A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume Issue 3 DOI: /v
|
|
|
- Marek Tomczak
- 4 lat temu
- Przeglądów:
Transkrypt
1 A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume Issue 3 DOI: /v B. NIŻNIK, M. PIETRZYK MODEL OF PHASE TRANSFORMATION FOR NIOBIUM MICROALLOYED STEELS MODEL PRZEMIANY FAZOWEJ DLA STALI Z MIKRODODATKIEM NIOBU The paper presents the results of physical and numerical modeling of the kinetics of phase transformation, taking into account the precipitation of niobium carbonitride. Strain induced precipitation is a phenomenon, which controls the evolution of the microstructure in these steels during thermo-mechanical treatment. For the numerical simulation of precipitation Dutta-Sellars model was used, which describes the precipitation kinetics of Nb (C, N) at dislocations in the deformed and non-deformed austenite. The size of precipitates after continuous cooling of steel was calculated using the additivity rule. Numerical model combines a solution of the finite element method with model of phase transitions. Physical modeling included dilatometric study and rolling of rods made of niobium microalloyed steel. Microstructure studies were also carried out. Developed model allowed the assessment of the influence of precipitation on the progress of phase transition. Verification of model prediction by comparison with the experiments carried out in conditions close to semi-industrial is described in the paper, as well. Keywords: niobium microalloyed steels, model of phase transformation, carbonitride precipitation process, thermomechanical treatment, multiscale modelling W pracy przedstawiono wyniki modelowania fizycznego oraz model numeryczny opisujący kinetykę przemiany fazowej z uwzględnieniem procesu wydzieleniowego węglikoazotku niobu. Proces ten silnie wpływa na zmiany zachodzące w mikrostrukturze tych stali w trakcie obróbki cieplno plastycznej. Do symulacji numerycznej procesu wydzieleniowego wykorzystano model Dutty-Sellarsa opisujący kinetykę procesu wydzieleniowego Nb(C,N) na dyslokacjach w austenicie odkształconym i nieodkształconym. Wielkość wydzieleń w warunkach ciągłego chłodzenia stali obliczona została z wykorzystaniem reguły addytywności. Model numeryczny łączy rozwiązanie metodą elementów skończonych z modelem przemian fazowych. Modelowanie fizyczne obejmowało badania dylatometryczne oraz walcowanie prętów ze stali z mikrododatkiem niobu uzupełnione badaniami mikrostruktury. Opracowany model pozwolił na ocenę wpływu procesu wydzieleniowego na postęp przemiany fazowej. Wyniki modelowania zweryfikowano doświadczalnie w warunkach zbliżonych do półprzemysłowych. 1. Introduction The model of phase transformation was developed for carbon-manganese steel by a combination of conventional equations describing the kinetics of the transformation [1] with the solutions by finite element method (FEM) [2,3]. In the case of microalloyed steels the model should also consider the influence of precipitation processes. The general objective of this study is experimental verification of the developed multi-scale model under conditions similar to industrial. In this order dilatometric tests were performed using the dilatometer DIL 805 at the Institute of Ferrous Metallurgy in Gliwice (Poland) and rod rolling in a continuous hot rolling mill at the TU Bergakademie Freiberg, Institut für Metallformung. Rods were rolled in four elongating passes of oval-round type. These experiments were used to identify the material models and to verify the global model of phase transformations. The particular objectives of the work include quantitative description of the transformation fraction of ferrite in pearlite, the determination of ferrite transformation start temperature, and quantitative analysis of carbide niobium precipitation. Inverse analysis of experiments is used to determine the coefficients for the model of phase transitions. Quantitative analysis of niobium carbonitride particles is the final objective of the paper. It is performed on INSTITUTE FOR FERROUS METALLURGY, GLIWICE, K. MIARKI STR., POLAND AGH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, FACULTY OF METALS ENGINEERING AND INDUSTRIAL COMPUTER SCIENCE, DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICAL AND POWDER METALLURGY, KRAKÓW, 30 MICKIEWICZA AV., POLAND
2 732 the basis of comparison of microstructures obtained from experiments with the results of the model predictions. 2. Material for testing Laboratory ingots weighing 20 kg and made of niobium microalloyed steel, which chemical composition shown in Table 1, were used in dilatometric and industrial tests. The study of phase transformation consisted of heating the material at the rate of 3 C/s to the austenitizing temperature 1230 C, keeping at this temperature for 30 s, cooling to a temperature of deformation 850 C, deformation of a given reduction ε = 0.2 and ε = 0.4 and then cooled to ambient temperature at a constant speed. In studies cooling rates of 40, 20, 10, 5 C/s were applied. In the semi-industrial rolling process rod of dimensions and a length of about 400 mm was heated to an austenitizing temperature of 1200 C, maintained for 20 min, cooled to a temperature of 1050 C in air and rolled. The interval between the passes was about 10 s. The temperature after the last pass was 930 C and the linear velocity of strip was 12 m/s. After leaving the last pass, the rod was cooled with compressed air to a temperature of 350 C. Illustration and parameters of the hot rolling mill in Freiberg can be found in [4]. Figure 1 shows the cooling curve of the rolled rod from the temperature 912 to 350 C. On this curve, the selected section was extrapolated from the temperature 912 C to a temperature of 930 C, in which the material was rolled in the last pass. The final diameter of the rolled bar was 12 mm. Chemical composition of steel used in the dilatometer tests and rolling, % mass TABLE 1 C Mn Si P S Cr Ni Cu Al V Nb N Fig. 1. Measured cooling curve of the steel rod niobium microalloyed temperature 930 to 350 C
3 Numerical modeling Finite element method Flow of metal in the plastometric tests was modeled using rigid-plastic finite element solution, where heat transport was described by the Fourier equation. A detailed description of the solution presented in publication [5] and it is not quoted in this paper. Model of phase transitions Models of phase transitions (ferritic, pearlitic and bainitic) consist of differential equations describing the incubation period and kinetics of the transformation. Design concept is described in [1], and its numerical implementation in [2,3,6]. In this model, the calculation of the progress of ferrite transformation begins at the equilibrium temperature A c3. Constitutive equations for ferrite transformation in general form are given below: incubation period for the ferritic transformation τ f = x 1 (A c3 T) x 3 exp ( x2 RT volume fraction of ferrite ( dx f = x 5 Sv 0.25 G 0.75 I [ln dt 1 X f ) )] 0.75 ( 1 X f ) dx f 6 = x 4 dt D G ( ) 1 X f (3) where: t time since the beginning of the transformation, D austenite grain size, S v relative area of grain boundaries, G the speed of the transformation front, T temperature [K], R gas constant, I nucleation rate, x 1 x 5 coefficients, X f volume fraction of ferrite. The full model of phase transitions, including the other changes taking place in steels, is described in the literature [2]. A method of identification of coefficients in the model is based on the algorithm of [7] and is described in [3], while work [6] presents results of this identification for a niobium microalloyed steel. Dutta and Sellars Model (1) (2) The model, which describes the incubation period and the progress of precipitation [8 10], is used in the present work to calculate the number of precipitates per unit volume and average diameter of precipitates. The precipitation process of carbonitride Nb (C,N) strongly influences the final microstructure and properties of products. Precipitates inhibit the recrystallization of austenite, which leads to reduction of the size of the ferrite grains after transformation of non-recrystallized austenite. In this paper, the Dutta-Sellars model is used in the calculation of the precipitation kinetics of Nb (C,N) at dislocations, while it omitts others nucleation sites of carbonitride, such as grain/subgrain boundaries, sites with large plastic deformation or direct precipitation in the matrix. The basic equations of the model are quoted below. Solubility product of Nb, C and N in austenite [8]: k s = log[nb] [ C N] 10 q q = T (4) where [Nb] and [C + N] the contents of niobium and suitably adjusted for the atomic weight aggregate content of interstitial elements in austenite, expressed in percentage by mass. Critical radius for nucleation, R c is determined by propelling force and the equation is: R c = 2γ G v (5) where: γ energy of the interface equal to 0.5 [Jm 2 ], V m molar volume. For Nb (C, N), V m = [m 3 mol 1 ]. The difference in free energy per unit volume G v is calculated from the formula: G v = RT ln ks V m (6) A special feature of metallic systems at elevated temperatures is coagulation of the particles of precipitates. Kinetics of the coagulation equation is described by the Wagner equation [9]: r 3 r 3 0 = 8 9 γd Nb C 0 Vm 2 t (7) RT where r 0, r initial radius of particles and the radius after time t at temperature T, D Nb diffusion coefficient of Nb as an element controlling the speed of coagulation, C 0 the concentration of N (C 0 = k s C r wherec r = [Nb]) Time to start the process of precipitation, t 0.05p is calculated from equation of classical nucleation theory, modified on the basis of experimental studies [9]: ( ) t 0.05p = [Nb] 1 ε 1 Z 0.5 exp [ ] RT (8) exp T 3 (ln k s ) 2 where [Nb] percentage by mass of niobium in solid solution in equilibrium with carbon and nitrogen calculated from equation (5) for the applied temperature of soaking stock, T temperature at which the precipitation process proceed.
4 734 Critical energy for the process of nucleus of carbonitride formation [9]: G = 16π f 3 γ 3 3( G v ) 2 (9) where: f = 0.41 (empirical constant) Model described above is used to calculate the number of precipitates per unit volume and average diameter of precipitates. The above components of the precipitation model were combined with the FEM program and the model of the kinetics of phase transitions, as it is described in detail in [10]. 4. Results Diagram of the developed multiscale model is shown in Figure 2. The general idea of the multiscale modeling [11,12,13] is applied. Description of rheological model for the investigated steel and the model of evolution of dislocation density are in the works [14,15]. Below are the results of testing and validation of the two components of the complex model: parts which calculate the phase transformation and the kinetics of precipitates. Start temperature of ferrite transformation for the deformed austenite (ε = 0.2 and ε = 0.4) was calculated using the developed model of phase transformation with the coefficients set by inverse analysis, which are presented in Table 2. Figure 3 shows the results of measurements and calculations of start temperature for ferrite transformation (F s ). As can be seen, a good agreement of measurement and calculation of that temperature is obtained. Pictures of microstructures of rolled bar, which were obtained using an optical microscope NEOPHOT, are presented in Fig. 4. Table 3 summarizes the results of measurements and calculations of start temperature of ferrite transformation for the two strains: 0.2 and 0.4 and the hardness of the samples measured by Vickers method. Quantitative analysis of chemical composition is based on 300 measurements of grains and process simulation for the experimental conditions, and the result is volume fraction of ferrite of 94.7, while the predicted volume fraction is It confirms good compatibility of the results of the volume fractions of phases obtained from modeling and measurement. Fig. 2. Block diagram of the multiscale model simulating the deformation process of two-phase steel
5 735 Fig. 3. The results of measurements and calculations ferrite transformation start temperature for the rolled bar Coefficients of phase transformation model determined by inverse analysis TABLE 2 ε x 1 x 2 x 3 x 4 x 5 x TABLE 3 The results of measurement and modeling of start temperature of ferrite transformation and hardness of the samples for different cooling rates Cooling speed C/s F s. model C ε = 0.2 ε = 0.4 F s. measurement. C Hardness HV 10 F s. model. C F s. measurement. C Hardness HV
6 736 Fig. 4. Microstructure of the rolled steel rod microalloyed niobium after cooling to a temperature of 350 C
7 737 To calculate the fraction of static recrystallization (t rx ), the JMAK equation was used for the two models: Sellars [8,9] (t rx Dutta Sellars) and Hodgson [16] (t rx Hodgson), and time of beginning of precipitation (t 0.05p ) was obtained by the Dutta-Sellars model (Figure 5). Times, after which there was a beginning of a process of precipitation (t 0.05p ) for non-isothermal conditions is calculated on the basis of the additivity rule: x i+1 = x i + t i t 0.05p (T i ) (10) where: t i time step, t 0.05p (T i ) the time of the transformation under isothermal conditions at the temperature T i. When the total incubation period reaches the value of one, the precipitation begins: n t i t 0.05p (T i ) = 1 (11) i=1 Figure 5 shows the incubation period of formation of precipitates and the static recrystallization calculated for the experimental process. It is clear that precipitates after the last pass calculated by Dutta-Sellars model occur after the time a bit shorter than the time of static recrystallization, and the results obtained using the model of Hodgson gives a much longer times recrystallization. This is justified because the study by Hodgson covered steel with a higher content of niobium. The computer simulations provide information on incubation period of the formation of precipitates and fraction of recrystallization during the rolling of the material at different temperatures, and different linear speeds of deformed strip (Table 4). Austenite grain size after each pass through the rolling stand were calculated based on the Sellars [17] and Hodgson [16] models, see Figure 6. Characteristics of parameters of experimental rolling of bars TABLE 4 Parameter Stand 1 Stand 2 Stand 3 Stand 4 deformation temperature, C linear velocity spectrum, m/s strain rate, s Fig. 5. Calculation of time of the beginning of the precipitation (t 0.05p ) and the fraction of static recrystallization, calculated on the basis of the Dutta-Sellars (t rx Dutta Sellars) and Hodgson (t rx Hodgson) models
8 738 Fig. 6. Austenite grain sizes before and after the exit from the rolling stand Quantitative analysis of carbides of niobium Nb (C, N) obtained on the basis of measurement and model TABLE 5 Parameters Measurement Model Number of precipitates per unit volume 5.014x10 22 /m x10 22 /m 3 The average diameter of precipitates 6.3 nm 4.0 nm
9 739
10 740 Fig. 7. Pictures of the scanning electron microscope showing a carbonitride particle Nb (C,N)
11 741 After the thermal-mechanical treatment microstructures were tested in different areas of rolled bar, using a scanning electron microscope FEGSEM. Selected results are presented in Fig. 7. A lot of small niobium carbonitride precipitates are seen inside the ferrite grains. Quantitative analysis of these particles was performed on the basis of microstructure in Figure 7d and on the basis of simulations. The results are presented in Table 5. The number of precipitates per unit area (450/µm 2 ), which was obtained from measurements, was converted to per unit volume by the inverse of the diameters of Saltykov [18]. 5. Discussion The use of multiscale model, which combines the macro-scale (where temperature, stresses and deformation are calculate) with micro and nano scale (where the kinetics of phase transformation and the precipitation process of carbonitride niobium are calculated), allows the modeling of quantitative changes in fractions of phases during the thermo-mechanical processes. In order to verify the multiscale model, the rolling of rods and dilatometric tests were performed. It is seen from calculations and the measurements that the start temperature of ferrite transformation increases with the decreasing speed of cooling and with increasing strain in the material. Hardness of niobium microalloyed steel increases with increasing cooling rate and decrease of strain. For the rolling process precipitates are formed after a shorter time comparing to static recrystallization time in the last pass. These calculations provide information on the incubation period, a fraction of the formation of precipitates and recrystallization during rolling of the material at different temperatures and speeds. A good agreement between measurement and prediction of temperature of start of ferritic transition (F s ) for different conditions of thermo-mechanical treatment for the executed rod rolling process was obtained. The calculations of ferrite and pearlite grain size, radius and number of precipitates and the volume fraction of ferrite and pearlite, are compared with the results of the measurements and a good agreement is observed. Therefore, it can be stated that consideration of the kinetics of precipitation and the dislocation density in the γ α transition model and combination of these models with the finite element method allows the realistic prediction of microstructure evolution for different conditions of thermo-mechanical treatment. The simulations provide information about the influence of the precipitation processes on the phase transformation, the period of incubation for the formation of precipitation, austenite grain size and fraction of recrystallization during rolling of the material at different temperatures, strain rates, and different linear band speed. Model of the phase transformation γ α combined with model of the kinetics of precipitation gives good agreement with the measurement of start temperature of ferrite transformation Fs, and good quantitative agreement for volume fractions of phases in the deformed austenite. REFERENCES [1] M. S u e h i r o, T. S e n u m a, H. Y a d a, Application of mathematical model for predicting microstructural evolution to high carbon steels, ISIJ Int. 32, (1992). [2] M. P i e t r z y k, R. K u z i a k, T. K o n d e k, Physical and numerical modelling of plastic deformation of steels in two-phase region, Proc. 46 th Conf. MWSP, Chicago, , (2003). [3] T. K o n d e k, M. P i e t r z y k, Identyfikacja modeli przemian fazowych w stalach na podstawie próby dylatometrycznej przy stałej prędkości chłodzenia, Informatyka w Technologii Materiałów 2, (2002). [4] E. H a d a s i k, R. K u z i a k, R. K a w a l l a, M. A d a m c z y k, M. P i e t r z y k, Rheological model for simulation of hot rolling of new generation steel strips for automotive industry, Steel Research Int. 77, (2006). [5] J.G. L e n a r d, M. P i e t r z y k, L. C s e r, Mathematical and Physical Simulation of the Properties of Hot Rolled Products, Elsevier, Amsterdam, (1999). [6] M. P i e t r z y k, R. K u z i a k, Development of the constitutive law for microalloyed steels deformed in the two-phase range of temperatures, Steel GRIPS 2, (2004). [7] D. S z e l i g a, J. G a w ą d, M. P i e t r z y k, Inverse Analysis for Identification of Rheological and Friction Models in Metal Forming, Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech. Engrg. 195, (2006). [8] B. D u t t a, E.J. P a l m i e r e, C.M. S e l l a r s, Modeling the kinetics of strain induced precipitation in Nb microalloyed steels, Acta Mater. 49, (2001). [9] B. D u t t a, E. V a l d e s, C. S e l a r s, Mechanism and kinetics of Strain Induced Precipitation of Nb (C,N) in austenite, Acta Metal. Mater. 40, (1991). [10] R. K u z i a k, M. P i e t r z y k, Finite Element Modelling of Accelerated Cooling of Rods after Rolling, Proc. 41st Conf. MWSP, Baltimore, (1999). [11] A. B a c k, M. U r b a n, C. K e u l, W. B l e c k, G. H i r t, Numerical prediction of microstructure in high-strength ductile forgings, Computer Methods in Materials Science 10, (2010. [12] M. P i e t r z y k, Ł. M a d e j, Ł. R a u c h, R. G o ł ą b, Multiscale modelling of microstructure evolution during laminar cooling of hot rolled DP steel, Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering 10, (2010). [13] D. K u c, J. G a w ą d, Modelling of microstructure changes during hot deformation using cellular automa-
12 742 ta, Archives of Metallurgy and Materials 56, (2011). [14] B. N i ż n i k, M. P i e t r z y k, Rheological model for microalloyed steel in the two phase region of temperatures, accounting for the influence of deformation and precipitation on the phase transformation, Acta Metallurgica Slovaca 13, (2007). [15] B. N i ż n i k, M. P i e t r z y k, R. K u z i a k, Fizyczna i numeryczna symulacja odkształcania stali z mikrododatkiem niobu w zakresie dwufazowym, Proc. Conf. FiMM, Warszawa, 7-12 (2005). [16] P.D. H o d g s o n, R.K. G i b b s, A mathematical model to predict the mechanical properties of hot rolled C-Mn and microalloyed steels, ISIJ Int. 32, (1992). [17] C.M. S e l l a r s, Physical metallurgy of hot working in: hot working and forming processes, ed. Sellars C.M., Davies G.J., The Metals Soc., 3-15 (1979). [18] J. R y ś, Stereologia materiałów, Fotobit-Design, (1995). Received: 10 February 2011.
APPLICATION OF THE EXPERT COMPUTER SYSTEM TO DESIGN THE HOT STRIP ROLLING TECHNOLOGY IN THE LPS LINE
 104 Prace IMŻ 1 (2012) Łukasz RAUCH, Rafał GOŁĄB AGH, Akademia Górniczo-Hutnicza, Wydział Inżynierii Metali i Informatyki Przemysłowej Roman KUZIAK, Valeriy PIDVYSOTS KYY Instytut Metalurgii Żelaza im.
104 Prace IMŻ 1 (2012) Łukasz RAUCH, Rafał GOŁĄB AGH, Akademia Górniczo-Hutnicza, Wydział Inżynierii Metali i Informatyki Przemysłowej Roman KUZIAK, Valeriy PIDVYSOTS KYY Instytut Metalurgii Żelaza im.
Tytuł pracy w języku angielskim: Microstructural characterization of Ag/X/Ag (X = Sn, In) joints obtained as the effect of diffusion soledering.
 Dr inż. Przemysław Skrzyniarz Kierownik pracy: Prof. dr hab. inż. Paweł Zięba Tytuł pracy w języku polskim: Charakterystyka mikrostruktury spoin Ag/X/Ag (X = Sn, In) uzyskanych w wyniku niskotemperaturowego
Dr inż. Przemysław Skrzyniarz Kierownik pracy: Prof. dr hab. inż. Paweł Zięba Tytuł pracy w języku polskim: Charakterystyka mikrostruktury spoin Ag/X/Ag (X = Sn, In) uzyskanych w wyniku niskotemperaturowego
ZASTOSOWANIE MODELU NUMERYCZNEGO DO ANALIZY PRZEMYSŁOWEGO PROCESU WALCOWANIA PRĘTÓW
 Prace IMŻ 4 (2010) 15 Barbara NIŻNIK Instytut Metalurgii Żelaza Maciej PIERZYK Akademia Górniczo-Hutnicza w Krakowie ZASOSOWANIE MODELU NUMERYCZNEGO DO ANALIZY PRZEMYSŁOWEGO PROCESU WALCOWANIA PRĘÓW W
Prace IMŻ 4 (2010) 15 Barbara NIŻNIK Instytut Metalurgii Żelaza Maciej PIERZYK Akademia Górniczo-Hutnicza w Krakowie ZASOSOWANIE MODELU NUMERYCZNEGO DO ANALIZY PRZEMYSŁOWEGO PROCESU WALCOWANIA PRĘÓW W
Proposal of thesis topic for mgr in. (MSE) programme in Telecommunications and Computer Science
 Proposal of thesis topic for mgr in (MSE) programme 1 Topic: Monte Carlo Method used for a prognosis of a selected technological process 2 Supervisor: Dr in Małgorzata Langer 3 Auxiliary supervisor: 4
Proposal of thesis topic for mgr in (MSE) programme 1 Topic: Monte Carlo Method used for a prognosis of a selected technological process 2 Supervisor: Dr in Małgorzata Langer 3 Auxiliary supervisor: 4
Fig 5 Spectrograms of the original signal (top) extracted shaft-related GAD components (middle) and
 Fig 4 Measured vibration signal (top). Blue original signal. Red component related to periodic excitation of resonances and noise. Green component related. Rotational speed profile used for experiment
Fig 4 Measured vibration signal (top). Blue original signal. Red component related to periodic excitation of resonances and noise. Green component related. Rotational speed profile used for experiment
Lecture 18 Review for Exam 1
 Spring, 2019 ME 323 Mechanics of Materials Lecture 18 Review for Exam 1 Reading assignment: HW1-HW5 News: Ready for the exam? Instructor: Prof. Marcial Gonzalez Announcements Exam 1 - Wednesday February
Spring, 2019 ME 323 Mechanics of Materials Lecture 18 Review for Exam 1 Reading assignment: HW1-HW5 News: Ready for the exam? Instructor: Prof. Marcial Gonzalez Announcements Exam 1 - Wednesday February
Krytyczne czynniki sukcesu w zarządzaniu projektami
 Seweryn SPAŁEK Krytyczne czynniki sukcesu w zarządzaniu projektami MONOGRAFIA Wydawnictwo Politechniki Śląskiej Gliwice 2004 SPIS TREŚCI WPROWADZENIE 5 1. ZARZĄDZANIE PROJEKTAMI W ORGANIZACJI 13 1.1. Zarządzanie
Seweryn SPAŁEK Krytyczne czynniki sukcesu w zarządzaniu projektami MONOGRAFIA Wydawnictwo Politechniki Śląskiej Gliwice 2004 SPIS TREŚCI WPROWADZENIE 5 1. ZARZĄDZANIE PROJEKTAMI W ORGANIZACJI 13 1.1. Zarządzanie
 www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
Adres do korespondencji: Instytut Metalurgii i Inżynierii Materiałowej PAN, Kraków, ul. Reymonta 25
 Adres do korespondencji: Instytut Metalurgii i Inżynierii Materiałowej PAN, 30059 Kraków, ul. Reymonta 25 Tel.: (012) 295 28 86, pokój 10, fax: (012) 295 28 04 email: w.wajda@imim.pl Miejsca zatrudnienia
Adres do korespondencji: Instytut Metalurgii i Inżynierii Materiałowej PAN, 30059 Kraków, ul. Reymonta 25 Tel.: (012) 295 28 86, pokój 10, fax: (012) 295 28 04 email: w.wajda@imim.pl Miejsca zatrudnienia
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume Issue 4
 A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 54 2009 Issue 4 D. LEŚNIAK STRUCTURE AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF EXTRUDED AlCuMg SECTIONS IN T5 TEMPER STRUKTURA I WŁASNOŚCI MECHANICZNE
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 54 2009 Issue 4 D. LEŚNIAK STRUCTURE AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF EXTRUDED AlCuMg SECTIONS IN T5 TEMPER STRUKTURA I WŁASNOŚCI MECHANICZNE
Knovel Math: Jakość produktu
 Knovel Math: Jakość produktu Knovel jest agregatorem materiałów pełnotekstowych dostępnych w formacie PDF i interaktywnym. Narzędzia interaktywne Knovel nie są stworzone wokół specjalnych algorytmów wymagających
Knovel Math: Jakość produktu Knovel jest agregatorem materiałów pełnotekstowych dostępnych w formacie PDF i interaktywnym. Narzędzia interaktywne Knovel nie są stworzone wokół specjalnych algorytmów wymagających
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume Issue 3 DOI: /amm
 A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 58 2013 Issue 3 DOI: 10.2478/amm-2013-0064 D. DZIEDZIC, K. MUSZKA, J. MAJTA STRAIN-INDUCED AUSTENITIC STRUCTURE IN MICROALLOYED STEELS
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 58 2013 Issue 3 DOI: 10.2478/amm-2013-0064 D. DZIEDZIC, K. MUSZKA, J. MAJTA STRAIN-INDUCED AUSTENITIC STRUCTURE IN MICROALLOYED STEELS
Towards Stability Analysis of Data Transport Mechanisms: a Fluid Model and an Application
 Towards Stability Analysis of Data Transport Mechanisms: a Fluid Model and an Application Gayane Vardoyan *, C. V. Hollot, Don Towsley* * College of Information and Computer Sciences, Department of Electrical
Towards Stability Analysis of Data Transport Mechanisms: a Fluid Model and an Application Gayane Vardoyan *, C. V. Hollot, Don Towsley* * College of Information and Computer Sciences, Department of Electrical
PROCEEDINGS OF THE INSTITUTE OF VEHICLES 2(106)/2016 (12 pt)
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE INSTITUTE OF VEHICLES 2(106)/2016 Maciej Foremny 1, Szymon Gudowski 2, Michał Malesza 3, Henryk Bąkowski 4 TRIBOLOGICAL WEAR ESTIMATION OF THE ENGINE OILS USED IN DRIFTING 1. Introduction
PROCEEDINGS OF THE INSTITUTE OF VEHICLES 2(106)/2016 Maciej Foremny 1, Szymon Gudowski 2, Michał Malesza 3, Henryk Bąkowski 4 TRIBOLOGICAL WEAR ESTIMATION OF THE ENGINE OILS USED IN DRIFTING 1. Introduction
 www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
H γ0 - the standard enthalpy of g phase. H β γ - the transition enthalpy of b to g
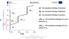 H α0 - the standard enthalpy of a phase H β0 - the standard enthalpy of b phase H γ0 - the standard enthalpy of g phase H α β - the transition enthalpy of a to b phase at T t1 H β γ - the transition enthalpy
H α0 - the standard enthalpy of a phase H β0 - the standard enthalpy of b phase H γ0 - the standard enthalpy of g phase H α β - the transition enthalpy of a to b phase at T t1 H β γ - the transition enthalpy
Dr inż. Łukasz Rogal zatrudniony jest w Instytucie Metalurgii i Inżynierii Materiałowej Polskiej Akademii Nauk na stanowisku adiunkta
 e-mail: l.rogal@imim.pl tel. 12 2952826 Miejsce zatrudnienia i zajmowane stanowiska Dr inż. Łukasz Rogal zatrudniony jest w Instytucie Metalurgii i Inżynierii Materiałowej Polskiej Akademii Nauk na stanowisku
e-mail: l.rogal@imim.pl tel. 12 2952826 Miejsce zatrudnienia i zajmowane stanowiska Dr inż. Łukasz Rogal zatrudniony jest w Instytucie Metalurgii i Inżynierii Materiałowej Polskiej Akademii Nauk na stanowisku
TYRE PYROLYSIS. REDUXCO GENERAL DISTRIBUTOR :: ::
 TYRE PYROLYSIS Installation for rubber waste pyrolysis designed for processing of used tyres and plastic waste (polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene), where the final product could be electricity,
TYRE PYROLYSIS Installation for rubber waste pyrolysis designed for processing of used tyres and plastic waste (polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene), where the final product could be electricity,
OPTIMIZATION OF THE HEAT TREATMENT PROCESS TO OBTAIN THE REQUIRED DISTRIBUTION OF MECHANICAL PROPERTIES IN THE RAIL HEAD OF PEARLITIC RAILS
 Roman KUZIAK Valeriy PIDVYSOTSK YY Krzysztof RADWAŃSKI Artur MAZUR DOI: 10.32730/imz.2657-747.19.1.1 Sieć Badawcza Łukasiewicz Instytut Metalurgii Żelaza im. Stanisława Staszica Tomasz ZYGMUNT ArcelorMittal
Roman KUZIAK Valeriy PIDVYSOTSK YY Krzysztof RADWAŃSKI Artur MAZUR DOI: 10.32730/imz.2657-747.19.1.1 Sieć Badawcza Łukasiewicz Instytut Metalurgii Żelaza im. Stanisława Staszica Tomasz ZYGMUNT ArcelorMittal
ROZPRAWY NR 128. Stanis³aw Mroziñski
 UNIWERSYTET TECHNOLOGICZNO-PRZYRODNICZY IM. JANA I JÊDRZEJA ŒNIADECKICH W BYDGOSZCZY ROZPRAWY NR 128 Stanis³aw Mroziñski STABILIZACJA W ASNOŒCI CYKLICZNYCH METALI I JEJ WP YW NA TRWA OŒÆ ZMÊCZENIOW BYDGOSZCZ
UNIWERSYTET TECHNOLOGICZNO-PRZYRODNICZY IM. JANA I JÊDRZEJA ŒNIADECKICH W BYDGOSZCZY ROZPRAWY NR 128 Stanis³aw Mroziñski STABILIZACJA W ASNOŒCI CYKLICZNYCH METALI I JEJ WP YW NA TRWA OŒÆ ZMÊCZENIOW BYDGOSZCZ
THERMODYNAMICS OF OXYGEN IN DILUTE LIQUID SILVER-TELLURIUM ALLOYS
 AGH University of Science and Technology Faculty of Non-Ferrous Metals Laboratory of Physical Chemistry and Electrochemistry THERMODYNAMICS OF OXYGEN IN DILUTE LIQUID SILVER-TELLURIUM ALLOYS Justyna Nyk,
AGH University of Science and Technology Faculty of Non-Ferrous Metals Laboratory of Physical Chemistry and Electrochemistry THERMODYNAMICS OF OXYGEN IN DILUTE LIQUID SILVER-TELLURIUM ALLOYS Justyna Nyk,
SYMULACJA TŁOCZENIA ZAKRYWEK KORONKOWYCH SIMULATION OF CROWN CLOSURES FORMING
 MARIUSZ DOMAGAŁA, STANISŁAW OKOŃSKI ** SYMULACJA TŁOCZENIA ZAKRYWEK KORONKOWYCH SIMULATION OF CROWN CLOSURES FORMING S t r e s z c z e n i e A b s t r a c t W artykule podjęto próbę modelowania procesu
MARIUSZ DOMAGAŁA, STANISŁAW OKOŃSKI ** SYMULACJA TŁOCZENIA ZAKRYWEK KORONKOWYCH SIMULATION OF CROWN CLOSURES FORMING S t r e s z c z e n i e A b s t r a c t W artykule podjęto próbę modelowania procesu
 www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
INSPECTION METHODS FOR QUALITY CONTROL OF FIBRE METAL LAMINATES IN AEROSPACE COMPONENTS
 Kompozyty 11: 2 (2011) 130-135 Krzysztof Dragan 1 * Jarosław Bieniaś 2, Michał Sałaciński 1, Piotr Synaszko 1 1 Air Force Institute of Technology, Non Destructive Testing Lab., ul. ks. Bolesława 6, 01-494
Kompozyty 11: 2 (2011) 130-135 Krzysztof Dragan 1 * Jarosław Bieniaś 2, Michał Sałaciński 1, Piotr Synaszko 1 1 Air Force Institute of Technology, Non Destructive Testing Lab., ul. ks. Bolesława 6, 01-494
Conception of reuse of the waste from onshore and offshore in the aspect of
 Conception of reuse of the waste from onshore and offshore in the aspect of environmental protection" Koncepcja zagospodarowania odpadów wiertniczych powstających podczas wierceń lądowych i morskich w
Conception of reuse of the waste from onshore and offshore in the aspect of environmental protection" Koncepcja zagospodarowania odpadów wiertniczych powstających podczas wierceń lądowych i morskich w
DETECTION OF MATERIAL INTEGRATED CONDUCTORS FOR CONNECTIVE RIVETING OF FUNCTION-INTEGRATIVE TEXTILE-REINFORCED THERMOPLASTIC COMPOSITES
 Kompozyty 11: 2 (2011) 152-156 Werner A. Hufenbach, Frank Adam, Maik Gude, Ivonne Körner, Thomas Heber*, Anja Winkler Technische Universität Dresden, Institute of Lightweight Engineering and Polymer Technology
Kompozyty 11: 2 (2011) 152-156 Werner A. Hufenbach, Frank Adam, Maik Gude, Ivonne Körner, Thomas Heber*, Anja Winkler Technische Universität Dresden, Institute of Lightweight Engineering and Polymer Technology
Przewody do linii napowietrznych Przewody z drutów okrągłych skręconych współosiowo
 POPRAWKA do POLSKIEJ NORMY ICS 29.060.10 PNEN 50182:2002/AC Wprowadza EN 50182:2001/AC:2013, IDT Przewody do linii napowietrznych Przewody z drutów okrągłych skręconych współosiowo Poprawka do Normy Europejskiej
POPRAWKA do POLSKIEJ NORMY ICS 29.060.10 PNEN 50182:2002/AC Wprowadza EN 50182:2001/AC:2013, IDT Przewody do linii napowietrznych Przewody z drutów okrągłych skręconych współosiowo Poprawka do Normy Europejskiej
ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA. Model obliczeniowy ogrzewań mikroprzewodowych
 POLITECHNIKA WARSZAWSKA Wydział Inżynierii Środowiska Instytut Ogrzewnictwa i Wentylacji ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA mgr inż. Michał Strzeszewski Model obliczeniowy ogrzewań mikroprzewodowych (streszczenie) Promotor
POLITECHNIKA WARSZAWSKA Wydział Inżynierii Środowiska Instytut Ogrzewnictwa i Wentylacji ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA mgr inż. Michał Strzeszewski Model obliczeniowy ogrzewań mikroprzewodowych (streszczenie) Promotor
TECHNICAL CATALOGUE WHITEHEART MALLEABLE CAST IRON FITTINGS EE
 TECHNICAL CATALOGUE WHITEHEART MALLEABLE CAST IRON FITTINGS EE Poland GENERAL INFORMATION USE Whiteheart malleable cast iron fittings brand EE are used in threaded pipe joints, particularly in water, gas,
TECHNICAL CATALOGUE WHITEHEART MALLEABLE CAST IRON FITTINGS EE Poland GENERAL INFORMATION USE Whiteheart malleable cast iron fittings brand EE are used in threaded pipe joints, particularly in water, gas,
Fizyczne modelowanie walcowania normalizującego blach grubych ze stali S355J2G3
 S. 296 Hutnik Wiadomości hutniczen nr 6 Dr inż. JAROSŁAW markowski UKD 621.771.23.001.57:669-153:669-12: Dr inż. MARCIN KNAPIŃSKI, 669-413:669.14.018.298.3:669.017 Dr inż. BARTOSZ KOCZURKIEWICZ Dr inż.
S. 296 Hutnik Wiadomości hutniczen nr 6 Dr inż. JAROSŁAW markowski UKD 621.771.23.001.57:669-153:669-12: Dr inż. MARCIN KNAPIŃSKI, 669-413:669.14.018.298.3:669.017 Dr inż. BARTOSZ KOCZURKIEWICZ Dr inż.
IDENTYFIKACJA I ANALIZA PARAMETRÓW GEOMETRYCZNYCH I MECHANICZNYCH KOŚCI MIEDNICZNEJ CZŁOWIEKA
 POLITECHNIKA ŚLĄSKA ZESZYTY NAUKOWE Nr 1651 Antoni JOHN SUB Gottingen 7 217 780 458 2005 A 3012 IDENTYFIKACJA I ANALIZA PARAMETRÓW GEOMETRYCZNYCH I MECHANICZNYCH KOŚCI MIEDNICZNEJ CZŁOWIEKA Gliwice 2004
POLITECHNIKA ŚLĄSKA ZESZYTY NAUKOWE Nr 1651 Antoni JOHN SUB Gottingen 7 217 780 458 2005 A 3012 IDENTYFIKACJA I ANALIZA PARAMETRÓW GEOMETRYCZNYCH I MECHANICZNYCH KOŚCI MIEDNICZNEJ CZŁOWIEKA Gliwice 2004
Opracowanie technologii wytwarzania wyrobów ze. stopów Mg o podwyższonej biozgodności. Development of technologies of the production of Mg
 Opracowanie technologii wytwarzania wyrobów ze stopów Mg o podwyższonej biozgodności Development of technologies of the production of Mg alloy products with increased biocompatibility prof. Andrzej Milenin
Opracowanie technologii wytwarzania wyrobów ze stopów Mg o podwyższonej biozgodności Development of technologies of the production of Mg alloy products with increased biocompatibility prof. Andrzej Milenin
AFTER LONG-TERM OPERATION IN CREEP CONDITIONS FOR THE POWER INDUSTRY
 2 Prace Instytutu Metalurgii Żelaza 2018, 70 (2), s. 2 18 DOI: 10.32730/imz.0137-9941.18.2.01 Tadeusz JÓŹWIK EFFECT OF AUSTENITISING ON THE STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES OF LOW-ALLOY Cr-Mo-V STEELS AFTER LONG-TERM
2 Prace Instytutu Metalurgii Żelaza 2018, 70 (2), s. 2 18 DOI: 10.32730/imz.0137-9941.18.2.01 Tadeusz JÓŹWIK EFFECT OF AUSTENITISING ON THE STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES OF LOW-ALLOY Cr-Mo-V STEELS AFTER LONG-TERM
 www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume Issue 3
 A R C H I E S O M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S olume 55 200 Issue 3 T. REC, A. MILENIN NUMERICAL MODELING O MACROSEGREGATION AND STRESS-STRAIN STATE DISTRIBUTION IN SLAB DURING CONTINUE CASTING
A R C H I E S O M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S olume 55 200 Issue 3 T. REC, A. MILENIN NUMERICAL MODELING O MACROSEGREGATION AND STRESS-STRAIN STATE DISTRIBUTION IN SLAB DURING CONTINUE CASTING
Characteristic of DTA curves for cast ferrous alloys
 ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 8 Issue 1/2008 183 197 37/1 Characteristic of DTA curves
ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 8 Issue 1/2008 183 197 37/1 Characteristic of DTA curves
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 11. Spectral Embedding + Clustering
 Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 11 Spectral Embedding + Clustering MOTIVATING EXAMPLE What can you say from this network? MOTIVATING EXAMPLE How about now? THOUGHT EXPERIMENT For each
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 11 Spectral Embedding + Clustering MOTIVATING EXAMPLE What can you say from this network? MOTIVATING EXAMPLE How about now? THOUGHT EXPERIMENT For each
 !850016! www.irs.gov/form8879eo. e-file www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C,
!850016! www.irs.gov/form8879eo. e-file www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C,
WPŁYW PARAMETRÓW OBRÓBKI CIEPLNEJ TAŚM ZE STALI X6CR17 NA ICH WŁAŚCIWOŚCI MECHANICZNE I STRUKTURĘ
 2 Prace IMŻ 2 (2012) Krzysztof RADWAŃSKI, Jerzy WIEDERMANN Instytut Metalurgii Żelaza Andrzej ADAMIEC Przeróbka Plastyczna na Zimno Baildon Sp. z o.o. Jarosław GAZDOWICZ Instytut Metalurgii Żelaza WPŁYW
2 Prace IMŻ 2 (2012) Krzysztof RADWAŃSKI, Jerzy WIEDERMANN Instytut Metalurgii Żelaza Andrzej ADAMIEC Przeróbka Plastyczna na Zimno Baildon Sp. z o.o. Jarosław GAZDOWICZ Instytut Metalurgii Żelaza WPŁYW
Materiałowe i technologiczne uwarunkowania stanu naprężeń własnych i anizotropii wtórnej powłok cylindrycznych wytłaczanych z polietylenu
 POLITECHNIKA ŚLĄSKA ZESZYTY NAUKOWE NR 1676 SUB Gottingen 7 217 872 077 Andrzej PUSZ 2005 A 12174 Materiałowe i technologiczne uwarunkowania stanu naprężeń własnych i anizotropii wtórnej powłok cylindrycznych
POLITECHNIKA ŚLĄSKA ZESZYTY NAUKOWE NR 1676 SUB Gottingen 7 217 872 077 Andrzej PUSZ 2005 A 12174 Materiałowe i technologiczne uwarunkowania stanu naprężeń własnych i anizotropii wtórnej powłok cylindrycznych
Streszczenie rozprawy doktorskiej
 Doskonalenie pomiaru zawartości wody w produktach spożywczych z wykorzystaniem metody wagosuszarkowej bazującej na promieniowaniu IR mgr Sławomir Janas Streszczenie rozprawy doktorskiej Promotor pracy:
Doskonalenie pomiaru zawartości wody w produktach spożywczych z wykorzystaniem metody wagosuszarkowej bazującej na promieniowaniu IR mgr Sławomir Janas Streszczenie rozprawy doktorskiej Promotor pracy:
Rozpoznawanie twarzy metodą PCA Michał Bereta 1. Testowanie statystycznej istotności różnic między jakością klasyfikatorów
 Rozpoznawanie twarzy metodą PCA Michał Bereta www.michalbereta.pl 1. Testowanie statystycznej istotności różnic między jakością klasyfikatorów Wiemy, że możemy porównywad klasyfikatory np. za pomocą kroswalidacji.
Rozpoznawanie twarzy metodą PCA Michał Bereta www.michalbereta.pl 1. Testowanie statystycznej istotności różnic między jakością klasyfikatorów Wiemy, że możemy porównywad klasyfikatory np. za pomocą kroswalidacji.
Outline of a method for fatigue life determination for selected aircraft s elements
 Outline TRIBOLOGY of a method for fatigue life determination for selected aircraft s elements 71 SCIENTIFIC PROBLEMS OF MACHINES OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE 4 (164) 2010 HENRYK TOMASZEK *, MICHAŁ JASZTAL
Outline TRIBOLOGY of a method for fatigue life determination for selected aircraft s elements 71 SCIENTIFIC PROBLEMS OF MACHINES OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE 4 (164) 2010 HENRYK TOMASZEK *, MICHAŁ JASZTAL
MODEL ROZWOJU MIKROSTRUKTURY WSPÓŁPRACUJĄCY Z SYSTEMEM STEROWANIA WALCOWNIĄ BLACH GRUBYCH
 MODEL ROZWOJU MIKROSTRUKTURY WSPÓŁPRAUJĄY Z SYSTEMEM STEROWANIA WALOWNIĄ BLAH GRUBYH D. Svietlichnyj *, H. Kusiak **, J. Ujma ***, M. Pietrzyk ** * Akademia Metalurgiczna Ukrainy, Dniepropietrowsk ** Akademia
MODEL ROZWOJU MIKROSTRUKTURY WSPÓŁPRAUJĄY Z SYSTEMEM STEROWANIA WALOWNIĄ BLAH GRUBYH D. Svietlichnyj *, H. Kusiak **, J. Ujma ***, M. Pietrzyk ** * Akademia Metalurgiczna Ukrainy, Dniepropietrowsk ** Akademia
ANDRZEJ GONTARZ, ANNA DZIUBIŃSKA
 ANDRZEJ GONTARZ, ANNA DZIUBIŃSKA Politechnika Lubelska, Katedra Komputerowego Modelowania i Technologii Obróbki Plastycznej ul. Nadbystrzycka 36, 20-618 Lublin a.gontarz@pollub.pl Własności stopu magnezu
ANDRZEJ GONTARZ, ANNA DZIUBIŃSKA Politechnika Lubelska, Katedra Komputerowego Modelowania i Technologii Obróbki Plastycznej ul. Nadbystrzycka 36, 20-618 Lublin a.gontarz@pollub.pl Własności stopu magnezu
RESONANCE OF TORSIONAL VIBRATION OF SHAFTS COUPLED BY MECHANISMS
 SCIENTIFIC BULLETIN OF LOZ TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY Nr 78, TEXTILES 55, 997 ZESZYTY NAUKOWE POLITECHNIKI ŁÓZKIEJ Nr 78, WŁÓKIENNICTWO z. 55, 997 Pages: 8- http://bhp-k4.p.loz.pl/ JERZY ZAJACZKOWSKI Loz Technical
SCIENTIFIC BULLETIN OF LOZ TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY Nr 78, TEXTILES 55, 997 ZESZYTY NAUKOWE POLITECHNIKI ŁÓZKIEJ Nr 78, WŁÓKIENNICTWO z. 55, 997 Pages: 8- http://bhp-k4.p.loz.pl/ JERZY ZAJACZKOWSKI Loz Technical
WPŁYW OBRÓBKI CIEPLNO-PLASTYCZNEJ NA TEMPERATURĘ POCZĄTKU PRZEMIANY MARTENZYTYCZNEJ W STOPIE Fe-30Ni
 74/21 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 21(2/2) ARCHIVES OF FOUNDARY Year 2006, Volume 6, Nº 21 (2/2) PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 WPŁYW OBRÓBKI CIEPLNO-PLASTYCZNEJ NA TEMPERATURĘ POCZĄTKU
74/21 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 21(2/2) ARCHIVES OF FOUNDARY Year 2006, Volume 6, Nº 21 (2/2) PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 WPŁYW OBRÓBKI CIEPLNO-PLASTYCZNEJ NA TEMPERATURĘ POCZĄTKU
P/M COMPOSITES OF Al-Si-Fe-Cu ALLOY WITH SiC PARTICLES HOT-EXTRUDED AFTER PRELIMINARY COMPACTION
 Kompozyty 11: 4 (211) 336-341 Marek Wojtaszek AGH University of Science and Technology, Faculty of Metals Engineering and Industrial Computer Science, al. Mickiewicza 3, 3-59 Kraków, Poland * Corresponding
Kompozyty 11: 4 (211) 336-341 Marek Wojtaszek AGH University of Science and Technology, Faculty of Metals Engineering and Industrial Computer Science, al. Mickiewicza 3, 3-59 Kraków, Poland * Corresponding
The impact of the global gravity field models on the orbit determination of LAGEOS satellites
 models on the Satelitarne metody wyznaczania pozycji we współczesnej geodezji i nawigacji, Poland 2-4.06.2011 Krzysztof Sośnica, Daniela Thaller, Adrian Jäggi, Rolf Dach and Gerhard Beutler Astronomical
models on the Satelitarne metody wyznaczania pozycji we współczesnej geodezji i nawigacji, Poland 2-4.06.2011 Krzysztof Sośnica, Daniela Thaller, Adrian Jäggi, Rolf Dach and Gerhard Beutler Astronomical
TO ADVANCED MODELLING OF END PLATE JOINTS
 CZASOPISMO INŻYNIERII LĄDOWEJ, ŚRODOWISKA I ARCHITEKTURY JOURNAL OF CIVIL ENGINEERING, ENVIRONMENT AND ARCHITECTURE JCEEA, t. XXX, z. 60 (2/13), kwiecień -czerwiec 2013, s. 77-86 Lukáš GÖDRICH 1 František
CZASOPISMO INŻYNIERII LĄDOWEJ, ŚRODOWISKA I ARCHITEKTURY JOURNAL OF CIVIL ENGINEERING, ENVIRONMENT AND ARCHITECTURE JCEEA, t. XXX, z. 60 (2/13), kwiecień -czerwiec 2013, s. 77-86 Lukáš GÖDRICH 1 František
WENTYLATORY PROMIENIOWE SINGLE-INLET DRUM BĘBNOWE JEDNOSTRUMIENIOWE CENTRIFUGAL FAN
 WENTYLATORY PROMIENIOWE SINGLE-INLET DRUM BĘBNOWE JEDNOSTRUMIENIOWE CENTRIFUGAL FAN TYP WPB TYPE WPB Wentylatory promieniowe jednostrumieniowe bębnowe (z wirnikiem typu Single-inlet centrifugal fans (with
WENTYLATORY PROMIENIOWE SINGLE-INLET DRUM BĘBNOWE JEDNOSTRUMIENIOWE CENTRIFUGAL FAN TYP WPB TYPE WPB Wentylatory promieniowe jednostrumieniowe bębnowe (z wirnikiem typu Single-inlet centrifugal fans (with
The analysis of the energy demand for heating and cooling of the house built on the basis of the traditional Canadian wood-frame construction
 Annals of Warsaw University of Life Sciences - SGGW Forestry and Wood Technology 85, 2014: 40-44 (Ann. WULS - SGGW, For. and Wood Technol. 85, 2014) The analysis of the energy demand for heating and cooling
Annals of Warsaw University of Life Sciences - SGGW Forestry and Wood Technology 85, 2014: 40-44 (Ann. WULS - SGGW, For. and Wood Technol. 85, 2014) The analysis of the energy demand for heating and cooling
WPŁYW SZYBKOŚCI STYGNIĘCIA NA WŁASNOŚCI TERMOFIZYCZNE STALIWA W STANIE STAŁYM
 2/1 Archives of Foundry, Year 200, Volume, 1 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 200, Rocznik, Nr 1 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-308 WPŁYW SZYBKOŚCI STYGNIĘCIA NA WŁASNOŚCI TERMOFIZYCZNE STALIWA W STANIE STAŁYM D.
2/1 Archives of Foundry, Year 200, Volume, 1 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 200, Rocznik, Nr 1 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-308 WPŁYW SZYBKOŚCI STYGNIĘCIA NA WŁASNOŚCI TERMOFIZYCZNE STALIWA W STANIE STAŁYM D.
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume Issue 2 DOI: /v x
 A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 57 2012 Issue 2 DOI: 10.2478/v10172-012-0056-x T. WĘGRZYN, J. PIWNIK LOW ALLOY STEEL WELDING WITH MICRO-JET COOLING SPAWANIE STALI
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 57 2012 Issue 2 DOI: 10.2478/v10172-012-0056-x T. WĘGRZYN, J. PIWNIK LOW ALLOY STEEL WELDING WITH MICRO-JET COOLING SPAWANIE STALI
Streszczenia / Abstracts 7/ 2012
 Zbigniew Mirski Kamil Śpiewak Spawanie laserowe mechanizmu siedzenia samochodowego Laser welding of car seat mechanism W artykule przedstawiono wyniki badań połączeń spawanych elementów regulacji pochylenia
Zbigniew Mirski Kamil Śpiewak Spawanie laserowe mechanizmu siedzenia samochodowego Laser welding of car seat mechanism W artykule przedstawiono wyniki badań połączeń spawanych elementów regulacji pochylenia
Institutional Determinants of IncomeLevel Convergence in the European. Union: Are Institutions Responsible for Divergence Tendencies of Some
 Institutional Determinants of IncomeLevel Convergence in the European Union: Are Institutions Responsible for Divergence Tendencies of Some Countries? Dr Mariusz Próchniak Katedra Ekonomii II, Szkoła Główna
Institutional Determinants of IncomeLevel Convergence in the European Union: Are Institutions Responsible for Divergence Tendencies of Some Countries? Dr Mariusz Próchniak Katedra Ekonomii II, Szkoła Główna
WPŁYW WANADU I MOLIBDENU ORAZ OBRÓBKI CIEPLNEJ STALIWA Mn-Ni DLA UZYSKANIA GRANICY PLASTYCZNOŚCI POWYŻEJ 850 MPa
 7/8 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2003, Rocznik 3, Nr 8 Archives of Foundry Year 2003, Volume 3, Book 8 PAN - Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 WPŁYW WANADU I MOLIBDENU ORAZ OBRÓBKI CIEPLNEJ STALIWA Mn-Ni DLA UZYSKANIA
7/8 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2003, Rocznik 3, Nr 8 Archives of Foundry Year 2003, Volume 3, Book 8 PAN - Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 WPŁYW WANADU I MOLIBDENU ORAZ OBRÓBKI CIEPLNEJ STALIWA Mn-Ni DLA UZYSKANIA
Stopy metali nieżelaznych Non-Ferrous Alloys
 MODULE DESCRIPTION Module code Module name Module name in English Valid from academic year 201/2014 MODULE PLACEMENT IN THE SYLLABUS Stopy metali nieżelaznych Non-Ferrous Alloys Subject Level of education
MODULE DESCRIPTION Module code Module name Module name in English Valid from academic year 201/2014 MODULE PLACEMENT IN THE SYLLABUS Stopy metali nieżelaznych Non-Ferrous Alloys Subject Level of education
Osiągnięcia Uzyskane wyniki
 Osiągnięcia 1. Opracowano wieloskalowe narzędzie informatyczne, pozwalające na modelowanie procesów rekrystalizacji stopów magnezu w procesie ciągnienia drutów o średnicach 0.05-0.1 mm w podgrzewanych
Osiągnięcia 1. Opracowano wieloskalowe narzędzie informatyczne, pozwalające na modelowanie procesów rekrystalizacji stopów magnezu w procesie ciągnienia drutów o średnicach 0.05-0.1 mm w podgrzewanych
ZASTOSOWANIE MECHANIZMU PRZEMIANY BAINITYCZNEJ DO MODELOWANIA OKNA OBRÓBCZEGO ŻELIWA ADI
 21/19 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 26, Rocznik 6, Nr 19 Archives of Foundry Year 26, Volume 6, Book 19 PAN - Katowice PL ISSN 1642-538 ZASTOSOWANIE MECHANIZMU PRZEMIANY BAINITYCZNEJ DO MODELOWANIA OKNA OBRÓBCZEGO
21/19 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 26, Rocznik 6, Nr 19 Archives of Foundry Year 26, Volume 6, Book 19 PAN - Katowice PL ISSN 1642-538 ZASTOSOWANIE MECHANIZMU PRZEMIANY BAINITYCZNEJ DO MODELOWANIA OKNA OBRÓBCZEGO
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume Issue 2 DOI: /v
 A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 57 2012 Issue 2 DOI: 10.2478/v10172-012-0067-7 M. WOJTASZEK, P. CHYŁA, T. ŚLEBODA, A. ŁUKASZEK-SOŁEK, S. BEDNAREK FEM MODELLING AND
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 57 2012 Issue 2 DOI: 10.2478/v10172-012-0067-7 M. WOJTASZEK, P. CHYŁA, T. ŚLEBODA, A. ŁUKASZEK-SOŁEK, S. BEDNAREK FEM MODELLING AND
BIOPHYSICS. Politechnika Łódzka, ul. Żeromskiego 116, Łódź, tel. (042)
 BIOPHYSICS Prezentacja multimedialna współfinansowana przez Unię Europejską w ramach Europejskiego Funduszu Społecznego w projekcie pt. Innowacyjna dydaktyka bez ograniczeń - zintegrowany rozwój Politechniki
BIOPHYSICS Prezentacja multimedialna współfinansowana przez Unię Europejską w ramach Europejskiego Funduszu Społecznego w projekcie pt. Innowacyjna dydaktyka bez ograniczeń - zintegrowany rozwój Politechniki
DM-ML, DM-FL. Auxiliary Equipment and Accessories. Damper Drives. Dimensions. Descritpion
 DM-ML, DM-FL Descritpion DM-ML and DM-FL actuators are designed for driving round dampers and square multi-blade dampers. Example identification Product code: DM-FL-5-2 voltage Dimensions DM-ML-6 DM-ML-8
DM-ML, DM-FL Descritpion DM-ML and DM-FL actuators are designed for driving round dampers and square multi-blade dampers. Example identification Product code: DM-FL-5-2 voltage Dimensions DM-ML-6 DM-ML-8
Probabilistic Methods and Statistics. Computer Science 1 st degree (1st degree / 2nd degree) General (general / practical)
 MODULE DESCRIPTION Module code Module name Metody probabilistyczne i statystyka Module name in English Probabilistic Methods and Statistics Valid from academic year 2012/2013 MODULE PLACEMENT IN THE SYLLABUS
MODULE DESCRIPTION Module code Module name Metody probabilistyczne i statystyka Module name in English Probabilistic Methods and Statistics Valid from academic year 2012/2013 MODULE PLACEMENT IN THE SYLLABUS
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume Issue 4 DOI: /amm
 A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 58 2013 Issue 4 DOI: 10.2478/amm-2013-0145 M. WOJTASZEK, T. ŚLEBODA, A. CZULAK, G. WEBER, W.A. HUFENBACH QUASI-STATIC AND DYNAMIC
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 58 2013 Issue 4 DOI: 10.2478/amm-2013-0145 M. WOJTASZEK, T. ŚLEBODA, A. CZULAK, G. WEBER, W.A. HUFENBACH QUASI-STATIC AND DYNAMIC
Latent Dirichlet Allocation Models and their Evaluation IT for Practice 2016
 Latent Dirichlet Allocation Models and their Evaluation IT for Practice 2016 Paweł Lula Cracow University of Economics, Poland pawel.lula@uek.krakow.pl Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) Documents Latent
Latent Dirichlet Allocation Models and their Evaluation IT for Practice 2016 Paweł Lula Cracow University of Economics, Poland pawel.lula@uek.krakow.pl Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) Documents Latent
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume Issue 1 DOI: /amm
 A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 59 2014 Issue 1 DOI: 10.2478/amm-2014-0056 T. KNYCH, M. PIWOWARSKA-ULIASZ, P. ULIASZ ALUMINIUM ALLOYS WITH ZIRCONIUM ADDITIONS, IN
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 59 2014 Issue 1 DOI: 10.2478/amm-2014-0056 T. KNYCH, M. PIWOWARSKA-ULIASZ, P. ULIASZ ALUMINIUM ALLOYS WITH ZIRCONIUM ADDITIONS, IN
SPIS TREŚCI SPIS WAŻNIEJSZYCH OZNACZEŃ WSTĘP KRÓTKA CHARAKTERYSTYKA SEKTORA ENERGETYCZNEGO W POLSCE... 14
 SPIS TREŚCI SPIS WAŻNIEJSZYCH OZNACZEŃ... 9 1. WSTĘP... 11 2. KRÓTKA CHARAKTERYSTYKA SEKTORA ENERGETYCZNEGO W POLSCE... 14 2.1. Analiza aktualnego stanu struktury wytwarzania elektryczności i ciepła w
SPIS TREŚCI SPIS WAŻNIEJSZYCH OZNACZEŃ... 9 1. WSTĘP... 11 2. KRÓTKA CHARAKTERYSTYKA SEKTORA ENERGETYCZNEGO W POLSCE... 14 2.1. Analiza aktualnego stanu struktury wytwarzania elektryczności i ciepła w
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume Issue 2 DOI: /amm
 A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 59 2014 Issue 2 DOI: 10.2478/amm-2014-0113 J. ZYCH, J. WRÓBEL INFLUENCE OF THE SELECTED FACTORS ON THERMAL FATIGUE OF THE ADI IN AN
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 59 2014 Issue 2 DOI: 10.2478/amm-2014-0113 J. ZYCH, J. WRÓBEL INFLUENCE OF THE SELECTED FACTORS ON THERMAL FATIGUE OF THE ADI IN AN
SWPS Uniwersytet Humanistycznospołeczny. Wydział Zamiejscowy we Wrocławiu. Karolina Horodyska
 SWPS Uniwersytet Humanistycznospołeczny Wydział Zamiejscowy we Wrocławiu Karolina Horodyska Warunki skutecznego promowania zdrowej diety i aktywności fizycznej: dobre praktyki w interwencjach psychospołecznych
SWPS Uniwersytet Humanistycznospołeczny Wydział Zamiejscowy we Wrocławiu Karolina Horodyska Warunki skutecznego promowania zdrowej diety i aktywności fizycznej: dobre praktyki w interwencjach psychospołecznych
KONTROLA STALIWA NIESTOPOWEGO METODĄ ATD
 36/12 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2004, Rocznik 4, Nr 12 Archives of Foundry Year 2004, Volume 4, Book 12 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 KONTROLA STALIWA NIESTOPOWEGO METODĄ ATD S. PIETROWSKI 1, G. GUMIENNY
36/12 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2004, Rocznik 4, Nr 12 Archives of Foundry Year 2004, Volume 4, Book 12 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 KONTROLA STALIWA NIESTOPOWEGO METODĄ ATD S. PIETROWSKI 1, G. GUMIENNY
Selection of controller parameters Strojenie regulatorów
 Division of Metrology and Power Processes Automation Selection of controller parameters Strojenie regulatorów A-9 Automatics laboratory Laboratorium automatyki Developed by//opracował: mgr inż. Wojciech
Division of Metrology and Power Processes Automation Selection of controller parameters Strojenie regulatorów A-9 Automatics laboratory Laboratorium automatyki Developed by//opracował: mgr inż. Wojciech
Politechnika Krakowska im. Tadeusza Kościuszki. Karta przedmiotu. obowiązuje studentów rozpoczynających studia w roku akademickim 2017/2018
 Politechnika Krakowska im. Tadeusza Kościuszki Karta przedmiotu Wydział Inżynierii Lądowej obowiązuje studentów rozpoczynających studia w roku akademickim 017/018 Kierunek studiów: Budownictwo Forma sudiów:
Politechnika Krakowska im. Tadeusza Kościuszki Karta przedmiotu Wydział Inżynierii Lądowej obowiązuje studentów rozpoczynających studia w roku akademickim 017/018 Kierunek studiów: Budownictwo Forma sudiów:
DOI: / /32/37
 . 2015. 4 (32) 1:18 DOI: 10.17223/1998863 /32/37 -,,. - -. :,,,,., -, -.,.-.,.,.,. -., -,.,,., -, 70 80. (.,.,. ),, -,.,, -,, (1886 1980).,.,, (.,.,..), -, -,,,, ; -, - 346, -,.. :, -, -,,,,,.,,, -,,,
. 2015. 4 (32) 1:18 DOI: 10.17223/1998863 /32/37 -,,. - -. :,,,,., -, -.,.-.,.,.,. -., -,.,,., -, 70 80. (.,.,. ),, -,.,, -,, (1886 1980).,.,, (.,.,..), -, -,,,, ; -, - 346, -,.. :, -, -,,,,,.,,, -,,,
G14L LPG toroidal tank
 G14L LPG toroidal tank Product Description 4-hole version of the unique STAKO patented design of the full (centre-filled) toroidal tank. The valve plate enhances the functionality of the tank compared
G14L LPG toroidal tank Product Description 4-hole version of the unique STAKO patented design of the full (centre-filled) toroidal tank. The valve plate enhances the functionality of the tank compared
POLITECHNIKA WARSZAWSKA. Wydział Zarządzania ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA. mgr Marcin Chrząścik
 POLITECHNIKA WARSZAWSKA Wydział Zarządzania ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA mgr Marcin Chrząścik Model strategii promocji w zarządzaniu wizerunkiem regionu Warmii i Mazur Promotor dr hab. Jarosław S. Kardas, prof.
POLITECHNIKA WARSZAWSKA Wydział Zarządzania ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA mgr Marcin Chrząścik Model strategii promocji w zarządzaniu wizerunkiem regionu Warmii i Mazur Promotor dr hab. Jarosław S. Kardas, prof.
Typ VFR. Circular flow adjustment dampers for the adjustment of volume flow rates and pressures in supply air and extract air systems
 Typ VFR FOR THE RELIABLE BALANCING OF VOLUME FLOW RATES Circular flow adjustment dampers for the adjustment of volume flow rates and pressures in supply air and extract air systems Each flow adjustment
Typ VFR FOR THE RELIABLE BALANCING OF VOLUME FLOW RATES Circular flow adjustment dampers for the adjustment of volume flow rates and pressures in supply air and extract air systems Each flow adjustment
QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE CHARACTERISTICS OF FINGERPRINT BIOMETRIC TEMPLATES
 ZESZYTY NAUKOWE POLITECHNIKI ŚLĄSKIEJ 2014 Seria: ORGANIZACJA I ZARZĄDZANIE z. 74 Nr kol. 1921 Adrian KAPCZYŃSKI Politechnika Śląska Instytut Ekonomii i Informatyki QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE CHARACTERISTICS
ZESZYTY NAUKOWE POLITECHNIKI ŚLĄSKIEJ 2014 Seria: ORGANIZACJA I ZARZĄDZANIE z. 74 Nr kol. 1921 Adrian KAPCZYŃSKI Politechnika Śląska Instytut Ekonomii i Informatyki QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE CHARACTERISTICS
ANALIZA KINETYKI REKRYSTALIZACJI PO ODKSZTAŁCENIU ZA POMOCĄ METODY RELAKSACJI NAPRĘŻENIA
 10 Prace Instytutu Metalurgii Żelaza nr 2/2016, tom 68 Valeriy PIDVYSOTS KYY, Roman KUZIAK ANALIZA KINETYKI REKRYSTALIZACJI PO ODKSZTAŁCENIU ZA POMOCĄ METODY RELAKSACJI NAPRĘŻENIA Głównym celem niniejszej
10 Prace Instytutu Metalurgii Żelaza nr 2/2016, tom 68 Valeriy PIDVYSOTS KYY, Roman KUZIAK ANALIZA KINETYKI REKRYSTALIZACJI PO ODKSZTAŁCENIU ZA POMOCĄ METODY RELAKSACJI NAPRĘŻENIA Głównym celem niniejszej
Auditorium classes. Lectures
 Faculty of: Mechanical and Robotics Field of study: Mechatronic with English as instruction language Study level: First-cycle studies Form and type of study: Full-time studies Annual: 2016/2017 Lecture
Faculty of: Mechanical and Robotics Field of study: Mechatronic with English as instruction language Study level: First-cycle studies Form and type of study: Full-time studies Annual: 2016/2017 Lecture
Inverse problems - Introduction - Probabilistic approach
 Inverse problems - Introduction - Probabilistic approach Wojciech Dȩbski Instytut Geofizyki PAN debski@igf.edu.pl Wydział Fizyki UW, 13.10.2004 Wydział Fizyki UW Warszawa, 13.10.2004 (1) Plan of the talk
Inverse problems - Introduction - Probabilistic approach Wojciech Dȩbski Instytut Geofizyki PAN debski@igf.edu.pl Wydział Fizyki UW, 13.10.2004 Wydział Fizyki UW Warszawa, 13.10.2004 (1) Plan of the talk
EFFECT OF METALLURGIC PURITY OF THE 15CRMOV (15HGMV) STEEL ON TECHNOLOGICAL AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF COLD-DEFORMED PRODUCTS
 30 Prace Instytutu Metalurgii Żelaza 2018, 70 (2), s. 30 36 Marek BURDEK, Jarosław MARCISZ, Jerzy STĘPIEŃ DOI: 10.32730/imz.0137-9941.18.2.03 EFFECT OF METALLURGIC PURITY OF THE 15CRMOV6-10-3 (15HGMV)
30 Prace Instytutu Metalurgii Żelaza 2018, 70 (2), s. 30 36 Marek BURDEK, Jarosław MARCISZ, Jerzy STĘPIEŃ DOI: 10.32730/imz.0137-9941.18.2.03 EFFECT OF METALLURGIC PURITY OF THE 15CRMOV6-10-3 (15HGMV)
Rola obróbki cieplno-plastycznej w kształtowaniu struktury i właściwości mechanicznych stali przeznaczonych do walcowania walcówki
 Obróbka Plastyczna Metali vol. XXIX nr 2 (2018), s. 193 212 Metal Forming vol. XXIX no. 2 (2018), pp. 193 212 Inżynieria materiałowa w obróbce plastycznej Material engineering in metal forming Oryginalny
Obróbka Plastyczna Metali vol. XXIX nr 2 (2018), s. 193 212 Metal Forming vol. XXIX no. 2 (2018), pp. 193 212 Inżynieria materiałowa w obróbce plastycznej Material engineering in metal forming Oryginalny
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture11. Random Projections & Canonical Correlation Analysis
 Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture11 5 Random Projections & Canonical Correlation Analysis The Tall, THE FAT AND THE UGLY n X d The Tall, THE FAT AND THE UGLY d X > n X d n = n d d The
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture11 5 Random Projections & Canonical Correlation Analysis The Tall, THE FAT AND THE UGLY n X d The Tall, THE FAT AND THE UGLY d X > n X d n = n d d The
yft Lublin, June 1999
 Waldemar STAROŃ Janusz MIELNIK Henryk GURGUL Department of Sea Physics Chair of Physics Szczecin University Wielkopolska 15,70-451 Szczecin POLAND POLISH POLAR STUDIES XXVI Polar Symposium yft Lublin,
Waldemar STAROŃ Janusz MIELNIK Henryk GURGUL Department of Sea Physics Chair of Physics Szczecin University Wielkopolska 15,70-451 Szczecin POLAND POLISH POLAR STUDIES XXVI Polar Symposium yft Lublin,
XXIII Konferencja Naukowa POJAZDY SZYNOWE 2018
 XXIII Konferencja Naukowa POJAZDY SZYNOWE 2018 Abstract Application of longitudinal dynamics of the train in the simulator of catenary maintenance vehicles - experimental and numerical tests Robert Konowrocki
XXIII Konferencja Naukowa POJAZDY SZYNOWE 2018 Abstract Application of longitudinal dynamics of the train in the simulator of catenary maintenance vehicles - experimental and numerical tests Robert Konowrocki
Opis efektów kształcenia dla modułu zajęć
 Nazwa modułu: Narzędzia do przygotowywania tekstów naukowo-technicznych Rok akademicki: 2017/2018 Kod: MIM-1-506-n Punkty ECTS: 3 Wydział: Inżynierii Metali i Informatyki Przemysłowej Kierunek: Inżynieria
Nazwa modułu: Narzędzia do przygotowywania tekstów naukowo-technicznych Rok akademicki: 2017/2018 Kod: MIM-1-506-n Punkty ECTS: 3 Wydział: Inżynierii Metali i Informatyki Przemysłowej Kierunek: Inżynieria
Analysis of Movie Profitability STAT 469 IN CLASS ANALYSIS #2
 Analysis of Movie Profitability STAT 469 IN CLASS ANALYSIS #2 aaaklnictzzjb9tgfmcnadpg7oy0lxa9edva9kkapdarhyk2k7gourinlwsweyzikuyiigvyleiv/cv767fpf/5crc1xt9va5mx7w3m/ecuqw1kuztpx/rl3/70h73/w4cog9dhhn3z62d6jzy+yzj766txpoir9nzszisjynetqr+rvlfvyoozu5xbybpsxb1wahul8phczdt2v4zgchb7uecwphlyigrgkjcyiflfyci0kxnmr4z6kw0jsokvot8isntpa3gbknlcufiv/h+hh+eur4fomd417rvtfjoit5pfju6yxiab2fmwk0y/feuybobqk+axnke8xzjjhfyd8kkpl9zdoddkazd5j6bzpemjb64smjb6vb4xmehysu08lsrszopxftlzee130jcb0zjxy7r5wa2f1s2off2+dyatrughnrtpkuprlcpu55zlxpss/yqe2eamjkcf0jye8w8yas0paf6t0t2i9stmcua+inbi2rt01tz22tubbqwidypvgz6piynkpobirkxgu54ibzoti4pkw2i5ow9lnuaoabhuxfxqhvnrj6w15tb3furnbm+scyxobjhr5pmj5j/w5ix9wsa2tlwx9alpshlunzjgnrwvqbpwzjl9wes+ptyn+ypy/jgskavtl8j0hz1djdhzwtpjbbvpr1zj7jpg6ve7zxfngj75zee0vmp9qm2uvgu/9zdofq6r+g8l4xctvo+v+xdrfr8oxiwutycu0qgyf8icuyvp/sixfi9zxe11vp6mrjjovpmxm6acrtbia+wjr9bevlgjwlz5xd3rfna9g06qytaoofk8olxbxc7xby2evqjmmk6pjvvzxmpbnct6+036xp5vdbrnbdqph8brlfn/n/khnfumhf6z1v7h/80yieukkd5j0un82t9mynxzmk0s/bzn4tacdziszdhwrl8x5ako8qp1n1zn0k6w2em0km9zj1i4yt1pt3xiprw85jmc2m1ut2geum6y6es2fwx6c+wlrpykblopbuj5nnr2byygfy5opllv4+jmm7s6u+tvhywbnb0kv2lt5th4xipmiij+y1toiyo7bo0d+vzvovjkp6aoejsubhj3qrp3fjd/m23pay8h218ibvx3nicofvd1xi86+kh6nb/b+hgsjp5+qwpurzlir15np66vmdehh6tyazdm1k/5ejtuvurgcqux6yc+qw/sbsaj7lkt4x9qmtp7euk6zbdedyuzu6ptsu2eeu3rxcz06uf6g8wyuveznhkbzynajbb7r7cbmla+jbtrst0ow2v6ntkwv8svnwqnu5pa3oxfeexf93739p93chq/fv+jr8r0d9brhpcxr2w88bvqbr41j6wvrb+u5dzjpvx+veoaxwptzp/8cen+xbg==
Analysis of Movie Profitability STAT 469 IN CLASS ANALYSIS #2 aaaklnictzzjb9tgfmcnadpg7oy0lxa9edva9kkapdarhyk2k7gourinlwsweyzikuyiigvyleiv/cv767fpf/5crc1xt9va5mx7w3m/ecuqw1kuztpx/rl3/70h73/w4cog9dhhn3z62d6jzy+yzj766txpoir9nzszisjynetqr+rvlfvyoozu5xbybpsxb1wahul8phczdt2v4zgchb7uecwphlyigrgkjcyiflfyci0kxnmr4z6kw0jsokvot8isntpa3gbknlcufiv/h+hh+eur4fomd417rvtfjoit5pfju6yxiab2fmwk0y/feuybobqk+axnke8xzjjhfyd8kkpl9zdoddkazd5j6bzpemjb64smjb6vb4xmehysu08lsrszopxftlzee130jcb0zjxy7r5wa2f1s2off2+dyatrughnrtpkuprlcpu55zlxpss/yqe2eamjkcf0jye8w8yas0paf6t0t2i9stmcua+inbi2rt01tz22tubbqwidypvgz6piynkpobirkxgu54ibzoti4pkw2i5ow9lnuaoabhuxfxqhvnrj6w15tb3furnbm+scyxobjhr5pmj5j/w5ix9wsa2tlwx9alpshlunzjgnrwvqbpwzjl9wes+ptyn+ypy/jgskavtl8j0hz1djdhzwtpjbbvpr1zj7jpg6ve7zxfngj75zee0vmp9qm2uvgu/9zdofq6r+g8l4xctvo+v+xdrfr8oxiwutycu0qgyf8icuyvp/sixfi9zxe11vp6mrjjovpmxm6acrtbia+wjr9bevlgjwlz5xd3rfna9g06qytaoofk8olxbxc7xby2evqjmmk6pjvvzxmpbnct6+036xp5vdbrnbdqph8brlfn/n/khnfumhf6z1v7h/80yieukkd5j0un82t9mynxzmk0s/bzn4tacdziszdhwrl8x5ako8qp1n1zn0k6w2em0km9zj1i4yt1pt3xiprw85jmc2m1ut2geum6y6es2fwx6c+wlrpykblopbuj5nnr2byygfy5opllv4+jmm7s6u+tvhywbnb0kv2lt5th4xipmiij+y1toiyo7bo0d+vzvovjkp6aoejsubhj3qrp3fjd/m23pay8h218ibvx3nicofvd1xi86+kh6nb/b+hgsjp5+qwpurzlir15np66vmdehh6tyazdm1k/5ejtuvurgcqux6yc+qw/sbsaj7lkt4x9qmtp7euk6zbdedyuzu6ptsu2eeu3rxcz06uf6g8wyuveznhkbzynajbb7r7cbmla+jbtrst0ow2v6ntkwv8svnwqnu5pa3oxfeexf93739p93chq/fv+jr8r0d9brhpcxr2w88bvqbr41j6wvrb+u5dzjpvx+veoaxwptzp/8cen+xbg==
Typ VFR. Circular flow adjustment dampers for the adjustment of volume flow rates and pressures in supply air and extract air systems
 Typ VFR FOR THE RELIABLE BALANCING OF VOLUME FLOW RATES Circular flow adjustment dampers for the adjustment of volume flow rates and pressures in supply air and extract air systems Each flow adjustment
Typ VFR FOR THE RELIABLE BALANCING OF VOLUME FLOW RATES Circular flow adjustment dampers for the adjustment of volume flow rates and pressures in supply air and extract air systems Each flow adjustment
APPLICATION. Journal of Machine Construction and Maintenance Problemy eksploatacji QUARTERLY ISSN /2017 (107) p
 Journal of Machine Construction and Maintenance Problemy eksploatacji QUARTERLY ISSN 1232-9312 4/2017 (107) p. 71 80 Łukasz Kuczek, Marcin Mroczkowski, Maria Richert Faculty of Non-Ferrous Metals, AGH
Journal of Machine Construction and Maintenance Problemy eksploatacji QUARTERLY ISSN 1232-9312 4/2017 (107) p. 71 80 Łukasz Kuczek, Marcin Mroczkowski, Maria Richert Faculty of Non-Ferrous Metals, AGH
DUAL SIMILARITY OF VOLTAGE TO CURRENT AND CURRENT TO VOLTAGE TRANSFER FUNCTION OF HYBRID ACTIVE TWO- PORTS WITH CONVERSION
 ELEKTRYKA 0 Zeszyt (9) Rok LX Andrzej KUKIEŁKA Politechnika Śląska w Gliwicach DUAL SIMILARITY OF VOLTAGE TO CURRENT AND CURRENT TO VOLTAGE TRANSFER FUNCTION OF HYBRID ACTIVE TWO- PORTS WITH CONVERSION
ELEKTRYKA 0 Zeszyt (9) Rok LX Andrzej KUKIEŁKA Politechnika Śląska w Gliwicach DUAL SIMILARITY OF VOLTAGE TO CURRENT AND CURRENT TO VOLTAGE TRANSFER FUNCTION OF HYBRID ACTIVE TWO- PORTS WITH CONVERSION
NIESTACJONARNY PRZEPŁYW CIEPŁA W TŁOKU DOŁADOWANEGO SILNIKA Z ZAPŁONEM SAMOCZYNNYM
 TRANSPORT PROBLEMS 2010 PROBLEMY TRANSPORTU Volume 5 Issue 1 Turbocharged diesel engine, piston, nonstationary heat flow Piotr GUSTOF*, Aleksander HORNIK Silesian University of Technology, Faculty of Transport,
TRANSPORT PROBLEMS 2010 PROBLEMY TRANSPORTU Volume 5 Issue 1 Turbocharged diesel engine, piston, nonstationary heat flow Piotr GUSTOF*, Aleksander HORNIK Silesian University of Technology, Faculty of Transport,
THE INFLUENCE OF THE ENGINE LOAD ON VALUE AND TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTION IN THE VALVE SEATS OF TURBO DIESEL ENGINE
 TRANSPORT PROBLEMS 2009 PROBLEMY TRANSPORTU Volume 4 Issue 2 Piotr GUSTOF*, Aleksander. HORNIK Silesian University of Technology, Faculty of Transport, Department of Vehicle Service Krasińskiego St. 8,
TRANSPORT PROBLEMS 2009 PROBLEMY TRANSPORTU Volume 4 Issue 2 Piotr GUSTOF*, Aleksander. HORNIK Silesian University of Technology, Faculty of Transport, Department of Vehicle Service Krasińskiego St. 8,
Zaawansowane stale wysokowytrzymałe dla przemysłu motoryzacyjnego - geneza, cykl wytwarzania, właściwości mechaniczne i użytkowe. R.
 Zaawansowane stale wysokowytrzymałe dla przemysłu motoryzacyjnego - geneza, cykl wytwarzania, właściwości mechaniczne i użytkowe R.Kuziak W prezentacji wykorzystano materiały: 1. Politechnika Śląska dr
Zaawansowane stale wysokowytrzymałe dla przemysłu motoryzacyjnego - geneza, cykl wytwarzania, właściwości mechaniczne i użytkowe R.Kuziak W prezentacji wykorzystano materiały: 1. Politechnika Śląska dr
MODEL ZJAWISK MECHANICZNYCH PROCESU HARTOWANIA STALI NISKOWĘGLOWEJ
 11/22 Archives of Foundry, Year 2006, Volume 6, 22 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 22 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 ODEL ZJAWISK ECHANICZNYCH PROCESU HARTOWANIA STALI NISKOWĘGLOWEJ A. BOKOTA
11/22 Archives of Foundry, Year 2006, Volume 6, 22 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 22 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 ODEL ZJAWISK ECHANICZNYCH PROCESU HARTOWANIA STALI NISKOWĘGLOWEJ A. BOKOTA
Formularz recenzji magazynu. Journal of Corporate Responsibility and Leadership Review Form
 Formularz recenzji magazynu Review Form Identyfikator magazynu/ Journal identification number: Tytuł artykułu/ Paper title: Recenzent/ Reviewer: (imię i nazwisko, stopień naukowy/name and surname, academic
Formularz recenzji magazynu Review Form Identyfikator magazynu/ Journal identification number: Tytuł artykułu/ Paper title: Recenzent/ Reviewer: (imię i nazwisko, stopień naukowy/name and surname, academic
PRZEMIANY FAZOWE I NAPRĘŻENIA PODCZAS HARTOWANIA STALI WĘGLOWYCH NARZĘDZIOWYCH
 7/14 Archives of Foundry, Year 2004, Volume 4, 14 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2004, Rocznik 4, Nr 14 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 PRZEMIANY FAZOWE I NAPRĘŻENIA PODCZAS HARTOWANIA STALI WĘGLOWYCH NARZĘDZIOWYCH
7/14 Archives of Foundry, Year 2004, Volume 4, 14 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2004, Rocznik 4, Nr 14 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 PRZEMIANY FAZOWE I NAPRĘŻENIA PODCZAS HARTOWANIA STALI WĘGLOWYCH NARZĘDZIOWYCH
Mikrostruktura, struktura magnetyczna oraz właściwości magnetyczne amorficznych i częściowo skrystalizowanych stopów Fe, Co i Ni
 mgr inż. Jakub Rzącki Praca doktorska p.t.: Mikrostruktura, struktura magnetyczna oraz właściwości magnetyczne amorficznych i częściowo skrystalizowanych stopów Fe, Co i Ni STRESZCZENIE W pracy przedstawiono
mgr inż. Jakub Rzącki Praca doktorska p.t.: Mikrostruktura, struktura magnetyczna oraz właściwości magnetyczne amorficznych i częściowo skrystalizowanych stopów Fe, Co i Ni STRESZCZENIE W pracy przedstawiono
THEORETICAL STUDIES ON CHEMICAL SHIFTS OF 3,6 DIIODO 9 ETHYL 9H CARBAZOLE
 THEORETICAL STUDIES ON CHEMICAL SHIFTS OF 3,6 DIIODO 9 ETHYL 9H CARBAZOLE Teobald Kupkaa, Klaudia Radula-Janika, Krzysztof Ejsmonta, Zdzisław Daszkiewicza, Stephan P. A. Sauerb a Faculty of Chemistry,
THEORETICAL STUDIES ON CHEMICAL SHIFTS OF 3,6 DIIODO 9 ETHYL 9H CARBAZOLE Teobald Kupkaa, Klaudia Radula-Janika, Krzysztof Ejsmonta, Zdzisław Daszkiewicza, Stephan P. A. Sauerb a Faculty of Chemistry,
