelina Anna Dziedzic Wpływ niedoboru witaminy D3 na stopień zaawansowania miażdżycy tętnic wieńcowych. Rozprawa na stopień naukowy doktora nauk medycznych Promotor: Prof. dr hab. n. med. Marek Dąbrowski
Lek. Ewelina Anna Dziedzic Wpływ niedoboru witaminy D3 na stopień zaawansowania miażdżycy tętnic wieńcowych. Rozprawa na stopień naukowy doktora nauk medycznych Promotor: Prof. dr hab. n. med. Marek Dąbrowski
Tychy, plan miasta: Skala 1: (Polish Edition)
 Tychy, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000 (Polish Edition) Poland) Przedsiebiorstwo Geodezyjno-Kartograficzne (Katowice Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Tychy, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000
Tychy, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000 (Polish Edition) Poland) Przedsiebiorstwo Geodezyjno-Kartograficzne (Katowice Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Tychy, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000
deep learning for NLP (5 lectures)
 TTIC 31210: Advanced Natural Language Processing Kevin Gimpel Spring 2019 Lecture 6: Finish Transformers; Sequence- to- Sequence Modeling and AJenKon 1 Roadmap intro (1 lecture) deep learning for NLP (5
TTIC 31210: Advanced Natural Language Processing Kevin Gimpel Spring 2019 Lecture 6: Finish Transformers; Sequence- to- Sequence Modeling and AJenKon 1 Roadmap intro (1 lecture) deep learning for NLP (5
Evaluation of the main goal and specific objectives of the Human Capital Operational Programme
 Pracownia Naukowo-Edukacyjna Evaluation of the main goal and specific objectives of the Human Capital Operational Programme and the contribution by ESF funds towards the results achieved within specific
Pracownia Naukowo-Edukacyjna Evaluation of the main goal and specific objectives of the Human Capital Operational Programme and the contribution by ESF funds towards the results achieved within specific
Krytyczne czynniki sukcesu w zarządzaniu projektami
 Seweryn SPAŁEK Krytyczne czynniki sukcesu w zarządzaniu projektami MONOGRAFIA Wydawnictwo Politechniki Śląskiej Gliwice 2004 SPIS TREŚCI WPROWADZENIE 5 1. ZARZĄDZANIE PROJEKTAMI W ORGANIZACJI 13 1.1. Zarządzanie
Seweryn SPAŁEK Krytyczne czynniki sukcesu w zarządzaniu projektami MONOGRAFIA Wydawnictwo Politechniki Śląskiej Gliwice 2004 SPIS TREŚCI WPROWADZENIE 5 1. ZARZĄDZANIE PROJEKTAMI W ORGANIZACJI 13 1.1. Zarządzanie
Zarządzanie sieciami telekomunikacyjnymi
 SNMP Protocol The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an application layer protocol that facilitates the exchange of management information between network devices. It is part of the Transmission
SNMP Protocol The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an application layer protocol that facilitates the exchange of management information between network devices. It is part of the Transmission
Helena Boguta, klasa 8W, rok szkolny 2018/2019
 Poniższy zbiór zadań został wykonany w ramach projektu Mazowiecki program stypendialny dla uczniów szczególnie uzdolnionych - najlepsza inwestycja w człowieka w roku szkolnym 2018/2019. Składają się na
Poniższy zbiór zadań został wykonany w ramach projektu Mazowiecki program stypendialny dla uczniów szczególnie uzdolnionych - najlepsza inwestycja w człowieka w roku szkolnym 2018/2019. Składają się na
Network Services for Spatial Data in European Geo-Portals and their Compliance with ISO and OGC Standards
 INSPIRE Conference 2010 INSPIRE as a Framework for Cooperation Network Services for Spatial Data in European Geo-Portals and their Compliance with ISO and OGC Standards Elżbieta Bielecka Agnieszka Zwirowicz
INSPIRE Conference 2010 INSPIRE as a Framework for Cooperation Network Services for Spatial Data in European Geo-Portals and their Compliance with ISO and OGC Standards Elżbieta Bielecka Agnieszka Zwirowicz
Klinika Neonatologii UM w Łodzi
 Klinika Neonatologii UM w Łodzi Oddział: 7 stanowisk intensywnej terapii 20 stanowisk terapii pośredniej 26 stanowisk rooming in 2013: 2500 porodów [47% CC ; 3% kleszczy] 502 pacjentów leczonych na intensywnej
Klinika Neonatologii UM w Łodzi Oddział: 7 stanowisk intensywnej terapii 20 stanowisk terapii pośredniej 26 stanowisk rooming in 2013: 2500 porodów [47% CC ; 3% kleszczy] 502 pacjentów leczonych na intensywnej
Comparison of the risk factors for adverse perinatal outcomes in adolescent age pregnancies and advanced age pregnancies
 poło nictwo Comparison of the risk factors for adverse perinatal outcomes in adolescent age pregnancies and advanced age pregnancies Porównanie czynników ryzyka niekorzystnych wyników położniczych u młodocianych
poło nictwo Comparison of the risk factors for adverse perinatal outcomes in adolescent age pregnancies and advanced age pregnancies Porównanie czynników ryzyka niekorzystnych wyników położniczych u młodocianych
Cracow University of Economics Poland. Overview. Sources of Real GDP per Capita Growth: Polish Regional-Macroeconomic Dimensions 2000-2005
 Cracow University of Economics Sources of Real GDP per Capita Growth: Polish Regional-Macroeconomic Dimensions 2000-2005 - Key Note Speech - Presented by: Dr. David Clowes The Growth Research Unit CE Europe
Cracow University of Economics Sources of Real GDP per Capita Growth: Polish Regional-Macroeconomic Dimensions 2000-2005 - Key Note Speech - Presented by: Dr. David Clowes The Growth Research Unit CE Europe
Ocena potrzeb pacjentów z zaburzeniami psychicznymi
 Mikołaj Trizna Ocena potrzeb pacjentów z zaburzeniami psychicznymi przebywających na oddziałach psychiatrii sądowej Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych Promotor: dr hab.n.med. Tomasz Adamowski,
Mikołaj Trizna Ocena potrzeb pacjentów z zaburzeniami psychicznymi przebywających na oddziałach psychiatrii sądowej Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych Promotor: dr hab.n.med. Tomasz Adamowski,
Udział czynników demograficznych w kształtowaniu wyników leczenia raka jajnika na podstawie materiału Gdyńskiego Centrum Onkologii
 Lek. med. Andrzej Kmieć Udział czynników demograficznych w kształtowaniu wyników leczenia raka jajnika na podstawie materiału Gdyńskiego Centrum Onkologii Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych Zakład
Lek. med. Andrzej Kmieć Udział czynników demograficznych w kształtowaniu wyników leczenia raka jajnika na podstawie materiału Gdyńskiego Centrum Onkologii Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych Zakład
Revenue Maximization. Sept. 25, 2018
 Revenue Maximization Sept. 25, 2018 Goal So Far: Ideal Auctions Dominant-Strategy Incentive Compatible (DSIC) b i = v i is a dominant strategy u i 0 x is welfare-maximizing x and p run in polynomial time
Revenue Maximization Sept. 25, 2018 Goal So Far: Ideal Auctions Dominant-Strategy Incentive Compatible (DSIC) b i = v i is a dominant strategy u i 0 x is welfare-maximizing x and p run in polynomial time
Jakie metody diagnostyki obrazowej powinny być zastosowane w przypadku niedotlenienia-niedokrwienia u noworodków?
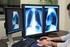 Jakie metody diagnostyki obrazowej powinny być zastosowane w przypadku niedotlenienia-niedokrwienia u noworodków? A. USG przezciemiączkowe B. USG i w drugiej kolejności TK C. USG i MR D. USG, TK i MR Badanie
Jakie metody diagnostyki obrazowej powinny być zastosowane w przypadku niedotlenienia-niedokrwienia u noworodków? A. USG przezciemiączkowe B. USG i w drugiej kolejności TK C. USG i MR D. USG, TK i MR Badanie
, Warszawa
 Kierunki rozwoju nowych leków w pediatrii z perspektywy Komitetu Pediatrycznego EMA. Wpływ Rozporządzenia Pediatrycznego na pediatryczne badania kliniczne w Europie Marek Migdał, Klinika Anestezjologii
Kierunki rozwoju nowych leków w pediatrii z perspektywy Komitetu Pediatrycznego EMA. Wpływ Rozporządzenia Pediatrycznego na pediatryczne badania kliniczne w Europie Marek Migdał, Klinika Anestezjologii
Hard-Margin Support Vector Machines
 Hard-Margin Support Vector Machines aaacaxicbzdlssnafiyn9vbjlepk3ay2gicupasvu4iblxuaw2hjmuwn7ddjjmxm1bkcg1/fjqsvt76fo9/gazqfvn8y+pjpozw5vx8zkpvtfxmlhcwl5zxyqrm2vrg5zw3vxmsoezi4ogkr6phieky5crvvjhriqvdom9l2xxftevuwcekj3lktmhghgniauiyutvrwxtvme34a77kbvg73gtygpjsrfati1+xc8c84bvraowbf+uwnipyehcvmkjrdx46vlykhkgykm3ujjdhcyzqkxy0chur6ax5cbg+1m4bbjptjcubuz4kuhvjoql93hkin5hxtav5x6yyqopnsyuneey5ni4keqrxbar5wqaxbik00icyo/iveiyqqvjo1u4fgzj/8f9x67bzmxnurjzmijtlybwfgcdjgfdtajwgcf2dwaj7ac3g1ho1n4814n7wwjgjmf/ys8fenfycuzq==
Hard-Margin Support Vector Machines aaacaxicbzdlssnafiyn9vbjlepk3ay2gicupasvu4iblxuaw2hjmuwn7ddjjmxm1bkcg1/fjqsvt76fo9/gazqfvn8y+pjpozw5vx8zkpvtfxmlhcwl5zxyqrm2vrg5zw3vxmsoezi4ogkr6phieky5crvvjhriqvdom9l2xxftevuwcekj3lktmhghgniauiyutvrwxtvme34a77kbvg73gtygpjsrfati1+xc8c84bvraowbf+uwnipyehcvmkjrdx46vlykhkgykm3ujjdhcyzqkxy0chur6ax5cbg+1m4bbjptjcubuz4kuhvjoql93hkin5hxtav5x6yyqopnsyuneey5ni4keqrxbar5wqaxbik00icyo/iveiyqqvjo1u4fgzj/8f9x67bzmxnurjzmijtlybwfgcdjgfdtajwgcf2dwaj7ac3g1ho1n4814n7wwjgjmf/ys8fenfycuzq==
Karpacz, plan miasta 1:10 000: Panorama Karkonoszy, mapa szlakow turystycznych (Polish Edition)
 Karpacz, plan miasta 1:10 000: Panorama Karkonoszy, mapa szlakow turystycznych (Polish Edition) J Krupski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Karpacz, plan miasta 1:10 000: Panorama
Karpacz, plan miasta 1:10 000: Panorama Karkonoszy, mapa szlakow turystycznych (Polish Edition) J Krupski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Karpacz, plan miasta 1:10 000: Panorama
Wstęp ARTYKUŁ REDAKCYJNY / LEADING ARTICLE
 Dzieciństwo w cieniu schizofrenii przegląd literatury na temat możliwych form pomocy i wsparcia dzieci z rodzin, gdzie jeden z rodziców dotknięty jest schizofrenią Childhood in the shadow of schizophrenia
Dzieciństwo w cieniu schizofrenii przegląd literatury na temat możliwych form pomocy i wsparcia dzieci z rodzin, gdzie jeden z rodziców dotknięty jest schizofrenią Childhood in the shadow of schizophrenia
Has the heat wave frequency or intensity changed in Poland since 1950?
 Has the heat wave frequency or intensity changed in Poland since 1950? Joanna Wibig Department of Meteorology and Climatology, University of Lodz, Poland OUTLINE: Motivation Data Heat wave frequency measures
Has the heat wave frequency or intensity changed in Poland since 1950? Joanna Wibig Department of Meteorology and Climatology, University of Lodz, Poland OUTLINE: Motivation Data Heat wave frequency measures
Updated Action Plan received from the competent authority on 4 May 2017
 1 To ensure that the internal audits are subject to Response from the GVI: independent scrutiny as required by Article 4(6) of Regulation (EC) No 882/2004. We plan to have independent scrutiny of the Recommendation
1 To ensure that the internal audits are subject to Response from the GVI: independent scrutiny as required by Article 4(6) of Regulation (EC) No 882/2004. We plan to have independent scrutiny of the Recommendation
 !850016! www.irs.gov/form8879eo. e-file www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C,
!850016! www.irs.gov/form8879eo. e-file www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C,
Analiza skuteczności i bezpieczeństwa leczenia systemowego najczęściej występujących nowotworów
 Uniwersytet Medyczny w Lublinie Rozprawa doktorska streszczenie rozprawy doktorskiej Analiza skuteczności i bezpieczeństwa leczenia systemowego najczęściej występujących nowotworów u chorych w podeszłym
Uniwersytet Medyczny w Lublinie Rozprawa doktorska streszczenie rozprawy doktorskiej Analiza skuteczności i bezpieczeństwa leczenia systemowego najczęściej występujących nowotworów u chorych w podeszłym
Ocena wpływu nasilenia objawów zespołu nadpobudliwości psychoruchowej na masę ciała i BMI u dzieci i młodzieży
 Ewa Racicka-Pawlukiewicz Ocena wpływu nasilenia objawów zespołu nadpobudliwości psychoruchowej na masę ciała i BMI u dzieci i młodzieży Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych PROMOTOR: Dr hab. n.
Ewa Racicka-Pawlukiewicz Ocena wpływu nasilenia objawów zespołu nadpobudliwości psychoruchowej na masę ciała i BMI u dzieci i młodzieży Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych PROMOTOR: Dr hab. n.
LEARNING AGREEMENT FOR STUDIES
 LEARNING AGREEMENT FOR STUDIES The Student First and last name(s) Nationality E-mail Academic year 2014/2015 Study period 1 st semester 2 nd semester Study cycle Bachelor Master Doctoral Subject area,
LEARNING AGREEMENT FOR STUDIES The Student First and last name(s) Nationality E-mail Academic year 2014/2015 Study period 1 st semester 2 nd semester Study cycle Bachelor Master Doctoral Subject area,
Radiologiczna ocena progresji zmian próchnicowych po zastosowaniu infiltracji. żywicą o niskiej lepkości (Icon). Badania in vivo.
 Renata Zielińska Radiologiczna ocena progresji zmian próchnicowych po zastosowaniu infiltracji żywicą o niskiej lepkości (Icon). Badania in vivo. Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych Zakład Stomatologii
Renata Zielińska Radiologiczna ocena progresji zmian próchnicowych po zastosowaniu infiltracji żywicą o niskiej lepkości (Icon). Badania in vivo. Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych Zakład Stomatologii
MaPlan Sp. z O.O. Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically
 Mierzeja Wislana, mapa turystyczna 1:50 000: Mikoszewo, Jantar, Stegna, Sztutowo, Katy Rybackie, Przebrno, Krynica Morska, Piaski, Frombork =... = Carte touristique (Polish Edition) MaPlan Sp. z O.O Click
Mierzeja Wislana, mapa turystyczna 1:50 000: Mikoszewo, Jantar, Stegna, Sztutowo, Katy Rybackie, Przebrno, Krynica Morska, Piaski, Frombork =... = Carte touristique (Polish Edition) MaPlan Sp. z O.O Click
Sargent Opens Sonairte Farmers' Market
 Sargent Opens Sonairte Farmers' Market 31 March, 2008 1V8VIZSV7EVKIRX8(1MRMWXIVSJ7XEXIEXXLI(ITEVXQIRXSJ%KVMGYPXYVI *MWLIVMIWERH*SSHTIVJSVQIHXLISJJMGMEPSTIRMRKSJXLI7SREMVXI*EVQIVW 1EVOIXMR0E]XS[R'S1IEXL
Sargent Opens Sonairte Farmers' Market 31 March, 2008 1V8VIZSV7EVKIRX8(1MRMWXIVSJ7XEXIEXXLI(ITEVXQIRXSJ%KVMGYPXYVI *MWLIVMIWERH*SSHTIVJSVQIHXLISJJMGMEPSTIRMRKSJXLI7SREMVXI*EVQIVW 1EVOIXMR0E]XS[R'S1IEXL
SWPS Uniwersytet Humanistycznospołeczny. Wydział Zamiejscowy we Wrocławiu. Karolina Horodyska
 SWPS Uniwersytet Humanistycznospołeczny Wydział Zamiejscowy we Wrocławiu Karolina Horodyska Warunki skutecznego promowania zdrowej diety i aktywności fizycznej: dobre praktyki w interwencjach psychospołecznych
SWPS Uniwersytet Humanistycznospołeczny Wydział Zamiejscowy we Wrocławiu Karolina Horodyska Warunki skutecznego promowania zdrowej diety i aktywności fizycznej: dobre praktyki w interwencjach psychospołecznych
 www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
Effective Governance of Education at the Local Level
 Effective Governance of Education at the Local Level Opening presentation at joint Polish Ministry OECD conference April 16, 2012, Warsaw Mirosław Sielatycki Ministry of National Education Doskonalenie
Effective Governance of Education at the Local Level Opening presentation at joint Polish Ministry OECD conference April 16, 2012, Warsaw Mirosław Sielatycki Ministry of National Education Doskonalenie
Zespół Omenna u kuzynów: różny przebieg kliniczny i identyczna mutacja genu RAG1.
 PRACE KAZUISTYCZNE / CASE REPORTS 367 Zespół Omenna u kuzynów: różny przebieg kliniczny i identyczna mutacja genu RAG1. Omenn s syndrome in cousins: different clinical course and identical RAG1 mutation
PRACE KAZUISTYCZNE / CASE REPORTS 367 Zespół Omenna u kuzynów: różny przebieg kliniczny i identyczna mutacja genu RAG1. Omenn s syndrome in cousins: different clinical course and identical RAG1 mutation
Analysis of infectious complications inf children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated in Voivodship Children's Hospital in Olsztyn
 Analiza powikłań infekcyjnych u dzieci z ostrą białaczką limfoblastyczną leczonych w Wojewódzkim Specjalistycznym Szpitalu Dziecięcym w Olsztynie Analysis of infectious complications inf children with
Analiza powikłań infekcyjnych u dzieci z ostrą białaczką limfoblastyczną leczonych w Wojewódzkim Specjalistycznym Szpitalu Dziecięcym w Olsztynie Analysis of infectious complications inf children with
Profil alergenowy i charakterystyka kliniczna dorosłych. pacjentów uczulonych na grzyby pleśniowe
 lek. Krzysztof Kołodziejczyk Profil alergenowy i charakterystyka kliniczna dorosłych pacjentów uczulonych na grzyby pleśniowe Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych Promotor: dr hab. n. med. Andrzej
lek. Krzysztof Kołodziejczyk Profil alergenowy i charakterystyka kliniczna dorosłych pacjentów uczulonych na grzyby pleśniowe Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych Promotor: dr hab. n. med. Andrzej
Patient Protection in Clinical Trials
 Patient Protection in Clinical Trials Marek Czarkowski Bioethic Committee Warsaw Chamber of Physicians Factors affecting security and rights of research participants International regulations Domestic
Patient Protection in Clinical Trials Marek Czarkowski Bioethic Committee Warsaw Chamber of Physicians Factors affecting security and rights of research participants International regulations Domestic
Ocena częstości występowania bólów głowy u osób chorych na padaczkę.
 lek. med. Ewa Czapińska-Ciepiela Ocena częstości występowania bólów głowy u osób chorych na padaczkę. Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych Promotor Prof. dr hab. n. med. Jan Kochanowski II Wydział
lek. med. Ewa Czapińska-Ciepiela Ocena częstości występowania bólów głowy u osób chorych na padaczkę. Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych Promotor Prof. dr hab. n. med. Jan Kochanowski II Wydział
European Crime Prevention Award (ECPA) Annex I - new version 2014
 European Crime Prevention Award (ECPA) Annex I - new version 2014 Załącznik nr 1 General information (Informacje ogólne) 1. Please specify your country. (Kraj pochodzenia:) 2. Is this your country s ECPA
European Crime Prevention Award (ECPA) Annex I - new version 2014 Załącznik nr 1 General information (Informacje ogólne) 1. Please specify your country. (Kraj pochodzenia:) 2. Is this your country s ECPA
Cytrynian kofeiny w codziennej praktyce u wcześniaków z Zespołem Zaburzeń Oddychania wyniki badania ogólnopolskiego
 Cytrynian kofeiny w codziennej praktyce u wcześniaków z Zespołem Zaburzeń Oddychania wyniki badania ogólnopolskiego Iwona Sadowska-Krawczenko Oddział Kliniczny Noworodków, Wcześniaków z Intensywną Terapią
Cytrynian kofeiny w codziennej praktyce u wcześniaków z Zespołem Zaburzeń Oddychania wyniki badania ogólnopolskiego Iwona Sadowska-Krawczenko Oddział Kliniczny Noworodków, Wcześniaków z Intensywną Terapią
Please fill in the questionnaire below. Each person who was involved in (parts of) the project can respond.
 Project CARETRAINING PROJECT EVALUATION QUESTIONNAIRE Projekt CARETRAINING KWESTIONARIUSZ EWALUACJI PROJEKTU Please fill in the questionnaire below. Each person who was involved in (parts of) the project
Project CARETRAINING PROJECT EVALUATION QUESTIONNAIRE Projekt CARETRAINING KWESTIONARIUSZ EWALUACJI PROJEKTU Please fill in the questionnaire below. Each person who was involved in (parts of) the project
Unit of Social Gerontology, Institute of Labour and Social Studies ageing and its consequences for society
 Prof. Piotr Bledowski, Ph.D. Institute of Social Economy, Warsaw School of Economics local policy, social security, labour market Unit of Social Gerontology, Institute of Labour and Social Studies ageing
Prof. Piotr Bledowski, Ph.D. Institute of Social Economy, Warsaw School of Economics local policy, social security, labour market Unit of Social Gerontology, Institute of Labour and Social Studies ageing
Clinical Trials. Anna Dziąg, MD, ąg,, Associate Director Site Start Up Quintiles
 Polandchallenges in Clinical Trials Anna Dziąg, MD, ąg,, Associate Director Site Start Up Quintiles Poland- legislation 1996-2003 Ustawa z dnia 5 grudnia 1996 r o zawodach lekarza i lekarza dentysty, z
Polandchallenges in Clinical Trials Anna Dziąg, MD, ąg,, Associate Director Site Start Up Quintiles Poland- legislation 1996-2003 Ustawa z dnia 5 grudnia 1996 r o zawodach lekarza i lekarza dentysty, z
Pielgrzymka do Ojczyzny: Przemowienia i homilie Ojca Swietego Jana Pawla II (Jan Pawel II-- pierwszy Polak na Stolicy Piotrowej) (Polish Edition)
 Pielgrzymka do Ojczyzny: Przemowienia i homilie Ojca Swietego Jana Pawla II (Jan Pawel II-- pierwszy Polak na Stolicy Piotrowej) (Polish Edition) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically
Pielgrzymka do Ojczyzny: Przemowienia i homilie Ojca Swietego Jana Pawla II (Jan Pawel II-- pierwszy Polak na Stolicy Piotrowej) (Polish Edition) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition)
 Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
Chronotyp i struktura temperamentu jako predyktory zaburzeń nastroju i niskiej jakości snu wśród studentów medycyny
 WYDZIAŁ LEKARSKI Chronotyp i struktura temperamentu jako predyktory zaburzeń nastroju i niskiej jakości snu wśród studentów medycyny Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych lek. Łukasz Mokros Praca
WYDZIAŁ LEKARSKI Chronotyp i struktura temperamentu jako predyktory zaburzeń nastroju i niskiej jakości snu wśród studentów medycyny Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych lek. Łukasz Mokros Praca
Emilka szuka swojej gwiazdy / Emily Climbs (Emily, #2)
 Emilka szuka swojej gwiazdy / Emily Climbs (Emily, #2) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Emilka szuka swojej gwiazdy / Emily Climbs (Emily, #2) Emilka szuka swojej gwiazdy / Emily
Emilka szuka swojej gwiazdy / Emily Climbs (Emily, #2) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Emilka szuka swojej gwiazdy / Emily Climbs (Emily, #2) Emilka szuka swojej gwiazdy / Emily
Weronika Mysliwiec, klasa 8W, rok szkolny 2018/2019
 Poniższy zbiór zadań został wykonany w ramach projektu Mazowiecki program stypendialny dla uczniów szczególnie uzdolnionych - najlepsza inwestycja w człowieka w roku szkolnym 2018/2019. Tresci zadań rozwiązanych
Poniższy zbiór zadań został wykonany w ramach projektu Mazowiecki program stypendialny dla uczniów szczególnie uzdolnionych - najlepsza inwestycja w człowieka w roku szkolnym 2018/2019. Tresci zadań rozwiązanych
ABOUT NEW EASTERN EUROPE BESTmQUARTERLYmJOURNAL
 ABOUT NEW EASTERN EUROPE BESTmQUARTERLYmJOURNAL Formanminsidemlookmatmpoliticsxmculturexmsocietymandm economyminmthemregionmofmcentralmandmeasternm EuropexmtheremismnomothermsourcemlikemNew Eastern EuropeImSincemitsmlaunchminmPw--xmthemmagazinemhasm
ABOUT NEW EASTERN EUROPE BESTmQUARTERLYmJOURNAL Formanminsidemlookmatmpoliticsxmculturexmsocietymandm economyminmthemregionmofmcentralmandmeasternm EuropexmtheremismnomothermsourcemlikemNew Eastern EuropeImSincemitsmlaunchminmPw--xmthemmagazinemhasm
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture11. Random Projections & Canonical Correlation Analysis
 Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture11 5 Random Projections & Canonical Correlation Analysis The Tall, THE FAT AND THE UGLY n X d The Tall, THE FAT AND THE UGLY d X > n X d n = n d d The
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture11 5 Random Projections & Canonical Correlation Analysis The Tall, THE FAT AND THE UGLY n X d The Tall, THE FAT AND THE UGLY d X > n X d n = n d d The
ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA. Mateusz Romanowski
 Mateusz Romanowski Wpływ krioterapii ogólnoustrojowej na aktywność choroby i sprawność chorych na zesztywniające zapalenie stawów kręgosłupa ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA Promotor: Dr hab., prof. AWF Anna Straburzyńska-Lupa
Mateusz Romanowski Wpływ krioterapii ogólnoustrojowej na aktywność choroby i sprawność chorych na zesztywniające zapalenie stawów kręgosłupa ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA Promotor: Dr hab., prof. AWF Anna Straburzyńska-Lupa
PROGRAM STAŻU. Nazwa podmiotu oferującego staż / Company name IBM Global Services Delivery Centre Sp z o.o.
 PROGRAM STAŻU Nazwa podmiotu oferującego staż / Company name IBM Global Services Delivery Centre Sp z o.o. Miejsce odbywania stażu / Legal address Muchoborska 8, 54-424 Wroclaw Stanowisko, obszar działania/
PROGRAM STAŻU Nazwa podmiotu oferującego staż / Company name IBM Global Services Delivery Centre Sp z o.o. Miejsce odbywania stażu / Legal address Muchoborska 8, 54-424 Wroclaw Stanowisko, obszar działania/
 www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
Strategia leczenia niewydolności oddechowej noworodków
 Strategia leczenia niewydolności oddechowej noworodków Andrzej Piotrowski Klinika Anestezjologii i Intensywnej Terapii Instytut Pomnik Centrum Zdrowia Dziecka Cele wentylacji 1. Zapewnienie wymiany gazowej
Strategia leczenia niewydolności oddechowej noworodków Andrzej Piotrowski Klinika Anestezjologii i Intensywnej Terapii Instytut Pomnik Centrum Zdrowia Dziecka Cele wentylacji 1. Zapewnienie wymiany gazowej
Dominika Janik-Hornik (Uniwersytet Ekonomiczny w Katowicach) Kornelia Kamińska (ESN Akademia Górniczo-Hutnicza) Dorota Rytwińska (FRSE)
 Czy mobilność pracowników uczelni jest gwarancją poprawnej realizacji mobilności studentów? Jak polskie uczelnie wykorzystują mobilność pracowników w programie Erasmus+ do poprawiania stopnia umiędzynarodowienia
Czy mobilność pracowników uczelni jest gwarancją poprawnej realizacji mobilności studentów? Jak polskie uczelnie wykorzystują mobilność pracowników w programie Erasmus+ do poprawiania stopnia umiędzynarodowienia
Uniwersytet Medyczny w Łodzi. Wydział Lekarski. Jarosław Woźniak. Rozprawa doktorska
 Uniwersytet Medyczny w Łodzi Wydział Lekarski Jarosław Woźniak Rozprawa doktorska Ocena funkcji stawu skokowego po leczeniu operacyjnym złamań kostek goleni z uszkodzeniem więzozrostu piszczelowo-strzałkowego
Uniwersytet Medyczny w Łodzi Wydział Lekarski Jarosław Woźniak Rozprawa doktorska Ocena funkcji stawu skokowego po leczeniu operacyjnym złamań kostek goleni z uszkodzeniem więzozrostu piszczelowo-strzałkowego
XT001_ INTRODUCTION TO EXIT INTERVIEW PYTANIE NIE JEST ZADAWANE W POLSCE W 2006 ROKU. WCIŚNIJ Ctrl+R BY PRZEJŚĆ DALEJ. 1.
 Share w2 Exit Questionnaire version 2.7 2006-09-29 XT001_ INTRODUCTION TO EXIT INTERVIEW 1. Kontynuuj XT006_ PROXY RESPONDENT'S SEX 1. Mężczyzna 2. Kobieta XT002_ RELATIONSHIP TO THE DECEASED IF XT002_
Share w2 Exit Questionnaire version 2.7 2006-09-29 XT001_ INTRODUCTION TO EXIT INTERVIEW 1. Kontynuuj XT006_ PROXY RESPONDENT'S SEX 1. Mężczyzna 2. Kobieta XT002_ RELATIONSHIP TO THE DECEASED IF XT002_
EGZAMIN MATURALNY Z JĘZYKA ANGIELSKIEGO
 Miejsce na naklejkę z kodem szkoły dysleksja MJA-R1_1P-072 EGZAMIN MATURALNY Z JĘZYKA ANGIELSKIEGO MAJ ROK 2007 Instrukcja dla zdającego POZIOM ROZSZERZONY CZĘŚĆ I Czas pracy 120 minut 1. Sprawdź, czy
Miejsce na naklejkę z kodem szkoły dysleksja MJA-R1_1P-072 EGZAMIN MATURALNY Z JĘZYKA ANGIELSKIEGO MAJ ROK 2007 Instrukcja dla zdającego POZIOM ROZSZERZONY CZĘŚĆ I Czas pracy 120 minut 1. Sprawdź, czy
DOI: / /32/37
 . 2015. 4 (32) 1:18 DOI: 10.17223/1998863 /32/37 -,,. - -. :,,,,., -, -.,.-.,.,.,. -., -,.,,., -, 70 80. (.,.,. ),, -,.,, -,, (1886 1980).,.,, (.,.,..), -, -,,,, ; -, - 346, -,.. :, -, -,,,,,.,,, -,,,
. 2015. 4 (32) 1:18 DOI: 10.17223/1998863 /32/37 -,,. - -. :,,,,., -, -.,.-.,.,.,. -., -,.,,., -, 70 80. (.,.,. ),, -,.,, -,, (1886 1980).,.,, (.,.,..), -, -,,,, ; -, - 346, -,.. :, -, -,,,,,.,,, -,,,
Skale w OIT. Jakub Pniak
 Skale w OIT Jakub Pniak SOFA Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment score Ocenia: układ oddechowy (Pa0 2 /FiO 2 ) [mmhg] 0-4 pkt. układ nerwowy (GCS) 0-4 pkt. układ krążenia (MAP i konieczność użycia
Skale w OIT Jakub Pniak SOFA Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment score Ocenia: układ oddechowy (Pa0 2 /FiO 2 ) [mmhg] 0-4 pkt. układ nerwowy (GCS) 0-4 pkt. układ krążenia (MAP i konieczność użycia
Ingrid Wenzel. Rozprawa doktorska. Promotor: dr hab. med. Dorota Dworakowska
 Ingrid Wenzel KLINICZNE ZNACZENIE EKSPRESJI RECEPTORA ESTROGENOWEGO, PROGESTERONOWEGO I ANDROGENOWEGO U CHORYCH PODDANYCH LECZNICZEMU ZABIEGOWI OPERACYJNEMU Z POWODU NIEDROBNOKOMÓRKOWEGO RAKA PŁUC (NDKRP)
Ingrid Wenzel KLINICZNE ZNACZENIE EKSPRESJI RECEPTORA ESTROGENOWEGO, PROGESTERONOWEGO I ANDROGENOWEGO U CHORYCH PODDANYCH LECZNICZEMU ZABIEGOWI OPERACYJNEMU Z POWODU NIEDROBNOKOMÓRKOWEGO RAKA PŁUC (NDKRP)
Raport bieżący: 44/2018 Data: g. 21:03 Skrócona nazwa emitenta: SERINUS ENERGY plc
 Raport bieżący: 44/2018 Data: 2018-05-23 g. 21:03 Skrócona nazwa emitenta: SERINUS ENERGY plc Temat: Zawiadomienie o zmianie udziału w ogólnej liczbie głosów w Serinus Energy plc Podstawa prawna: Inne
Raport bieżący: 44/2018 Data: 2018-05-23 g. 21:03 Skrócona nazwa emitenta: SERINUS ENERGY plc Temat: Zawiadomienie o zmianie udziału w ogólnej liczbie głosów w Serinus Energy plc Podstawa prawna: Inne
OpenPoland.net API Documentation
 OpenPoland.net API Documentation Release 1.0 Michał Gryczka July 11, 2014 Contents 1 REST API tokens: 3 1.1 How to get a token............................................ 3 2 REST API : search for assets
OpenPoland.net API Documentation Release 1.0 Michał Gryczka July 11, 2014 Contents 1 REST API tokens: 3 1.1 How to get a token............................................ 3 2 REST API : search for assets
Health Resorts Pearls of Eastern Europe Innovative Cluster Health and Tourism
 Health Resorts Pearls of Eastern Europe Innovative Cluster Health and Tourism Projekt finansowany Fundusze Europejskie z budżetu państwa dla rozwoju oraz ze Polski środków Wschodniej Unii Europejskiej
Health Resorts Pearls of Eastern Europe Innovative Cluster Health and Tourism Projekt finansowany Fundusze Europejskie z budżetu państwa dla rozwoju oraz ze Polski środków Wschodniej Unii Europejskiej
Podsumowanie sezonu zachorowań oraz program profilaktyki zakażeń 2016/2017
 Profilaktyka zakażeń RSV w Polsce od 1.1.213 Profilaktyka zakażeń wirusem RS (ICD-1 P 7.2, P 27.1) Podsumowanie sezonu zachorowań oraz program profilaktyki zakażeń 216/217 Ewa Helwich Klinika Neonatologii
Profilaktyka zakażeń RSV w Polsce od 1.1.213 Profilaktyka zakażeń wirusem RS (ICD-1 P 7.2, P 27.1) Podsumowanie sezonu zachorowań oraz program profilaktyki zakażeń 216/217 Ewa Helwich Klinika Neonatologii
Katowice, plan miasta: Skala 1: = City map = Stadtplan (Polish Edition)
 Katowice, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000 = City map = Stadtplan (Polish Edition) Polskie Przedsiebiorstwo Wydawnictw Kartograficznych im. Eugeniusza Romera Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically
Katowice, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000 = City map = Stadtplan (Polish Edition) Polskie Przedsiebiorstwo Wydawnictw Kartograficznych im. Eugeniusza Romera Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically
CEE 111/211 Agenda Feb 17
 CEE 111/211 Agenda Feb 17 Tuesday: SW for project work: Jetstream, MSP, Revit, Riuska, POP, SV On R: drive; takes time to install Acoustics today: \\cife server\files\classes\cee111\presentations Thursday:
CEE 111/211 Agenda Feb 17 Tuesday: SW for project work: Jetstream, MSP, Revit, Riuska, POP, SV On R: drive; takes time to install Acoustics today: \\cife server\files\classes\cee111\presentations Thursday:
SubVersion. Piotr Mikulski. SubVersion. P. Mikulski. Co to jest subversion? Zalety SubVersion. Wady SubVersion. Inne różnice SubVersion i CVS
 Piotr Mikulski 2006 Subversion is a free/open-source version control system. That is, Subversion manages files and directories over time. A tree of files is placed into a central repository. The repository
Piotr Mikulski 2006 Subversion is a free/open-source version control system. That is, Subversion manages files and directories over time. A tree of files is placed into a central repository. The repository
Trend in drug use in Poland
 Prevalence and patterns of drug use among general population Indicator (GPS) Annual Expert Meeting 214 Trend in drug use in Poland Janusz Sierosławski Institute of Psychiatry i Neurology Warsaw Lisbon,
Prevalence and patterns of drug use among general population Indicator (GPS) Annual Expert Meeting 214 Trend in drug use in Poland Janusz Sierosławski Institute of Psychiatry i Neurology Warsaw Lisbon,
OPTYMALIZACJA PUBLICZNEGO TRANSPORTU ZBIOROWEGO W GMINIE ŚRODA WIELKOPOLSKA
 Politechnika Poznańska Wydział Maszyn Roboczych i Transportu Inż. NATALIA LEMTIS OPTYMALIZACJA PUBLICZNEGO TRANSPORTU ZBIOROWEGO W GMINIE ŚRODA WIELKOPOLSKA Promotor: DR INŻ. MARCIN KICIŃSKI Poznań, 2016
Politechnika Poznańska Wydział Maszyn Roboczych i Transportu Inż. NATALIA LEMTIS OPTYMALIZACJA PUBLICZNEGO TRANSPORTU ZBIOROWEGO W GMINIE ŚRODA WIELKOPOLSKA Promotor: DR INŻ. MARCIN KICIŃSKI Poznań, 2016
CENTRALNA PRZYCHODNIA REHABILITACYJNO- LECZNICZA POLSKIEGO ZWIĄZKU NIEWIDOMYCH w WARSZAWIE KRZYSZTOF STARZYK
 CENTRALNA PRZYCHODNIA REHABILITACYJNO- LECZNICZA POLSKIEGO ZWIĄZKU NIEWIDOMYCH w WARSZAWIE KRZYSZTOF STARZYK OCENA JAKOŚCI ŻYCIA OSÓB SŁABOWIDZĄCYCH STOSUJĄCYCH POMOCE OPTYCZNE PROMOTOR: PROF. DR HAB.
CENTRALNA PRZYCHODNIA REHABILITACYJNO- LECZNICZA POLSKIEGO ZWIĄZKU NIEWIDOMYCH w WARSZAWIE KRZYSZTOF STARZYK OCENA JAKOŚCI ŻYCIA OSÓB SŁABOWIDZĄCYCH STOSUJĄCYCH POMOCE OPTYCZNE PROMOTOR: PROF. DR HAB.
Wpływ cukrzycy na jakość życia kobiet ciężarnych
 GDAŃSKI UNIWERSYTET MEDYCZNY Wpływ cukrzycy na jakość życia kobiet ciężarnych Praca na stopień doktora nauk medycznych mgr Joanna Preis-Orlikowska Promotor pracy: prof. dr hab. Mikołaj Majkowicz Gdańsk,
GDAŃSKI UNIWERSYTET MEDYCZNY Wpływ cukrzycy na jakość życia kobiet ciężarnych Praca na stopień doktora nauk medycznych mgr Joanna Preis-Orlikowska Promotor pracy: prof. dr hab. Mikołaj Majkowicz Gdańsk,
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition)
 Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
Ankiety Nowe funkcje! Pomoc magda.szewczyk@slo-wroc.pl. magda.szewczyk@slo-wroc.pl. Twoje konto Wyloguj. BIODIVERSITY OF RIVERS: Survey to students
 Ankiety Nowe funkcje! Pomoc magda.szewczyk@slo-wroc.pl Back Twoje konto Wyloguj magda.szewczyk@slo-wroc.pl BIODIVERSITY OF RIVERS: Survey to students Tworzenie ankiety Udostępnianie Analiza (55) Wyniki
Ankiety Nowe funkcje! Pomoc magda.szewczyk@slo-wroc.pl Back Twoje konto Wyloguj magda.szewczyk@slo-wroc.pl BIODIVERSITY OF RIVERS: Survey to students Tworzenie ankiety Udostępnianie Analiza (55) Wyniki
GDAŃSKI UNIWERSYTET MEDYCZNY
 GDAŃSKI UNIWERSYTET MEDYCZNY mgr Magdalena Pinkowicka WPŁYW TRENINGU EEG-BIOFEEDBACK NA POPRAWĘ WYBRANYCH FUNKCJI POZNAWCZYCH U DZIECI Z ADHD Rozprawa doktorska Promotor dr hab. n. med. Andrzej Frydrychowski,
GDAŃSKI UNIWERSYTET MEDYCZNY mgr Magdalena Pinkowicka WPŁYW TRENINGU EEG-BIOFEEDBACK NA POPRAWĘ WYBRANYCH FUNKCJI POZNAWCZYCH U DZIECI Z ADHD Rozprawa doktorska Promotor dr hab. n. med. Andrzej Frydrychowski,
Marta Uzdrowska. PRACA NA STOPIEŃ DOKTORA NAUK MEDYCZNYCH Promotor: Dr hab. n. med. prof. UM Anna Broniarczyk-Loba
 Marta Uzdrowska Ocena wad refrakcji i przyczyn niedowidzenia u osób z niepełnosprawnością intelektualną z wykorzystaniem zdalnego autorefraktometru Plusoptix PRACA NA STOPIEŃ DOKTORA NAUK MEDYCZNYCH Promotor:
Marta Uzdrowska Ocena wad refrakcji i przyczyn niedowidzenia u osób z niepełnosprawnością intelektualną z wykorzystaniem zdalnego autorefraktometru Plusoptix PRACA NA STOPIEŃ DOKTORA NAUK MEDYCZNYCH Promotor:
