Identification and analysis of mutations in the katg gene in multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates
|
|
|
- Dagmara Pawłowska
- 6 lat temu
- Przeglądów:
Transkrypt
1 PRACA ORYGINALNA Tomasz Jagielski 1, Magdalena Grzeszczuk 1, Michał Kamiński 1, Katarzyna Roeske 1, Agnieszka Napiórkowska 2, Radosław Stachowiak 1, Ewa Augustynowicz-Kopeć 2, Zofia Zwolska 2, Jacek Bielecki 1 1 Department of Applied Microbiology, Institute of Microbiology, Faculty of Biology, University of Warsaw Head: Prof. J. Bielecki, PhD 2 Department of Microbiology, National Tuberculosis and Lung Diseases Research Institute, Warsaw Head: Prof. E. Augustynowicz-Kopeć, PhD Identification and analysis of mutations in the katg gene in multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates Identyfikacja i analiza mutacji w genie katg w szczepach klinicznych Mycobacterium tuberculosis o wielolekooporności typu MDR This study was financed by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education. Iuventus Plus grant. (Project No. IP ) Abstract Introduction: A major role in the development of resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to isoniazid (INH) is attributed to mutations in the katg gene coding for the catalase/peroxidase, an enzyme required for obtaining a pharmacologically active form of the drug. Analysis of mutations in the katg gene in M. tuberculosis strains may contribute to the development of reliable and rapid tests for detection of INH resistance. The aim of the study was to identify and characterize mutations in the katg gene in multidrug-resistant M. tuberculosis clinical isolates. Material and methods: The study included 46 strains of M. tuberculosis, recovered from MDR-TB patients in Poland in Mutations in the katg gene were detected by comparing DNA sequences with the corresponding sequence of a wild-type reference laboratory strain (M. tuberculosis H 37 Rv). The obtained results were interpreted in the context of MIC values of INH and catalase activity of the strains tested. Results: A total of 43 (93%) strains contained mutations in the katg gene. The most frequently observed were mutations at codon 315, found in 34 (74%) strains. Mutations at other codons were rare: 4 strains contained mutations at codon 463, 2 at codon 131 and another 2 at codon 234. Mutations at codons 68, 91, 101, 126, 128 and 194 were found in single strains only. Two strains, for which no mutations at codon 315 of the katg gene were identified, had a unique translation termination mutation, which would invariably result in polypeptide truncation leading to the generation of dysfunctional catalase polypeptides. Both these strains presented the highest MIC values for INH (80 and 100 µg/ml) and showed a complete loss of catalase activity. For the remaining 41 strains with katg mutations, the MICs of INH were within the range µg/ml. Thirty-six (88%) of those strains retained their catalase activity. Conclusions: Mutations at codon 315 within the katg gene, depending on their type might be useful for the prediction of INH resistance. Whereas the missense mutations do not affect the catalase activity or the level of INH resistance, the nonsense mutations result in high-level resistance to INH and a total loss of catalase activity. Key words: sequence analysis, tuberculosis, katg, mutations, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, multidrug resistance Pneumonol. Alergol. Pol. 2013; 81: Streszczenie Wstęp: Główną rolę w kształtowaniu oporności prątków gruźlicy (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) na izoniazyd (INH) przypisuje się mutacjom w genie katg kodującym białko katalazy/peroksydazy, enzym niezbędny do otrzymania aktywnej farmakologicznie formy leku. Analiza występowania mutacji w genie katg w szczepach M. tuberculosis może być podstawą dla opracowania wiarygodnych i szybkich testów wykrywania INH-oporności. Address for correspondence: Tomasz Jagielski, PhD, Department of Applied Microbiology, Institute of Microbiology, Faculty of Biology, University of Warsaw; ul. I. Miecznikowa 1, Warszawa. Tel.: ; Fax: , t.jagielski@biol.uw.edu.pl Praca wpłynęła do Redakcji: Copyright 2013 PTChP ISSN
2 Tomasz Jagielski et al., Mutations in the katg gene in MDR M. tuberculosis strains Celem pracy jest dentyfikacja i charakterystyka mutacji w genie katg w szczepach klinicznych M. tuberculosis o wielolekooporności typu MDR. Materiał i metody: Badanie objęło 46 szczepów wyizolowanych od chorych na gruźlicę MDR w Polsce w 2004 roku. Mutacje wykrywano, analizując sekwencje genu katg (2 223 pz) w porównaniu z sekwencją genu katg w szczepie M. tuberculosis H 37 Rv. Wyniki sekwencjonowania interpretowano w kontekście miana oporności na INH oraz aktywności katalazowej badanych szczepów. Wyniki: Mutacje w genie katg wykryto w 43 (93%) szczepach. Najczęściej obserwowaną była mutacja w kodonie 315, którą stwierdzono w 34 (74%) szczepach. Mutacje w innych kodonach występowały znacznie rzadziej; w 4 szczepach wykryto zmianę w kodonie 463, w 2 w kodonie 131, a w innych 2 w kodonie 234. Mutacje w kodonach 68, 91, 101, 126, 128 i 194 dotyczyły pojedynczych szczepów. W 2 szczepach wykryto pojedyncze mutacje typu nonsens, które, wprowadzając przedwczesne kodony terminacji translacji, powodowały powstanie skróconego, niefunkcjonalnego białka katalazy. Szczepy te charakteryzowały się najwyższym mianem oporności na INH (MIC = 80 i 100 µg/ml) oraz całkowitą utratą aktywności katalazy. Dla pozostałych 41 szczepów niosących mutacje w genie katg, wartości MIC INH mieściły się w zakresie µg/ml. Trzydzieści sześć (88%) spośród tych szczepów miało dodatni odczyn katalazy. Wnioski: Rodzaj mutacji w kodonie 315 genu katg może służyć jako czynnik predykcyjny oporności na INH. Mutacje typu missens nie wpływają na aktywność katalazy oraz miano oporności na INH. Mutacje typu nonsens skutkują wysokim mianem INH-oporności oraz utratą aktywności katalazy. Słowa kluczowe: analiza sekwencyjna, gruźlica, katg, mutacje, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, oporność typu MDR Pneumonol. Alergol. Pol. 2013; 81: Introduction Tuberculosis (TB) is still one of the greatest threats to human health in the contemporary world. It is estimated that 1/3 of the human population (more than 2 billion people) is infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. About 9 million new TB cases and 2 million deaths from the disease are noted each year [1]. The biggest challenge for a control and treatment system of TB is multidrug resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The multidrug resistance (MDR), i.e. resistance of mycobacteria to at least isoniazid (INH) and rifampicin (RMP), which are key drugs used in anti-tb therapy, is of crucial importance. It is estimated that MDR-TB constitutes about 5% of all TB cases in the world. In Poland multidrug resistance concerns almost exclusively previously treated patients. The proportion of MDR-TB cases in this group of patients is about 8% [2]. A significant parameter, which describes the phenotype of drug-resistant strains of M. tuberculosis, including MDR strains, is the enzymatic activity of the catalase-peroxidase system. In the middle of the previous century it was shown that many INH-resistant strains are characterized by a partial or complete loss of catalase and peroxidase activity [3 5]. This phenomenon has been used for diagnostic purposes. The examination of catalase activity has become an easy and rapid test that allows the susceptibility of clinical isolates to INH to be asessed. Genetic research conducted in the early 1990s has been of vital importance in explaining the relation between catalase activity of mycobacteria and their resistance to INH. Zhang et al. proved that transformation of the INH-resistant strains of Mycobacterium smegmatis and M. tuberculosis, made with the help of the functional katg gene coding for catalase-peroxidase protein (KatG), restored these strains sensitivity to INH [6, 7]. Hence it has been proved that KatG plays a major role in the biological activity of INH and the conditions the susceptibility of mycobacteria to this drug. However, the molecular mechanisms behind the INH activity are still unknown. Generally, it is assumed that INH is a prodrug, which after penetrating into the pathogen s cell is oxidized in the reaction catalysed by KatG to pharmacologically active derivatives. Then they form adducts with molecules of the NAD+ or NADP+ coenzyme. These adducts operate as inhibitors of the enzyme participating in the biosynthesis of nucleic acids and mycolic acids, the latter being constituents of the mycobacterial cell wall [8]. The katg gene deletion observed in some INH-resistant strains has proven to be the main mechanism of resistance to INH. This hypothesis has not been confirmed by numerous subsequent studies. They have shown that a complete katg gene deletion occurs rarely and usually concerns strains with a high level of INH resistance (MIC > 5 μg/ml) [9 12]. Currently it is considered that the main role in developing INH resistance is played by spontaneous mutations in the katg gene. They are usually single point mutations (missense mutations) or small (from 1 to 3 nucleotides) insertions or deletions. It is important that single mutations 299
3 Pneumonologia i Alergologia Polska 2013, tom 81, nr 4, strony occur at different frequencies and influence, in various ways, the activity of the KatG protein. The phenotypic effect of mutations, i.e. changed enzymatic activity of KatG, is evaluated in the in vitro tests. The purpose of this study was to investigate the occurrence of mutations in the katg gene of multidrug-resistant M. tuberculosis clinical isolates recovered from MDR-TB patients in Poland in Material and methods Bacterial strains The study included 46 strains of M. tuberculosis, which are part of the collection of the Department of Microbiology of the National Tuberculosis and Lung Diseases Research Institute in Warsaw. The strains were isolated from 46 Polish patients, diagnosed with TB in 20 medical facilities located in 11 provinces, and from whom MDR M. tuberculosis were cultured during the 12 months from January 1 st to December 31 st, The culture of mycobacterial strains was done using a conventional method on Löwenstein- -Jensen (L.-J.) medium [13]. Species identification was performed with the help of the niacin test, NAP test (the Bactec 460-Tb system), genetic probe AccuProbe (Gen-Probe), ProbeTec (Becton-Dickinson) and the analysis of mycolic acids by high pressure liquid chromatography (Varian). Drug susceptibility testing Drug susceptibility of M. tuberculosis strains was determined in subculture on L.-J. medium, in accordance with the methodology applied in all mycobacteria laboratories in Poland. Briefly, the following drug concentrations were used: 0.2 µg/ /ml for INH, 40 µg/ml for RMP, 4 µg/ml for streptomycin (SM) and 2 µg/ml for ethambutol (EMB). The strains whose growth was at least 1% of that on drug-free medium, and with resistance ratio (RR) at least four times higher in relation to the reference strain H 37 Rv (RR 4), were recognized as resistant [13]. To determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of INH for the studied strains, a series of 10 different concentrations, i.e. 0.2, 0.5, 1, 2.5, 5, 10, 20, 40, 80 and 100 µg/ml was used. Catalase activity The catalase activity of M. tuberculosis strains was determined semi-quantitatively using the Kubica method [14]. The catalase activity was expressed as the height of the foam column (h), measured in millimetres. The following scale was used: h 5, negative reaction; h > 5, positive reaction; h > 45, strongly positive reaction. DNA isolation Isolation of chromosomal DNA of mycobacteria was conducted from the culture on L.-J. medium, according to the method using cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) [15]. Detection of mutations in the katg gene Mutations in the katg gene were detected by sequencing the entire gene, obtained as a result of amplification performed by PCR method, as described by Cardoso et al. [16]. Amplification of the katg gene (2,223 pz) was performed in 4 PCR assays (A-D), with the primers, using the following scheme: 1. KatG-1-KatG-5 (A); 2. KatG-4-KatG-9 (B); 3. KatG-8-KatG-13 (C); 4. KatG-12-KatG-14 (D) (Tab. 1). Reaction mixtures were prepared by using a TopTaq MasterMix (Qiagen). The mixture of a final volume of 50 μl contained: 25 μl 2x TopTaq MasterMix (final concentration 1x), 0.5 μl of each primer (final concentration 0.2 μm), 22 μl of water and 2 μl of template genomic DNA (earlier diluted with water in a ratio of 1:50). The following PCR conditions were used: 95 C for 5 min (initial denaturation), followed by 35 cycles of: 95 C for 30 s, 68 C or 62 C (only in amplification with primers KatG-12-KatG-14) for 30 s and 72 C for 1 min. The final elongation step was performed at a temperature of 72 C for 7 min. Homogeneity of PCR products was assessed electrophoretically. Electrophoresis was conducted in 1.5% agarose gels in TBE buffer. The gels were stained with ethidium bromide (0.5 µg/ml), and the DNA was visualized under UV light. The gel images were captured and analysed using ImageMaster VDS (Video Documentation System) software (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech.). The obtained PCR products were purified by using a PCR Clean Up kit (A&A, Biotechnology), according to the manufacturer s instructions. The purified PCR products of at least 10 ng/ /µl concentration were sequenced by using the ABI PRISM 310 analyser (Applied Biosystems, CA, USA). Sequencing was performed in both forward and reverse directions (i.e. 5 Æ3 and 3 Æ5 ). Sequencing was done with the help of the same primers used for thepcr amplification of the katg gene (Tab. 1). Analysis of the obtained nucleotide sequences was conducted using Chromas 1.45 software and programs from the EMBOSS package (Matcher, 300
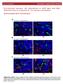
4 Tomasz Jagielski et al., Mutations in the katg gene in MDR M. tuberculosis strains Table 1. Primers used for PCR amplification and sequencing of the katg gene of M. tuberculosis and their basic characteristics Primer designation Sequence (5 Æ 3 ) Location (bp) b Ta ( C) c PCR product size (bp) X68081 a KatG 1 GCCCGATAACACCAACTCCTG KatG 5 KatG 4 KatG 9 KatG 8 KatG 13 KatG 12 KatG 14 CAGATCCCGCTACCGCTGTA CCTGGCTCGGCGATGA CTCGGTGGATCAGCTTGTACC GAGGAATTGGCCGACGAGTT TCTCAGGGGCACTGAGCGTAA GCCGAGTACATGCTGCTCGAC CGGCGGGTTGTGGTTGA a GenBank accession number for the M. tuberculosis H 37Rv katg gene b Positioning of the primers; Numbers refer to the nucleotide position within the referenced GenBank sequence (X68081) c Annealing temperature of the primers Revseq, Transeq). Sequences were analysed by comparing with the wild-type katg gene sequence originating from the M. tuberculosis H 37 Rv reference strain available in GenBank (GenBank accession number: X68081). Results The occurrence of mutations in the katg gene in 46 MDR-resistant M. tuberculosis strains with different resistance levels to INH and different catalase activity was investigated. Electrophoretic separation of 4 products of the katg gene amplification revealed, for each of the studied strains, the presence of a single DNA band of an expected size of 680, 648, 667 and 452 bp, for the katg gene fragments amplified by using primers KatG-1-KatG-5 (A), KatG-4-KatG-9 (B), KatG-8-KatG-13 (C) and KatG-12-KatG-14 (D), respectively (Fig. 1). Among the 46 examined M. tuberculosis strains, mutations in the katg gene were found in 43 strains (93%). Three strains did not show any mutation in the katg gene sequence (Tab. 2). Among strains with an altered katg gene sequence, 34 (74%) had mutations at nucleotide position 944; in 32 strains (69%) it was transition GÆC, in 1 strain (no. 4832) it was transversion GÆT, and in one strain (no. 1377) it was transversion GÆA. Mutations other than those at position 944 were rare. Mutation at position 1388 (GÆT) was found in 4 strains (nos. K131, 3430, 3020 and 1334). Mutation at position 392 was found in 2 strains; in one case it was transition CÆG (strain no. 101), in another - transversion CÆA (535). In two strains (nos and 12489) mutation at position 945, being a transversion CÆT was found. In another two strains (nos. 590 and 5895) mutation at position 701 (CÆG) was discovered. Furthermore, substitutions were found in single strains at the following positions: 203 (TÆG) (strain no. 590), 271 (TÆC) (4991), 302 (TÆC) (2497), 378 (GÆA) (103), 383 (GÆA) (4619), 580 (GÆT) (101) and 1360 (GÆT) (590). All discovered mutations were point mutations and relied on substitution of individual nucleotides. Only one strain (no. 5895) had a mutation which was an insertion of thymine at position 135 (inst135). As for the number of mutations per individual strains, 35 strains (76%) had single mutations in the katg gene, whereas 8 (17%) had one or two additional mutations. More precisely, 3 strains had, apart from a mutation at position 944, a change at position 1388 (strains nos. K131, 3430, 1334), 2 strains had mutations at positions 944 and at position 945 (11420, 12489), one strain had mutations at positions 392 and 580 (no. 101), and another strain (5895) at positions 135 and 701. Only one strain (no. 590) had 3 mutations, i.e. at positions 203, 701 and Among the 16 different changes at the nucleotide sequence level, 14 resulted in amino acid substitution in the polypeptide chain of KatG (Fig. 2). It concerned mainly codon 315 (34 tested strains (74%)) resulting in 94% of the strains (32 strains), in substitution SerÆThr. At the nucleotide sequence level it concerned AGCÆACC substitution for 30 strains (88% of strains with mutation at this codon) or AGCÆACT substitution for 2 strains. Two other mutations at codon 315 were changes SerÆAsn (AGCÆAAC) and SerÆIle (AGCÆATC), both found in single strains. The ArgÆLeu (CGGÆCTG) substitution within the KatG codon 463 was observed in 4 strains (9%). In two cases there was a change 301
5 Pneumonologia i Alergologia Polska 2013, tom 81, nr 4, strony MW A B C D A B C D MW pz 648 pz 667 pz 680 pz 648 pz 667 pz pz 452 pz [pz] [pz] Figure 1. Products of the amplification of the entire katg gene in 4 PCR assays (A D) generated for two selected M. tuberculosis strains (nos. 590 and 5895); MW, molecular weight marker (Perfect TM 100 bp DNA Ladder, EURx) in codon 131: in the first case it was ProÆGln (CCGÆCAG) and in the second ProÆArg (CC- GÆCGG). The substitution AlaÆGly (GCGÆGGG) within the KatG codon 234 was noted in the next two strains. In the remaining cases only single mutations were present: Val68Gly (GTGÆGGG), Trp91Arg (TGGÆCGG), Leu101Pro (CTGÆCCG), Met126Ile (ATGÆATA), Arg128Gln (CGGÆCAG) and Asp194Tyr (GATÆTAT). Among the 43 strains in which mutations in the katg gene sequence occurred, in 41 (95%) strains the mutations led to amino acid substitutions in the KatG peptide chain (the missense mutations). In 2 strains single nonsense mutations were demonstrated. By introducing unique translation termination codons (STOP), these mutations resulted in polypeptide truncation. While transversion GÆT at position 1360 generated codon STOP (TAG) at position 454 of the amino acid sequence, an insertion of thymine at position 135 (inst135) generated a frameshift mutation and produced termination codon (TAA) at protein position 46. As a result of the described mutations, catalase polypeptide was shortened by 287 and 695 amino acid residues, accordingly, as compared to the wild-type protein (740 amino acids). Thirty-seven (80%) strains had single substitutions in the amino acid sequence of the KatG. Six (13%) strains had additional changes: in 3 cases next to the change Ser315Thr, substitution Arg463Leu (strains nos. K131, 3430, 1334) was found; a change being a substitution Ala234Gly and another introducing codon STOP (5895) were discovered in one strain, whereas changes Pro131Arg and Asp194Tyr (101) were found in another strain. One strain (no. 590) had 3 different changes: Val68Gly, Ala- 234Gly and Glu454STOP. Among the 43 strains with mutations within the katg gene, thirty-six (84%) retained catalase activity (Tab. 2). In the group of strains without mutations, catalase reaction was positive in 2 strains (nos and 11844), whereas in the case of one strain (73) the reaction was negative. Thirty-two (94%) out of 34 strains with mutations associated with codon 315 showed catalase activity: in 20 strains the catalase reaction was positive, and in 12 strains it was strongly positive. Two strains (nos and 647) showed no catalase activity. The MIC values for INH in strains with mutations in the katg gene were within the range of the following concentrations: 0.1 µg/ml MIC 100 µg/ml. The MICs for INH of strains with a wild- -type version of of the katg gene were 1 µg/ml for 2 strains (nos and 11844) and 10 µg/ml for one strain (no. 73). The MICs for strains with mutations at codon 315 ranged as follows: 1 MIC 10 µg/ml. For the majority of these strains (26 strains, 76%) the MIC value of INH was 2.5 µg/ml (Tab. 2). Discussion According to different studies, mutations in the katg gene occur in 50-95% of INH-resistant strains [11, 12, 16 19]. The most commonly observed mutations in locus katg are substitutions at codon 315. The most frequent is transition GÆC (AGCÆACC), resulting in the replacement of serine with threonine (SerÆThr) in the amino acid 302
6 Tomasz Jagielski et al., Mutations in the katg gene in MDR M. tuberculosis strains [pz] [pz] C392A(1; 2%) C392G(1; 2%) G383A(1; 2%) T302C(1; 2%) T271C(1; 2%) T 203G(1; 2%) 135 inst (1; 2%) G378A(1; 2%) C701G(2; 4%) G 580T(1; 2%) C945T(1; 4%) G944T(1; 2%) G944A(1; 2%) G1388T(4; 9%) G944C(32; 69%) G1360T(1; 2%) 2223 pz 46 STOP Leu 101 Pro Trp91 Arg Val68 Gly Pro 131 Gln Pro 131 Arg Arg 128 Gln Met 126 Ile Ser 315 Thr Ser 315 Ile Asp 194 Tyr Ser 315 Asn Ala 234 Gly Ser 315 Thr Arg 463 Leu 454 STOP 740 aa [aa] [aa] Figure 2. Schematic representation of the katg gene mutations identified among 46 multidrug-resistant M. tuberculosis strains, evaluated in this study. Nucleotide alleles and corresponding amino acid alleles at which mutations occurred are indicated by their codon positions in light grey boxes at the top and bottom of the figure, respectively. Number and percentage of strains bearing the specific mutation are given in brackets 303
7 Pneumonologia i Alergologia Polska 2013, tom 81, nr 4, strony Table 2. Mutations in the katg gene, identified among 46 multidrug-resistant M. tuberculosis strains and their selected phenotypic characteristics No. Strain no. Drug resistance profile a MIC INH [μgxml 1] INH+RMP 1 > 45 Catalase Changes identified at c : activity b Nucleotide level Amino acid level C Æ G (392) G Æ T (580) Pro Æ Arg (131) Asp Æ Tyr (194) SM+INH+RMP+EMB G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) INH+RMP+EMB 1 3 T Æ C (271) Trp Æ Arg (91) SM+INH+RMP 2.5 > 45 G Æ C (944) G Æ T (1388) Ser Æ Thr (315) Arg Æ Leu (463) SM+INH+RMP 1 7 G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) SM+INH+RMP 0.1 > 45 T Æ C (302) Leu Æ Pro (101) SM+INH+RMP+EMB 0.5 > 45 G Æ A (383) Arg Æ Gln (128) SM+INH+RMP G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) SM+INH+RMP 2.5 > 45 G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) SM+INH+RMP 2.5 > 45 G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) SM+INH+RMP G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) SM+INH+RMP+EMB 2.5 > 45 G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) SM+INH+RMP G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) SM+INH+RMP G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) SM+INH+RMP+EMB INH+RMP 1 4 C Æ A (392) Pro Æ Gln (131) SM+INH+RMP G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) SM+INH+RMP 2.5 > 45 G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) INH+RMP G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) SM+INH+RMP+EMB 2.5 > 45 G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) SM+INH+RMP G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) SM+INH+RMP T Æ G (203) C Æ G (701) G Æ T (1360) SM+INH+RMP 1 27 G Æ C (944) C Æ T (945) INH+RMP 1 32 G Æ C (944) C Æ T (945) Val Æ Gly (68) Ala Æ Gly (234) STOP (454) Ser Æ Thr (315) Ser Æ Thr (315) INH+RMP G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) INH+RMP G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) INH+RMP G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) SM+INH+RMP 2.5 > 45 G Æ A (944) Ser Æ Asn (315) INH+RMP G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) INH+RMP 2.5 > 45 G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) INH+RMP 2.5 > 45 G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) SM+INH+RMP 1 19 G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) SM+INH+RMP SM+INH+RMP+EMB G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) SM+INH+RMP+EMB G Æ T (1388) Arg Æ Leu (463) SM+INH+RMP G Æ C (944) G Æ T (1388) Ser Æ Thr (315) Arg Æ Leu (463) Æ 304
8 Tomasz Jagielski et al., Mutations in the katg gene in MDR M. tuberculosis strains Table 2. continuation 37. K131 SM+INH+RMP G Æ C (944) G Æ T (1388) Ser Æ Thr (315) Arg Æ Leu (463) INH+RMP 2.5 >45 G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) INH+RMP 80 0 inst (135) C Æ G (701) STOP (46) Ala Æ Gly (234) SM+INH+RMP G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) SM+INH+RMP 2.5 > 45 G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) SM+INH+RMP G Æ A (378) Met Æ Ile (126) SM+INH+RMP 2.5 > 45 G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) SM+INH+RMP G Æ T (944) Ser Æ Ile (315) INH+RMP+EMB INH+RMP 5 3 G Æ C (944) Ser Æ Thr (315) a INH, isoniazid; RMP, rifampicin; SM, streptomycin; EMB, ethambutol b Catalase activity according to Kubica test, measured (in millimetres) as the height of the foam column c Nucleotide or amino acid positions are given in brackets chain. Much more unusual are other nucleotide substitutions generating codons: ACA (Thr), ATC (Ile), AGA (Arg), AGG (Arg), CGC (Arg), AAC (Asn) and GGC (Gly) [11, 12, 16, 18 31]. The frequency at which mutations at codon 315 of the katg gene occur differs between geographical regions. Such mutations have been discovered in 97% of INH-resistant strains isolated in South Africa [32], 86 94% of strains isolated in Russia, Lithuania and Latvia [24, 33, 34], 60-87% in Brazil [16, 35], about 65% in Australia, China and Kuwait [12, 22, 27], 53% in the Netherlands [36], 46% in Spain [37] and 38% in Italy [38]. A relatively small proportion of mutations at codon 315 have been noted in INH-resistant strains obtained from patients from Japan (28%) [21], even lower from patients from Finland (7%) [32], and the lowest from South Korea and the United States (4%) [39]. Pretorius et al. described 39 INH-resistant strains isolated from patients from South Africa, the United States and Switzerland, all of which had an unchanged (wild-type) version of the katg gene [40]. Thus far there have been only two studies on genetic determination of INH resistance in M. tuberculosis strains from Poland. Molecular analysis conducted by Sajduda et al. has shown that 55 (66%) out of 83 INH-resistant strains had mutations at codon 315 within the katg gene. Fifty (90%) strains had the most frequent mutation AGCÆACC [41]. In another study, Wojtyczka et al., while investigating the occurrence of mutation Ser315Thr among 23 INH-resistant strains (including 6 MDR strains) isolated from patients from Silesia, found it only in 2 strains (9%) (including 1 MDR strain) [42]. In this study, the presence of mutation at codon 315 was found in 34 (74%) out of 46 MDR-TB strains (for 32 strains it was mutation Ser315Thr, which in case of 30 strains was a AGCÆACC substitution). All but 2 strains (32; 94%) with mutation at codon 315 were catalase-positive, which indicates that this type of mutation does not adversely influence the enzymatic activity of the KatG protein. Similarly, studies by other authors have proved that the majority of INH-resistant strains with mutations at codon 315 retained their catalase activity [11, 17, 18, 20] (differences in the level of the enzymatic activity that occur between these strains may be a result, for example, of the presence of additional mutations in the katg gene). In order to find the physiological role of the mutation at codon 315, Wengenack et al. compared the enzymatic activity of the wild-type protein KatG with the KatG protein bearing a single Ser315Thr mutation [43]. They showed that the mutated protein retained significant catalase activity while showing a lowered ability to activate INH. The loss of the ability to metabolize INH is due to the fact that mutation Ser315Thr changes the stereochemical structure of the protein that decreases its affinity to the drug [44]. Furthermore, as it has been proven on a mouse model that the virulence of the katg Ser315Thr mutants is similar to that observed in wild-type strains [45]. Analysis of the phenotype of M. tuberculosis strains with the katg Ser315Thr mutation shows explicitly that it is physiologically profitable. The high prevalence of this mutation among INH-resistant strains may be attributed to the positive selective pressure. A number of studies have shown that the presence of a mutation at codon 315 in the katg gene is often associated with a high level of INH 305
9 Pneumonologia i Alergologia Polska 2013, tom 81, nr 4, strony resistance (MIC 4 μg/ml) [12, 16, 17, 25, 35, 36]. This correlation was confirmed only partially by the results of the present study. All strains with mutations at codon 315 had their MIC values for INH within the range of 1 10 μg/ml. For the majority of these strains (26, 76%) the MIC value was 2.5 μg/ml. Among the strains in which mutations at codon 315 were absent, 2 strains had the highest level of INH resistance (MIC = 80 and 100 μg/ml). These strains were also the only ones for which the catalase reaction was entirely negative (h = 0). In the katg sequence of these two strains the presence of single nonsense mutations (Lys46STOP, Glu454STOP) was reported. These mutations led to catalase polypeptide truncation and thus abolished its enzymatic activity. It is plausible that the lack of functional KatG also conditioned a particularly high resistance to INH in those strains, as can be seen in the case of katg gene deletion [9 12]. Many authors emphasize the usefulness of the analysis of mutation at codon 315 (mainly Ser- 315Thr) in the katg gene for detecting resistance to INH in M. tuberculosis. The diagnostic value of such analysis is particularly important in countries with high TB prevalence and high TB transmission rate of drug-resistant M. tuberculosis strains. Here, mutations at codon 315 occur in more than 90% of INH-resistant strains [32 34, 46]. However, in countries where the frequency of mutations at codon 315 is significantly lower, the usefulness of finding such mutations such mutations for the detection of INH resistance is rather limited. Although mutations at codon 315 within the katg gene occur only in some MDR M. tuberculosis strains, which was confirmed by the present study (such mutations were absent in a quarter of the studied MDR- -resistant strains), examination of their occurrence may serve as a rapid screening test for drug resistance. Such an approach is justified by the fact that the above mensioned mutations are 100% specific for INH-resistant strains, and their identification takes significantly less time than determination of drug resistance using a conventional method. Amplification techniques used for detecting mutations associated with drug resistance do not require the growth of mycobacteria and may be applied directly to clinical specimens [47]. A fast screening test for mutations at codon 315 may be of great significance for detection of MDR resistance. According to many authors, mutations at codon 315 in the katg gene occur more frequently in MDR strains than in the INH- -monoresistant strains [24, 26, 36, 48]. Additionally, 78 94% of MDR tubercle bacilli harbour these mutations [24, 31, 34, 46]. One of the hypotheses explaining this phenomenon assumes that mutations within katg codon 315 increase the fitness of mycobacteria, thus strengthening their ability to survive in the human host, be transmitted, and develop complex drug resistance patterns [26]. This hypothesis has recently been supported by the studies of van Doorn et al. from the Netherlands [49] and Gagneux et al. from San Francisco [50], who demonstrated that INH-resistant M. tuberculosis strains with mutations at codon 315 (especially Ser315Thr mutation) are more frequently involved in recent TB transmission than other INH-resistant strains without this mutation. Conclusions Mutations in the katg gene were found in 43 (93%) of the MDR M. tuberculosis strains tested. The most frequent mutation was substitution at codon 315, which was demonstrated in 34 (74%) strains. The presence of mutations at this codon may serve as a predictive factor for INH resistance. Among the 16 different mutations discovered at the level of the katg nucleotide sequence, 14 (87.5%) resulted in the amino acid change in the KatG polypeptide chain (the missense mutations). In the case of 2 strains, single nonsense mutations were disclosed. By introducing unique translation termination codons, they led to polypeptide truncation. While the missense mutations did not influence catalase activity or the level of INH resistance, the nonsense mutations resulted in a high level of INH resistance and a complete loss of catalase activity. Conflict of interest The authors declare no conflict of interest. References: 1. Jagielski T., Augustynowicz-Kopeć E., Zwolska Z. Epidemiologia gruźlicy w perspektywie świata, Europy i Polski. Wiad. Lek. 2010; 63: Jagielski T., Augustynowicz-Kopeć E., Zwolska Z. Epidemiologia gruźlicy lekoopornej: świat Europa Polska. Wiad. Lek. 2010; 63: Hedgecock L.W., Faucher I.O. Relation of pyrogallol-peroxidative activity to isoniazid resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Am. Rev. Tuberc. 1957; 75: Middlebrook, G. Isoniazid-resistance and catalase activity of tubercle bacilli; a preliminary report. Am. Rev. Tuberc. 1964; 69: Tirunarayanan M.O., Vischer W.A. Relationship of isoniazid to the metabolism of mycobacteria; catalase and peroxidase. Am. Rev. Tuberc. 1957; 75: Zhang Y., Garbe T., Young D. Transformation with katg restores isoniazid-sensitivity in Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates resistant to a range of drug concentrations. Mol. Microbiol. 1993; 8: Zhang Y., Heym B., Allen B., Young D., Cole S. The catalase- -peroxidase gene and isoniazid resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Nature 1992; 358:
10 Tomasz Jagielski et al., Mutations in the katg gene in MDR M. tuberculosis strains 8. Timmins G.S., Deretic V. Mechanisms of action of isoniazid. Mol. Microbiol. 2006; 62: Ferrazoli L., Palaci M., Telles M.A., i wsp. Catalase expression, katg, and MIC of isoniazid for Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from Sao Paulo, Brazil. J. Infect. Dis. 1995; 171: Goto M., Oka S., Tachikawa N., i wsp. KatG sequence deletion is not the major cause of isoniazid resistance in Japanese and Yemeni Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates. Mol. Cell. Probes 1995; 9: Ramaswamy S.V., Reich R., Dou S.J. i wsp. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in genes associated with isoniazid resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003; 47: Zhang M., Yue J., Yang Y.P. i wsp. Detection of mutations associated with isoniazid resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from China. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005; 43: Zwolska Z., Augustynowicz Kopeć E., Klatt M. Pierwotna i nabyta lekooporność prątków gruźlicy w Polsce. Pneumonol. Alergol. Pol. 1999; 67: van Embden J.D., Cave M.D., Crawford J.T. i wsp. Strain identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by DNA fingerprinting: recommendations for a standardized methodology. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993; 31: Youmans, G.P. The laboratory diagnosis of mycobacterial disease. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders Co. 1979; Cardoso R.F., Cooksey R.C., Morlock G.P. i wsp. Screening and characterization of mutations in isoniazid resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates obtained in Brazil. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004; 48: Coll P., Aragon L.M., Alcaide F. i wsp. Molecular analysis of isoniazid and rifampin resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates recovered from Barcelona. Microb. Drug Resist. 2005; 11: Guo H., Seet Q., Denkin S., Parsons L., Zhang Y. Molecular characterization of isoniazid-resistant clinical isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from the USA. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006; 55: Herrera L., Valverde A., Saiz P., Saez-Nieto J.A., Portero J.L., Jimenez M.S. Molecular characterization of isoniazid-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical strains isolated in the Philippines. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2004; 23: Abate G., Hoffner S.E., ThomsenV.O., Miorner H. Characterization of isoniazid-resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis on the basis of phenotypic properties and mutations in katg. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2001; 20: Abe C., Kobayashi I., Mitarai S. i wsp. Biological and molecular characteristics of Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates with low-level resistance to isoniazid in Japan. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008; 46: Ahmad S., Mokaddas E. Contribution of AGC to ACC and other mutations at codon 315 of the katg gene in isoniazid-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from the Middle East. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2004; 23: Baker L.V., Brown T.J., Maxwell O. i wsp. Molecular analysis of isoniazid-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from England and Wales reveals the phylogenetic significance of the ahpc-46a polymorphism. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005; 49: Bakonyte D., Baranauskaite A., Cicenaite J., Sosnovskaja A., Stakenas P. Molecular characterization of isoniazid-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates in Lithuania. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003; 47: Clemente W.T., Soares Lima S.S., Palaci M. i wsp. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of drug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008; 62: Hazbon, M.H., Brimacombe, M., Bobadilla del Valle, M. i wsp. Population genetics study of isoniazid resistance mutations and evolution of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006; 50: Lavender C., Globan M., Sievers A., Billman-Jacobe H., Fyfe J. Molecular characterization of isoniazid-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates collected in Australia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005; 49: Musser J.M., Kapur V., Williams D.L., Kreiswirth B.N., van Soolingen D., van Embden J.D. Characterization of the catalase-peroxidase gene (katg) and inha locus in isoniazid-resistant and susceptible strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by automated DNA sequencing: restricted array of mutations associated with drug resistance. J. Infect. Dis. 1996; 173: Shemyakin I.G., Stepanshina V.N., Ivanov I.Y. i wsp. Characterization of drug-resistant isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis derived from Russian inmates. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2004; 8: Zakerbostanabad S., Titov L.P., Bahrmand A.R. Frequency and molecular characterization of isoniazid resistance in katg region of MDR isolates from tuberculosis patients in southern endemic border of Iran. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2008; 8: Zhang S.L., Qi H., Qiu D.L. i wsp. Genotypic analysis of multidrug- -resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates recovered from central China. Biochem. Genet. 2007; 45: Kiepiela P., Bishop K.S., Smith A.N., Roux L., York D.F. Genomic mutations in the katg, inha and aphc genes are useful for the prediction of isoniazid resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from Kwazulu Natal, South Africa. Tuber. Lung Dis. 2000; 80: Mokrousov I., Narvskaya O., Otten T., Limeschenko E., Steklova L., Vyshnevskiy B. High prevalence of KatG Ser315Thr substitution among isoniazid resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates from northwestern Russia, 1996 to Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002; 46: Tracevska T., Jansone I., Broka L., Marga O., Baumanis V. Mutations in the rpob and katg genes leading to drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Latvia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002; 40: Silva M.S., Senna S.G., Ribeiro M.O. i wsp. Mutations in katg, inha, and ahpc genes of Brazilian isoniazid-resistant isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003; 41: van Soolingen D., de Haas P.E., van Doorn H.R., Kuijper E., Rinder H., Borgdorff M.W. Mutations at amino acid position 315 of the katg gene are associated with high-level resistance to isoniazid, other drug resistance, and successful transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the Netherlands. J. Infect. Dis. 2000; 182: Garcia de Viedma D., del Sol Diaz Infantes M., Lasala F., Chaves F., Alcala L., Bouza E. New real-time PCR able to detect in a single tube multiple rifampin resistance mutations and high-level isoniazid resistance mutations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002; 40: Rindi L., Bianchi L., Tortoli E., Lari N., Bonanni D., Garzelli C. Mutations responsible for Mycobacterium tuberculosis isoniazid resistance in Italy. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2005; 9: Rouse D.A., Li Z., Bai G.H., Morris S.L. Characterization of the katg and inha genes of isoniazid-resistant clinical isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995; 39: Pretorius G.S., van Helden P.D., Sirgel F., Eisenach K.D., Victor T.C. Mutations in katg gene sequences in isoniazid-resistant clinical isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis are rare. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995; 39: Sajduda A., Brzostek A., Popławska M. i wsp. Molecular characterization of rifampin- and isoniazid-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains isolated in Poland. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004; 42: Wojtyczka R.D., Dworniczak S., Pacha J. i wsp. PCR-RFLP analysis of a point mutation in codons 315 and 463 of the katg gene of Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolated from patients in Silesia, Poland. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2004; 53: Wengenack N.L., Uhl J.R., St Amand A.L. i wsp. Recombinant Mycobacterium tuberculosis KatG (S315T) is a competent catalase- -peroxidase with reduced activity toward isoniazid. J. Infect. Dis. 1997; 176: Zhao X., Yu H., Yu S., Wang F., Sacchettini J.C., Magliozzo R.S. Hydrogen peroxide-mediated isoniazid activation catalyzed by Mycobacterium tuberculosis catalase-peroxidase (KatG) and its S315T mutant. Biochemistry 2006; 45: Pym A.S., Saint-Joanis B., Cole S.T. Effect of katg mutations on the virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and the implication for transmission in humans. Infect. Immun. 2002; 70: Marttila H.J., Soini H., Eerola E. i wsp. A Ser315Thr substitution in KatG is predominant in genetically heterogeneous multidrug- -resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates originating from the St. Petersburg area in Russia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998; 42: Marín M., García de Viedma D., Ruíz-Serrano M.J., Bouza E. Rapid direct detection of multiple rifampin and isoniazid resistance mutations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis in respiratory samples by real-time PCR. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004; 48: Piatek A.S., Telenti A., Murray M.R. i wsp. Genotypic analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in two distinct populations using molecular beacons: implications for rapid susceptibility testing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000; 44: van Doorn H.R., de Haas P.E., Kremer K., Vandenbroucke-Grauls C.M., Borgdorff M.W., van Soolingen D. Public health impact of isoniazid-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains with a mutation at amino-acid position 315 of katg: a decade of experience in The Netherlands. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2006; 12: Gagneux S., Burgos M.V., DeRiemer K. i wsp. Impact of bacterial genetics on the transmission of isoniazid-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. PLoS Pathog. 2006; 2:
 www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
 www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
Fig 5 Spectrograms of the original signal (top) extracted shaft-related GAD components (middle) and
 Fig 4 Measured vibration signal (top). Blue original signal. Red component related to periodic excitation of resonances and noise. Green component related. Rotational speed profile used for experiment
Fig 4 Measured vibration signal (top). Blue original signal. Red component related to periodic excitation of resonances and noise. Green component related. Rotational speed profile used for experiment
Pro-tumoral immune cell alterations in wild type and Shbdeficient mice in response to 4T1 breast carcinomas
 www.oncotarget.com Oncotarget, Supplementary Materials Pro-tumoral immune cell alterations in wild type and Shbdeficient mice in response to 4T1 breast carcinomas SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS Supplementary
www.oncotarget.com Oncotarget, Supplementary Materials Pro-tumoral immune cell alterations in wild type and Shbdeficient mice in response to 4T1 breast carcinomas SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS Supplementary
Cracow University of Economics Poland. Overview. Sources of Real GDP per Capita Growth: Polish Regional-Macroeconomic Dimensions 2000-2005
 Cracow University of Economics Sources of Real GDP per Capita Growth: Polish Regional-Macroeconomic Dimensions 2000-2005 - Key Note Speech - Presented by: Dr. David Clowes The Growth Research Unit CE Europe
Cracow University of Economics Sources of Real GDP per Capita Growth: Polish Regional-Macroeconomic Dimensions 2000-2005 - Key Note Speech - Presented by: Dr. David Clowes The Growth Research Unit CE Europe
 aforementioned device she also has to estimate the time when the patients need the infusion to be replaced and/or disconnected. Meanwhile, however, she must cope with many other tasks. If the department
aforementioned device she also has to estimate the time when the patients need the infusion to be replaced and/or disconnected. Meanwhile, however, she must cope with many other tasks. If the department
Patients price acceptance SELECTED FINDINGS
 Patients price acceptance SELECTED FINDINGS October 2015 Summary With growing economy and Poles benefiting from this growth, perception of prices changes - this is also true for pharmaceuticals It may
Patients price acceptance SELECTED FINDINGS October 2015 Summary With growing economy and Poles benefiting from this growth, perception of prices changes - this is also true for pharmaceuticals It may
WPŁYW AKTYWNOŚCI FIZYCZNEJ NA STAN FUNKCJONALNY KOBIET PO 65 ROKU ŻYCIA Z OSTEOPOROZĄ
 WPŁYW AKTYWNOŚCI FIZYCZNEJ NA STAN FUNKCJONALNY KOBIET PO 65 ROKU ŻYCIA Z OSTEOPOROZĄ Streszczenie: Wstęp: Proces starzenia się w naturalny sposób wpływa na ograniczenie sprawności, nawet w sytuacji zachowania
WPŁYW AKTYWNOŚCI FIZYCZNEJ NA STAN FUNKCJONALNY KOBIET PO 65 ROKU ŻYCIA Z OSTEOPOROZĄ Streszczenie: Wstęp: Proces starzenia się w naturalny sposób wpływa na ograniczenie sprawności, nawet w sytuacji zachowania
uzyskanymi przy zastosowaniu innych metod użyto testu Manna-Whitney a. Jako miarę korelacji wykorzystano współczynnik. Przedstawiona w dysertacji
 STRESZCZENIE Zakażenia mykoplazmowe u bydła, a zwłaszcza na tle M. bovis, stanowią istotny problem epidemiologiczny i ekonomiczny w wielu krajach świata. Uważa się, że M. bovis jest odpowiedzialna za 25%
STRESZCZENIE Zakażenia mykoplazmowe u bydła, a zwłaszcza na tle M. bovis, stanowią istotny problem epidemiologiczny i ekonomiczny w wielu krajach świata. Uważa się, że M. bovis jest odpowiedzialna za 25%
EDYTA KATARZYNA GŁAŻEWSKA METALOPROTEINAZY ORAZ ICH TKANKOWE INHIBITORY W OSOCZU OSÓB CHORYCH NA ŁUSZCZYCĘ LECZONYCH METODĄ FOTOTERAPII UVB.
 Wydział Farmaceutyczny z Oddziałem Medycyny Laboratoryjnej Uniwersytet Medyczny w Białymstoku EDYTA KATARZYNA GŁAŻEWSKA METALOPROTEINAZY ORAZ ICH TKANKOWE INHIBITORY W OSOCZU OSÓB CHORYCH NA ŁUSZCZYCĘ
Wydział Farmaceutyczny z Oddziałem Medycyny Laboratoryjnej Uniwersytet Medyczny w Białymstoku EDYTA KATARZYNA GŁAŻEWSKA METALOPROTEINAZY ORAZ ICH TKANKOWE INHIBITORY W OSOCZU OSÓB CHORYCH NA ŁUSZCZYCĘ
 www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
Katarzyna Durda STRESZCZENIE STĘŻENIE KWASU FOLIOWEGO ORAZ ZMIANY W OBRĘBIE GENÓW REGULUJĄCYCH JEGO METABOLIZM JAKO CZYNNIK RYZYKA RAKA W POLSCE
 Pomorski Uniwersytet Medyczny Katarzyna Durda STRESZCZENIE STĘŻENIE KWASU FOLIOWEGO ORAZ ZMIANY W OBRĘBIE GENÓW REGULUJĄCYCH JEGO METABOLIZM JAKO CZYNNIK RYZYKA RAKA W POLSCE Promotor: dr hab. prof. nadzw.
Pomorski Uniwersytet Medyczny Katarzyna Durda STRESZCZENIE STĘŻENIE KWASU FOLIOWEGO ORAZ ZMIANY W OBRĘBIE GENÓW REGULUJĄCYCH JEGO METABOLIZM JAKO CZYNNIK RYZYKA RAKA W POLSCE Promotor: dr hab. prof. nadzw.
Cracow University of Economics Poland
 Cracow University of Economics Poland Sources of Real GDP per Capita Growth: Polish Regional-Macroeconomic Dimensions 2000-2005 - Keynote Speech - Presented by: Dr. David Clowes The Growth Research Unit,
Cracow University of Economics Poland Sources of Real GDP per Capita Growth: Polish Regional-Macroeconomic Dimensions 2000-2005 - Keynote Speech - Presented by: Dr. David Clowes The Growth Research Unit,
HemoRec in Poland. Summary of bleeding episodes of haemophilia patients with inhibitor recorded in the years 2008 and 2009 04/2010
 HemoRec in Poland Summary of bleeding episodes of haemophilia patients with inhibitor recorded in the years 2008 and 2009 04/2010 Institute of Biostatistics and Analyses. Masaryk University. Brno Participating
HemoRec in Poland Summary of bleeding episodes of haemophilia patients with inhibitor recorded in the years 2008 and 2009 04/2010 Institute of Biostatistics and Analyses. Masaryk University. Brno Participating
Krytyczne czynniki sukcesu w zarządzaniu projektami
 Seweryn SPAŁEK Krytyczne czynniki sukcesu w zarządzaniu projektami MONOGRAFIA Wydawnictwo Politechniki Śląskiej Gliwice 2004 SPIS TREŚCI WPROWADZENIE 5 1. ZARZĄDZANIE PROJEKTAMI W ORGANIZACJI 13 1.1. Zarządzanie
Seweryn SPAŁEK Krytyczne czynniki sukcesu w zarządzaniu projektami MONOGRAFIA Wydawnictwo Politechniki Śląskiej Gliwice 2004 SPIS TREŚCI WPROWADZENIE 5 1. ZARZĄDZANIE PROJEKTAMI W ORGANIZACJI 13 1.1. Zarządzanie
Network Services for Spatial Data in European Geo-Portals and their Compliance with ISO and OGC Standards
 INSPIRE Conference 2010 INSPIRE as a Framework for Cooperation Network Services for Spatial Data in European Geo-Portals and their Compliance with ISO and OGC Standards Elżbieta Bielecka Agnieszka Zwirowicz
INSPIRE Conference 2010 INSPIRE as a Framework for Cooperation Network Services for Spatial Data in European Geo-Portals and their Compliance with ISO and OGC Standards Elżbieta Bielecka Agnieszka Zwirowicz
Unit of Social Gerontology, Institute of Labour and Social Studies ageing and its consequences for society
 Prof. Piotr Bledowski, Ph.D. Institute of Social Economy, Warsaw School of Economics local policy, social security, labour market Unit of Social Gerontology, Institute of Labour and Social Studies ageing
Prof. Piotr Bledowski, Ph.D. Institute of Social Economy, Warsaw School of Economics local policy, social security, labour market Unit of Social Gerontology, Institute of Labour and Social Studies ageing
PRZEBIEG KARIERY NAUKOWEJ:
 Dr n. biol. KATARZYNA ROESKE STANOWISKO: ADIUNKT PRZEBIEG KARIERY NAUKOWEJ: WYKSZTAŁCENIE: 2009 r. mgr biotechnologii w zakresie mikrobiologii, Wydział Biologii, Uniwersytet Warszawski 2015 r. dr nauk
Dr n. biol. KATARZYNA ROESKE STANOWISKO: ADIUNKT PRZEBIEG KARIERY NAUKOWEJ: WYKSZTAŁCENIE: 2009 r. mgr biotechnologii w zakresie mikrobiologii, Wydział Biologii, Uniwersytet Warszawski 2015 r. dr nauk
Mutacje w genie pnca jako główny mechanizm oporności na pirazynamid wśród prątków gruźlicy**
 Postępy Nauk Medycznych, t. XXVIII, nr 4, 05 Borgis *Agnieszka Napiórkowska, Zofia Zwolska, Ewa Augustynowicz-Kopeć Mutacje w genie pnca jako główny mechanizm oporności na pirazynamid wśród prątków gruźlicy**
Postępy Nauk Medycznych, t. XXVIII, nr 4, 05 Borgis *Agnieszka Napiórkowska, Zofia Zwolska, Ewa Augustynowicz-Kopeć Mutacje w genie pnca jako główny mechanizm oporności na pirazynamid wśród prątków gruźlicy**
Lek. Ewelina Anna Dziedzic. Wpływ niedoboru witaminy D3 na stopień zaawansowania miażdżycy tętnic wieńcowych.
 Lek. Ewelina Anna Dziedzic Wpływ niedoboru witaminy D3 na stopień zaawansowania miażdżycy tętnic wieńcowych. Rozprawa na stopień naukowy doktora nauk medycznych Promotor: Prof. dr hab. n. med. Marek Dąbrowski
Lek. Ewelina Anna Dziedzic Wpływ niedoboru witaminy D3 na stopień zaawansowania miażdżycy tętnic wieńcowych. Rozprawa na stopień naukowy doktora nauk medycznych Promotor: Prof. dr hab. n. med. Marek Dąbrowski
pojedynczych mutacji punktowych, lokalizujących się we fragmencie genu o wielkości około 600 pz. Uważa się, że poszczególne układy mutacji są
 Streszczenie Spośród herpeswirusów występujących u koni najważniejsze znaczenie, zarówno z klinicznego jak i ekonomicznego punktu widzenia posiada EHV-1. Wirus ten powoduje zapalenie górnych dróg oddechowych
Streszczenie Spośród herpeswirusów występujących u koni najważniejsze znaczenie, zarówno z klinicznego jak i ekonomicznego punktu widzenia posiada EHV-1. Wirus ten powoduje zapalenie górnych dróg oddechowych
Gdański Uniwersytet Medyczny Wydział Nauk o Zdrowiu z Oddziałem Pielęgniarstwa i Instytutem Medycyny Morskiej i Tropikalnej. Beata Wieczorek-Wójcik
 Gdański Uniwersytet Medyczny Wydział Nauk o Zdrowiu z Oddziałem Pielęgniarstwa i Instytutem Medycyny Morskiej i Tropikalnej Beata Wieczorek-Wójcik Poziom obsad pielęgniarskich a częstość i rodzaj zdarzeń
Gdański Uniwersytet Medyczny Wydział Nauk o Zdrowiu z Oddziałem Pielęgniarstwa i Instytutem Medycyny Morskiej i Tropikalnej Beata Wieczorek-Wójcik Poziom obsad pielęgniarskich a częstość i rodzaj zdarzeń
Zespół Omenna u kuzynów: różny przebieg kliniczny i identyczna mutacja genu RAG1.
 PRACE KAZUISTYCZNE / CASE REPORTS 367 Zespół Omenna u kuzynów: różny przebieg kliniczny i identyczna mutacja genu RAG1. Omenn s syndrome in cousins: different clinical course and identical RAG1 mutation
PRACE KAZUISTYCZNE / CASE REPORTS 367 Zespół Omenna u kuzynów: różny przebieg kliniczny i identyczna mutacja genu RAG1. Omenn s syndrome in cousins: different clinical course and identical RAG1 mutation
 !850016! www.irs.gov/form8879eo. e-file www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C,
!850016! www.irs.gov/form8879eo. e-file www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C,
Wydział Fizyki, Astronomii i Informatyki Stosowanej Uniwersytet Mikołaja Kopernika w Toruniu
 IONS-14 / OPTO Meeting For Young Researchers 2013 Khet Tournament On 3-6 July 2013 at the Faculty of Physics, Astronomy and Informatics of Nicolaus Copernicus University in Torun (Poland) there were two
IONS-14 / OPTO Meeting For Young Researchers 2013 Khet Tournament On 3-6 July 2013 at the Faculty of Physics, Astronomy and Informatics of Nicolaus Copernicus University in Torun (Poland) there were two
Is there a relationship between age and side dominance of tubal ectopic pregnancies? A preliminary report
 Is there a relationship between age and side dominance of tubal ectopic pregnancies? A preliminary report Czy istnieje zależność pomiędzy wiekiem i stroną, po której umiejscawia się ciąża ektopowa jajowodowa?
Is there a relationship between age and side dominance of tubal ectopic pregnancies? A preliminary report Czy istnieje zależność pomiędzy wiekiem i stroną, po której umiejscawia się ciąża ektopowa jajowodowa?
Ocena częstości występowania bólów głowy u osób chorych na padaczkę.
 lek. med. Ewa Czapińska-Ciepiela Ocena częstości występowania bólów głowy u osób chorych na padaczkę. Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych Promotor Prof. dr hab. n. med. Jan Kochanowski II Wydział
lek. med. Ewa Czapińska-Ciepiela Ocena częstości występowania bólów głowy u osób chorych na padaczkę. Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych Promotor Prof. dr hab. n. med. Jan Kochanowski II Wydział
 www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
Raport bieżący: 44/2018 Data: g. 21:03 Skrócona nazwa emitenta: SERINUS ENERGY plc
 Raport bieżący: 44/2018 Data: 2018-05-23 g. 21:03 Skrócona nazwa emitenta: SERINUS ENERGY plc Temat: Zawiadomienie o zmianie udziału w ogólnej liczbie głosów w Serinus Energy plc Podstawa prawna: Inne
Raport bieżący: 44/2018 Data: 2018-05-23 g. 21:03 Skrócona nazwa emitenta: SERINUS ENERGY plc Temat: Zawiadomienie o zmianie udziału w ogólnej liczbie głosów w Serinus Energy plc Podstawa prawna: Inne
Has the heat wave frequency or intensity changed in Poland since 1950?
 Has the heat wave frequency or intensity changed in Poland since 1950? Joanna Wibig Department of Meteorology and Climatology, University of Lodz, Poland OUTLINE: Motivation Data Heat wave frequency measures
Has the heat wave frequency or intensity changed in Poland since 1950? Joanna Wibig Department of Meteorology and Climatology, University of Lodz, Poland OUTLINE: Motivation Data Heat wave frequency measures
Uniwersytet Przyrodniczy we Wrocławiu. Wydział Medycyny Weterynaryjnej. Katedra Biochemii, Farmakologii i Toksykologii.
 Uniwersytet Przyrodniczy we Wrocławiu Wydział Medycyny Weterynaryjnej Katedra Biochemii, Farmakologii i Toksykologii Aleksandra Pawlak CHARAKTERYSTYKA FENOTYPOWA KOMÓREK CHŁONIAKÓW I BIAŁACZEK PSÓW ORAZ
Uniwersytet Przyrodniczy we Wrocławiu Wydział Medycyny Weterynaryjnej Katedra Biochemii, Farmakologii i Toksykologii Aleksandra Pawlak CHARAKTERYSTYKA FENOTYPOWA KOMÓREK CHŁONIAKÓW I BIAŁACZEK PSÓW ORAZ
Radiologiczna ocena progresji zmian próchnicowych po zastosowaniu infiltracji. żywicą o niskiej lepkości (Icon). Badania in vivo.
 Renata Zielińska Radiologiczna ocena progresji zmian próchnicowych po zastosowaniu infiltracji żywicą o niskiej lepkości (Icon). Badania in vivo. Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych Zakład Stomatologii
Renata Zielińska Radiologiczna ocena progresji zmian próchnicowych po zastosowaniu infiltracji żywicą o niskiej lepkości (Icon). Badania in vivo. Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych Zakład Stomatologii
Tytuł rozprawy na stopień doktora nauk medycznych:
 Instytut Pomnik Centrum Zdrowia Dziecka Zakład Patologii Pracownia Medycyny Mitochondrialnej Al. Dzieci Polskich 20 04-730 Warszawa Tytuł rozprawy na stopień doktora nauk medycznych: Ocena parametrów stresu
Instytut Pomnik Centrum Zdrowia Dziecka Zakład Patologii Pracownia Medycyny Mitochondrialnej Al. Dzieci Polskich 20 04-730 Warszawa Tytuł rozprawy na stopień doktora nauk medycznych: Ocena parametrów stresu
Zarządzanie sieciami telekomunikacyjnymi
 SNMP Protocol The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an application layer protocol that facilitates the exchange of management information between network devices. It is part of the Transmission
SNMP Protocol The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an application layer protocol that facilitates the exchange of management information between network devices. It is part of the Transmission
Rozpoznawanie twarzy metodą PCA Michał Bereta 1. Testowanie statystycznej istotności różnic między jakością klasyfikatorów
 Rozpoznawanie twarzy metodą PCA Michał Bereta www.michalbereta.pl 1. Testowanie statystycznej istotności różnic między jakością klasyfikatorów Wiemy, że możemy porównywad klasyfikatory np. za pomocą kroswalidacji.
Rozpoznawanie twarzy metodą PCA Michał Bereta www.michalbereta.pl 1. Testowanie statystycznej istotności różnic między jakością klasyfikatorów Wiemy, że możemy porównywad klasyfikatory np. za pomocą kroswalidacji.
Ocena wpływu ludzkiego antygenu leukocytarnego HLA B5701 na progresję zakażenia HIV 1 i odpowiedź na leczenie antyretrowirusowe.
 ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA Ocena wpływu ludzkiego antygenu leukocytarnego HLA B5701 na progresję zakażenia HIV 1 i odpowiedź na leczenie antyretrowirusowe. Promotor: Dr hab. n. med. Justyna D. Kowalska Klinika
ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA Ocena wpływu ludzkiego antygenu leukocytarnego HLA B5701 na progresję zakażenia HIV 1 i odpowiedź na leczenie antyretrowirusowe. Promotor: Dr hab. n. med. Justyna D. Kowalska Klinika
Instrukcja obsługi User s manual
 Instrukcja obsługi User s manual Konfigurator Lanberg Lanberg Configurator E-mail: support@lanberg.pl support@lanberg.eu www.lanberg.pl www.lanberg.eu Lanberg 2015-2018 WERSJA VERSION: 2018/11 Instrukcja
Instrukcja obsługi User s manual Konfigurator Lanberg Lanberg Configurator E-mail: support@lanberg.pl support@lanberg.eu www.lanberg.pl www.lanberg.eu Lanberg 2015-2018 WERSJA VERSION: 2018/11 Instrukcja
Zakopane, plan miasta: Skala ok. 1: = City map (Polish Edition)
 Zakopane, plan miasta: Skala ok. 1:15 000 = City map (Polish Edition) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Zakopane, plan miasta: Skala ok. 1:15 000 = City map (Polish Edition) Zakopane,
Zakopane, plan miasta: Skala ok. 1:15 000 = City map (Polish Edition) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Zakopane, plan miasta: Skala ok. 1:15 000 = City map (Polish Edition) Zakopane,
POZYTYWNE I NEGATYWNE SKUTKI DOŚWIADCZANEJ TRAUMY U CHORYCH PO PRZEBYTYM ZAWALE SERCA
 POZYTYWNE I NEGATYWNE SKUTKI DOŚWIADCZANEJ TRAUMY U CHORYCH PO PRZEBYTYM ZAWALE SERCA mgr Magdalena Hendożko Praca doktorska Promotor: dr hab. med. Wacław Kochman prof. nadzw. Gdańsk 2015 STRESZCZENIE
POZYTYWNE I NEGATYWNE SKUTKI DOŚWIADCZANEJ TRAUMY U CHORYCH PO PRZEBYTYM ZAWALE SERCA mgr Magdalena Hendożko Praca doktorska Promotor: dr hab. med. Wacław Kochman prof. nadzw. Gdańsk 2015 STRESZCZENIE
Knovel Math: Jakość produktu
 Knovel Math: Jakość produktu Knovel jest agregatorem materiałów pełnotekstowych dostępnych w formacie PDF i interaktywnym. Narzędzia interaktywne Knovel nie są stworzone wokół specjalnych algorytmów wymagających
Knovel Math: Jakość produktu Knovel jest agregatorem materiałów pełnotekstowych dostępnych w formacie PDF i interaktywnym. Narzędzia interaktywne Knovel nie są stworzone wokół specjalnych algorytmów wymagających
Tytuł pracy w języku angielskim: Physical properties of liquid crystal mixtures of chiral and achiral compounds for use in LCDs
 Dr inż. Jan Czerwiec Kierownik pracy: dr hab. Monika Marzec Tytuł pracy w języku polskim: Właściwości fizyczne mieszanin ciekłokrystalicznych związków chiralnych i achiralnych w odniesieniu do zastosowań
Dr inż. Jan Czerwiec Kierownik pracy: dr hab. Monika Marzec Tytuł pracy w języku polskim: Właściwości fizyczne mieszanin ciekłokrystalicznych związków chiralnych i achiralnych w odniesieniu do zastosowań
Streszczenie rozprawy doktorskiej
 Doskonalenie pomiaru zawartości wody w produktach spożywczych z wykorzystaniem metody wagosuszarkowej bazującej na promieniowaniu IR mgr Sławomir Janas Streszczenie rozprawy doktorskiej Promotor pracy:
Doskonalenie pomiaru zawartości wody w produktach spożywczych z wykorzystaniem metody wagosuszarkowej bazującej na promieniowaniu IR mgr Sławomir Janas Streszczenie rozprawy doktorskiej Promotor pracy:
Sargent Opens Sonairte Farmers' Market
 Sargent Opens Sonairte Farmers' Market 31 March, 2008 1V8VIZSV7EVKIRX8(1MRMWXIVSJ7XEXIEXXLI(ITEVXQIRXSJ%KVMGYPXYVI *MWLIVMIWERH*SSHTIVJSVQIHXLISJJMGMEPSTIRMRKSJXLI7SREMVXI*EVQIVW 1EVOIXMR0E]XS[R'S1IEXL
Sargent Opens Sonairte Farmers' Market 31 March, 2008 1V8VIZSV7EVKIRX8(1MRMWXIVSJ7XEXIEXXLI(ITEVXQIRXSJ%KVMGYPXYVI *MWLIVMIWERH*SSHTIVJSVQIHXLISJJMGMEPSTIRMRKSJXLI7SREMVXI*EVQIVW 1EVOIXMR0E]XS[R'S1IEXL
SWPS Uniwersytet Humanistycznospołeczny. Wydział Zamiejscowy we Wrocławiu. Karolina Horodyska
 SWPS Uniwersytet Humanistycznospołeczny Wydział Zamiejscowy we Wrocławiu Karolina Horodyska Warunki skutecznego promowania zdrowej diety i aktywności fizycznej: dobre praktyki w interwencjach psychospołecznych
SWPS Uniwersytet Humanistycznospołeczny Wydział Zamiejscowy we Wrocławiu Karolina Horodyska Warunki skutecznego promowania zdrowej diety i aktywności fizycznej: dobre praktyki w interwencjach psychospołecznych
Uniwersytet Medyczny w Łodzi. Wydział Lekarski. Jarosław Woźniak. Rozprawa doktorska
 Uniwersytet Medyczny w Łodzi Wydział Lekarski Jarosław Woźniak Rozprawa doktorska Ocena funkcji stawu skokowego po leczeniu operacyjnym złamań kostek goleni z uszkodzeniem więzozrostu piszczelowo-strzałkowego
Uniwersytet Medyczny w Łodzi Wydział Lekarski Jarosław Woźniak Rozprawa doktorska Ocena funkcji stawu skokowego po leczeniu operacyjnym złamań kostek goleni z uszkodzeniem więzozrostu piszczelowo-strzałkowego
Ocena wpływu nasilenia objawów zespołu nadpobudliwości psychoruchowej na masę ciała i BMI u dzieci i młodzieży
 Ewa Racicka-Pawlukiewicz Ocena wpływu nasilenia objawów zespołu nadpobudliwości psychoruchowej na masę ciała i BMI u dzieci i młodzieży Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych PROMOTOR: Dr hab. n.
Ewa Racicka-Pawlukiewicz Ocena wpływu nasilenia objawów zespołu nadpobudliwości psychoruchowej na masę ciała i BMI u dzieci i młodzieży Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych PROMOTOR: Dr hab. n.
PORTS AS LOGISTICS CENTERS FOR CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION OF THE OFFSHORE WIND FARMS - CASE OF SASSNITZ
 Part-financed by EU South Baltic Programme w w w. p t m e w. p l PROSPECTS OF THE OFFSHORE WIND ENERGY DEVELOPMENT IN POLAND - OFFSHORE WIND INDUSTRY IN THE COASTAL CITIES AND PORT AREAS PORTS AS LOGISTICS
Part-financed by EU South Baltic Programme w w w. p t m e w. p l PROSPECTS OF THE OFFSHORE WIND ENERGY DEVELOPMENT IN POLAND - OFFSHORE WIND INDUSTRY IN THE COASTAL CITIES AND PORT AREAS PORTS AS LOGISTICS
SSW1.1, HFW Fry #20, Zeno #25 Benchmark: Qtr.1. Fry #65, Zeno #67. like
 SSW1.1, HFW Fry #20, Zeno #25 Benchmark: Qtr.1 I SSW1.1, HFW Fry #65, Zeno #67 Benchmark: Qtr.1 like SSW1.2, HFW Fry #47, Zeno #59 Benchmark: Qtr.1 do SSW1.2, HFW Fry #5, Zeno #4 Benchmark: Qtr.1 to SSW1.2,
SSW1.1, HFW Fry #20, Zeno #25 Benchmark: Qtr.1 I SSW1.1, HFW Fry #65, Zeno #67 Benchmark: Qtr.1 like SSW1.2, HFW Fry #47, Zeno #59 Benchmark: Qtr.1 do SSW1.2, HFW Fry #5, Zeno #4 Benchmark: Qtr.1 to SSW1.2,
Charakterystyka kliniczna chorych na raka jelita grubego
 Lek. Łukasz Głogowski Charakterystyka kliniczna chorych na raka jelita grubego Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych Opiekun naukowy: Dr hab. n. med. Ewa Nowakowska-Zajdel Zakład Profilaktyki Chorób
Lek. Łukasz Głogowski Charakterystyka kliniczna chorych na raka jelita grubego Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych Opiekun naukowy: Dr hab. n. med. Ewa Nowakowska-Zajdel Zakład Profilaktyki Chorób
European Crime Prevention Award (ECPA) Annex I - new version 2014
 European Crime Prevention Award (ECPA) Annex I - new version 2014 Załącznik nr 1 General information (Informacje ogólne) 1. Please specify your country. (Kraj pochodzenia:) 2. Is this your country s ECPA
European Crime Prevention Award (ECPA) Annex I - new version 2014 Załącznik nr 1 General information (Informacje ogólne) 1. Please specify your country. (Kraj pochodzenia:) 2. Is this your country s ECPA
MaPlan Sp. z O.O. Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically
 Mierzeja Wislana, mapa turystyczna 1:50 000: Mikoszewo, Jantar, Stegna, Sztutowo, Katy Rybackie, Przebrno, Krynica Morska, Piaski, Frombork =... = Carte touristique (Polish Edition) MaPlan Sp. z O.O Click
Mierzeja Wislana, mapa turystyczna 1:50 000: Mikoszewo, Jantar, Stegna, Sztutowo, Katy Rybackie, Przebrno, Krynica Morska, Piaski, Frombork =... = Carte touristique (Polish Edition) MaPlan Sp. z O.O Click
OPTYMALIZACJA PUBLICZNEGO TRANSPORTU ZBIOROWEGO W GMINIE ŚRODA WIELKOPOLSKA
 Politechnika Poznańska Wydział Maszyn Roboczych i Transportu Inż. NATALIA LEMTIS OPTYMALIZACJA PUBLICZNEGO TRANSPORTU ZBIOROWEGO W GMINIE ŚRODA WIELKOPOLSKA Promotor: DR INŻ. MARCIN KICIŃSKI Poznań, 2016
Politechnika Poznańska Wydział Maszyn Roboczych i Transportu Inż. NATALIA LEMTIS OPTYMALIZACJA PUBLICZNEGO TRANSPORTU ZBIOROWEGO W GMINIE ŚRODA WIELKOPOLSKA Promotor: DR INŻ. MARCIN KICIŃSKI Poznań, 2016
Evaluation of the main goal and specific objectives of the Human Capital Operational Programme
 Pracownia Naukowo-Edukacyjna Evaluation of the main goal and specific objectives of the Human Capital Operational Programme and the contribution by ESF funds towards the results achieved within specific
Pracownia Naukowo-Edukacyjna Evaluation of the main goal and specific objectives of the Human Capital Operational Programme and the contribution by ESF funds towards the results achieved within specific
STRESZCZENIE Słowa kluczowe: Wstęp Cel pracy
 STRESZCZENIE Słowa kluczowe: Noworodek urodzony przedwcześnie, granulocyt obojętnochłonny, molekuły adhezji komórkowej CD11a, CD11b, CD11c, CD18, CD54, CD62L, wczesne zakażenie, posocznica. Wstęp W ostatnich
STRESZCZENIE Słowa kluczowe: Noworodek urodzony przedwcześnie, granulocyt obojętnochłonny, molekuły adhezji komórkowej CD11a, CD11b, CD11c, CD18, CD54, CD62L, wczesne zakażenie, posocznica. Wstęp W ostatnich
Institutional Determinants of IncomeLevel Convergence in the European. Union: Are Institutions Responsible for Divergence Tendencies of Some
 Institutional Determinants of IncomeLevel Convergence in the European Union: Are Institutions Responsible for Divergence Tendencies of Some Countries? Dr Mariusz Próchniak Katedra Ekonomii II, Szkoła Główna
Institutional Determinants of IncomeLevel Convergence in the European Union: Are Institutions Responsible for Divergence Tendencies of Some Countries? Dr Mariusz Próchniak Katedra Ekonomii II, Szkoła Główna
QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE CHARACTERISTICS OF FINGERPRINT BIOMETRIC TEMPLATES
 ZESZYTY NAUKOWE POLITECHNIKI ŚLĄSKIEJ 2014 Seria: ORGANIZACJA I ZARZĄDZANIE z. 74 Nr kol. 1921 Adrian KAPCZYŃSKI Politechnika Śląska Instytut Ekonomii i Informatyki QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE CHARACTERISTICS
ZESZYTY NAUKOWE POLITECHNIKI ŚLĄSKIEJ 2014 Seria: ORGANIZACJA I ZARZĄDZANIE z. 74 Nr kol. 1921 Adrian KAPCZYŃSKI Politechnika Śląska Instytut Ekonomii i Informatyki QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE CHARACTERISTICS
INSPECTION METHODS FOR QUALITY CONTROL OF FIBRE METAL LAMINATES IN AEROSPACE COMPONENTS
 Kompozyty 11: 2 (2011) 130-135 Krzysztof Dragan 1 * Jarosław Bieniaś 2, Michał Sałaciński 1, Piotr Synaszko 1 1 Air Force Institute of Technology, Non Destructive Testing Lab., ul. ks. Bolesława 6, 01-494
Kompozyty 11: 2 (2011) 130-135 Krzysztof Dragan 1 * Jarosław Bieniaś 2, Michał Sałaciński 1, Piotr Synaszko 1 1 Air Force Institute of Technology, Non Destructive Testing Lab., ul. ks. Bolesława 6, 01-494
OpenPoland.net API Documentation
 OpenPoland.net API Documentation Release 1.0 Michał Gryczka July 11, 2014 Contents 1 REST API tokens: 3 1.1 How to get a token............................................ 3 2 REST API : search for assets
OpenPoland.net API Documentation Release 1.0 Michał Gryczka July 11, 2014 Contents 1 REST API tokens: 3 1.1 How to get a token............................................ 3 2 REST API : search for assets
GDAŃSKI UNIWERSYTET MEDYCZNY
 GDAŃSKI UNIWERSYTET MEDYCZNY mgr Magdalena Pinkowicka WPŁYW TRENINGU EEG-BIOFEEDBACK NA POPRAWĘ WYBRANYCH FUNKCJI POZNAWCZYCH U DZIECI Z ADHD Rozprawa doktorska Promotor dr hab. n. med. Andrzej Frydrychowski,
GDAŃSKI UNIWERSYTET MEDYCZNY mgr Magdalena Pinkowicka WPŁYW TRENINGU EEG-BIOFEEDBACK NA POPRAWĘ WYBRANYCH FUNKCJI POZNAWCZYCH U DZIECI Z ADHD Rozprawa doktorska Promotor dr hab. n. med. Andrzej Frydrychowski,
IDENTIFICATION OF THE RARE DYS393*10 ALLELE IN THE NORTHERN POLISH POPULATION
 IDENTIFICATION OF THE RARE DYS393*10 ALLELE IN THE NORTHERN POLISH POPULATION Anita DETTLAFF-K KOL 1, Ryszard PAW OWSKI 1, 2 1 Chair and Department of Forensic Medicine, Medical Academy, Gdañsk 2 Institute
IDENTIFICATION OF THE RARE DYS393*10 ALLELE IN THE NORTHERN POLISH POPULATION Anita DETTLAFF-K KOL 1, Ryszard PAW OWSKI 1, 2 1 Chair and Department of Forensic Medicine, Medical Academy, Gdañsk 2 Institute
Ingrid Wenzel. Rozprawa doktorska. Promotor: dr hab. med. Dorota Dworakowska
 Ingrid Wenzel KLINICZNE ZNACZENIE EKSPRESJI RECEPTORA ESTROGENOWEGO, PROGESTERONOWEGO I ANDROGENOWEGO U CHORYCH PODDANYCH LECZNICZEMU ZABIEGOWI OPERACYJNEMU Z POWODU NIEDROBNOKOMÓRKOWEGO RAKA PŁUC (NDKRP)
Ingrid Wenzel KLINICZNE ZNACZENIE EKSPRESJI RECEPTORA ESTROGENOWEGO, PROGESTERONOWEGO I ANDROGENOWEGO U CHORYCH PODDANYCH LECZNICZEMU ZABIEGOWI OPERACYJNEMU Z POWODU NIEDROBNOKOMÓRKOWEGO RAKA PŁUC (NDKRP)
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture11. Random Projections & Canonical Correlation Analysis
 Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture11 5 Random Projections & Canonical Correlation Analysis The Tall, THE FAT AND THE UGLY n X d The Tall, THE FAT AND THE UGLY d X > n X d n = n d d The
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture11 5 Random Projections & Canonical Correlation Analysis The Tall, THE FAT AND THE UGLY n X d The Tall, THE FAT AND THE UGLY d X > n X d n = n d d The
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition)
 Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
Latent Dirichlet Allocation Models and their Evaluation IT for Practice 2016
 Latent Dirichlet Allocation Models and their Evaluation IT for Practice 2016 Paweł Lula Cracow University of Economics, Poland pawel.lula@uek.krakow.pl Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) Documents Latent
Latent Dirichlet Allocation Models and their Evaluation IT for Practice 2016 Paweł Lula Cracow University of Economics, Poland pawel.lula@uek.krakow.pl Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) Documents Latent
Fenotyp oporności prątków gruźlicy na pirazynamid (PZA) w badaniach ogólnopolskich
 PRACA ORYGINALNA Agnieszka Napiórkowska, Ewa Augustynowicz-Kopeć, Zofia Zwolska Zakład Mikrobiologii, Instytut Gruźlicy i Chorób Płuc w Warszawie Kierownik: prof. dr hab. n. med. Z. Zwolska Fenotyp oporności
PRACA ORYGINALNA Agnieszka Napiórkowska, Ewa Augustynowicz-Kopeć, Zofia Zwolska Zakład Mikrobiologii, Instytut Gruźlicy i Chorób Płuc w Warszawie Kierownik: prof. dr hab. n. med. Z. Zwolska Fenotyp oporności
Weronika Mysliwiec, klasa 8W, rok szkolny 2018/2019
 Poniższy zbiór zadań został wykonany w ramach projektu Mazowiecki program stypendialny dla uczniów szczególnie uzdolnionych - najlepsza inwestycja w człowieka w roku szkolnym 2018/2019. Tresci zadań rozwiązanych
Poniższy zbiór zadań został wykonany w ramach projektu Mazowiecki program stypendialny dla uczniów szczególnie uzdolnionych - najlepsza inwestycja w człowieka w roku szkolnym 2018/2019. Tresci zadań rozwiązanych
Ankiety Nowe funkcje! Pomoc magda.szewczyk@slo-wroc.pl. magda.szewczyk@slo-wroc.pl. Twoje konto Wyloguj. BIODIVERSITY OF RIVERS: Survey to students
 Ankiety Nowe funkcje! Pomoc magda.szewczyk@slo-wroc.pl Back Twoje konto Wyloguj magda.szewczyk@slo-wroc.pl BIODIVERSITY OF RIVERS: Survey to students Tworzenie ankiety Udostępnianie Analiza (55) Wyniki
Ankiety Nowe funkcje! Pomoc magda.szewczyk@slo-wroc.pl Back Twoje konto Wyloguj magda.szewczyk@slo-wroc.pl BIODIVERSITY OF RIVERS: Survey to students Tworzenie ankiety Udostępnianie Analiza (55) Wyniki
Gdański Uniwersytet Medyczny. Polimorfizm genów receptorów estrogenowych (ERα i ERβ) a rozwój zespołu metabolicznego u kobiet po menopauzie
 Gdański Uniwersytet Medyczny Mgr Karolina Kuźbicka Polimorfizm genów receptorów estrogenowych (ERα i ERβ) a rozwój zespołu metabolicznego u kobiet po menopauzie Rozprawa doktorska Promotor: dr hab. n.
Gdański Uniwersytet Medyczny Mgr Karolina Kuźbicka Polimorfizm genów receptorów estrogenowych (ERα i ERβ) a rozwój zespołu metabolicznego u kobiet po menopauzie Rozprawa doktorska Promotor: dr hab. n.
CLINICAL GENETICS OF CANCER 2016
 International Conference CLINICAL GENETICS OF CANCER 2016 Szczecin, 14-15 September 2016 (Center for New Medical Technologies, Unii Lubelskiej 1, Szczecin) Wednesday (14 September 2016) 9:00-9:15 Conference
International Conference CLINICAL GENETICS OF CANCER 2016 Szczecin, 14-15 September 2016 (Center for New Medical Technologies, Unii Lubelskiej 1, Szczecin) Wednesday (14 September 2016) 9:00-9:15 Conference
Proposal of thesis topic for mgr in. (MSE) programme in Telecommunications and Computer Science
 Proposal of thesis topic for mgr in (MSE) programme 1 Topic: Monte Carlo Method used for a prognosis of a selected technological process 2 Supervisor: Dr in Małgorzata Langer 3 Auxiliary supervisor: 4
Proposal of thesis topic for mgr in (MSE) programme 1 Topic: Monte Carlo Method used for a prognosis of a selected technological process 2 Supervisor: Dr in Małgorzata Langer 3 Auxiliary supervisor: 4
Helena Boguta, klasa 8W, rok szkolny 2018/2019
 Poniższy zbiór zadań został wykonany w ramach projektu Mazowiecki program stypendialny dla uczniów szczególnie uzdolnionych - najlepsza inwestycja w człowieka w roku szkolnym 2018/2019. Składają się na
Poniższy zbiór zadań został wykonany w ramach projektu Mazowiecki program stypendialny dla uczniów szczególnie uzdolnionych - najlepsza inwestycja w człowieka w roku szkolnym 2018/2019. Składają się na
SNP SNP Business Partner Data Checker. Prezentacja produktu
 SNP SNP Business Partner Data Checker Prezentacja produktu Istota rozwiązania SNP SNP Business Partner Data Checker Celem produktu SNP SNP Business Partner Data Checker jest umożliwienie sprawdzania nazwy
SNP SNP Business Partner Data Checker Prezentacja produktu Istota rozwiązania SNP SNP Business Partner Data Checker Celem produktu SNP SNP Business Partner Data Checker jest umożliwienie sprawdzania nazwy
Tychy, plan miasta: Skala 1: (Polish Edition)
 Tychy, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000 (Polish Edition) Poland) Przedsiebiorstwo Geodezyjno-Kartograficzne (Katowice Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Tychy, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000
Tychy, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000 (Polish Edition) Poland) Przedsiebiorstwo Geodezyjno-Kartograficzne (Katowice Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Tychy, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000
TYRE PYROLYSIS. REDUXCO GENERAL DISTRIBUTOR :: ::
 TYRE PYROLYSIS Installation for rubber waste pyrolysis designed for processing of used tyres and plastic waste (polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene), where the final product could be electricity,
TYRE PYROLYSIS Installation for rubber waste pyrolysis designed for processing of used tyres and plastic waste (polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene), where the final product could be electricity,
ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA. Mateusz Romanowski
 Mateusz Romanowski Wpływ krioterapii ogólnoustrojowej na aktywność choroby i sprawność chorych na zesztywniające zapalenie stawów kręgosłupa ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA Promotor: Dr hab., prof. AWF Anna Straburzyńska-Lupa
Mateusz Romanowski Wpływ krioterapii ogólnoustrojowej na aktywność choroby i sprawność chorych na zesztywniające zapalenie stawów kręgosłupa ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA Promotor: Dr hab., prof. AWF Anna Straburzyńska-Lupa
Ocena skuteczności preparatów miejscowo znieczulających skórę w redukcji bólu w trakcie pobierania krwi u dzieci badanie z randomizacją
 234 Ocena skuteczności preparatów miejscowo znieczulających skórę w redukcji bólu w trakcie pobierania krwi u dzieci badanie z randomizacją The effectiveness of local anesthetics in the reduction of needle
234 Ocena skuteczności preparatów miejscowo znieczulających skórę w redukcji bólu w trakcie pobierania krwi u dzieci badanie z randomizacją The effectiveness of local anesthetics in the reduction of needle
Karpacz, plan miasta 1:10 000: Panorama Karkonoszy, mapa szlakow turystycznych (Polish Edition)
 Karpacz, plan miasta 1:10 000: Panorama Karkonoszy, mapa szlakow turystycznych (Polish Edition) J Krupski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Karpacz, plan miasta 1:10 000: Panorama
Karpacz, plan miasta 1:10 000: Panorama Karkonoszy, mapa szlakow turystycznych (Polish Edition) J Krupski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Karpacz, plan miasta 1:10 000: Panorama
INSTYTUT GENETYKI I HODOWLI ZWIERZĄT POLSKIEJ AKADEMII NAUK W JASTRZĘBCU. mgr inż. Ewa Metera-Zarzycka
 INSTYTUT GENETYKI I HODOWLI ZWIERZĄT POLSKIEJ AKADEMII NAUK W JASTRZĘBCU mgr inż. Ewa Metera-Zarzycka Profil metaboliczny osocza krwi i wartość biologiczna mleka krów w gospodarstwach ekologicznych Praca
INSTYTUT GENETYKI I HODOWLI ZWIERZĄT POLSKIEJ AKADEMII NAUK W JASTRZĘBCU mgr inż. Ewa Metera-Zarzycka Profil metaboliczny osocza krwi i wartość biologiczna mleka krów w gospodarstwach ekologicznych Praca
EXAMPLES OF CABRI GEOMETRE II APPLICATION IN GEOMETRIC SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH
 Anna BŁACH Centre of Geometry and Engineering Graphics Silesian University of Technology in Gliwice EXAMPLES OF CABRI GEOMETRE II APPLICATION IN GEOMETRIC SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH Introduction Computer techniques
Anna BŁACH Centre of Geometry and Engineering Graphics Silesian University of Technology in Gliwice EXAMPLES OF CABRI GEOMETRE II APPLICATION IN GEOMETRIC SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH Introduction Computer techniques
Instructions for student teams
 The EduGIS Academy Use of ICT and GIS in teaching of the biology and geography subjects and environmental education (junior high-school and high school level) Instructions for student teams Additional
The EduGIS Academy Use of ICT and GIS in teaching of the biology and geography subjects and environmental education (junior high-school and high school level) Instructions for student teams Additional
DOI: / /32/37
 . 2015. 4 (32) 1:18 DOI: 10.17223/1998863 /32/37 -,,. - -. :,,,,., -, -.,.-.,.,.,. -., -,.,,., -, 70 80. (.,.,. ),, -,.,, -,, (1886 1980).,.,, (.,.,..), -, -,,,, ; -, - 346, -,.. :, -, -,,,,,.,,, -,,,
. 2015. 4 (32) 1:18 DOI: 10.17223/1998863 /32/37 -,,. - -. :,,,,., -, -.,.-.,.,.,. -., -,.,,., -, 70 80. (.,.,. ),, -,.,, -,, (1886 1980).,.,, (.,.,..), -, -,,,, ; -, - 346, -,.. :, -, -,,,,,.,,, -,,,
ERASMUS + : Trail of extinct and active volcanoes, earthquakes through Europe. SURVEY TO STUDENTS.
 ERASMUS + : Trail of extinct and active volcanoes, earthquakes through Europe. SURVEY TO STUDENTS. Strona 1 1. Please give one answer. I am: Students involved in project 69% 18 Student not involved in
ERASMUS + : Trail of extinct and active volcanoes, earthquakes through Europe. SURVEY TO STUDENTS. Strona 1 1. Please give one answer. I am: Students involved in project 69% 18 Student not involved in
Probability definition
 Probability Probability definition Probability of an event P(A) denotes the frequency of it s occurrence in a long (infinite) series of repeats P( A) = A Ω Ω A 0 P It s s represented by a number in the
Probability Probability definition Probability of an event P(A) denotes the frequency of it s occurrence in a long (infinite) series of repeats P( A) = A Ω Ω A 0 P It s s represented by a number in the
POLITECHNIKA WARSZAWSKA. Wydział Zarządzania ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA. mgr Marcin Chrząścik
 POLITECHNIKA WARSZAWSKA Wydział Zarządzania ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA mgr Marcin Chrząścik Model strategii promocji w zarządzaniu wizerunkiem regionu Warmii i Mazur Promotor dr hab. Jarosław S. Kardas, prof.
POLITECHNIKA WARSZAWSKA Wydział Zarządzania ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA mgr Marcin Chrząścik Model strategii promocji w zarządzaniu wizerunkiem regionu Warmii i Mazur Promotor dr hab. Jarosław S. Kardas, prof.
STATISTICAL METHODS IN BIOLOGY
 STATISTICAL METHODS IN BIOLOGY 1. Introduction 2. Populations and samples 3. Hypotheses testing and parameter estimation 4. Experimental design for biological data 5. Most widely used statistical tests
STATISTICAL METHODS IN BIOLOGY 1. Introduction 2. Populations and samples 3. Hypotheses testing and parameter estimation 4. Experimental design for biological data 5. Most widely used statistical tests
Genotypy i antybiotykooporność izolatów Staphylococcus aureus wyosobnionych od świń, kur oraz z mięsa wieprzowego i drobiowego
 UNIWERSYTET PRZYRODNICZY WE WROCŁAWIU WYDZIAŁ MEDYCYNY WETERYNARYJNEJ Mgr inż. Paweł Krupa Genotypy i antybiotykooporność izolatów Staphylococcus aureus wyosobnionych od świń, kur oraz z mięsa wieprzowego
UNIWERSYTET PRZYRODNICZY WE WROCŁAWIU WYDZIAŁ MEDYCYNY WETERYNARYJNEJ Mgr inż. Paweł Krupa Genotypy i antybiotykooporność izolatów Staphylococcus aureus wyosobnionych od świń, kur oraz z mięsa wieprzowego
PROTEOLYTIC ACTIVITY OF Bacillus cereus STRAINS
 Proceedings of ECOpole Vol., No. Małgorzata NABRDALIK, Katarzyna GRATA and Adam LATAŁA PROTEOLYTIC ACTIVITY OF Bacillus cereus STRAINS AKTYWNOŚĆ PROTEOLITYCZNA SZCZEPÓW Bacillus cereus Abstract: The aim
Proceedings of ECOpole Vol., No. Małgorzata NABRDALIK, Katarzyna GRATA and Adam LATAŁA PROTEOLYTIC ACTIVITY OF Bacillus cereus STRAINS AKTYWNOŚĆ PROTEOLITYCZNA SZCZEPÓW Bacillus cereus Abstract: The aim
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 11. Spectral Embedding + Clustering
 Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 11 Spectral Embedding + Clustering MOTIVATING EXAMPLE What can you say from this network? MOTIVATING EXAMPLE How about now? THOUGHT EXPERIMENT For each
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 11 Spectral Embedding + Clustering MOTIVATING EXAMPLE What can you say from this network? MOTIVATING EXAMPLE How about now? THOUGHT EXPERIMENT For each
photo graphic Jan Witkowski Project for exhibition compositions typography colors : +48 506 780 943 : janwi@janwi.com
 Jan Witkowski : +48 506 780 943 : janwi@janwi.com Project for exhibition photo graphic compositions typography colors Berlin London Paris Barcelona Vienna Prague Krakow Zakopane Jan Witkowski ARTIST FROM
Jan Witkowski : +48 506 780 943 : janwi@janwi.com Project for exhibition photo graphic compositions typography colors Berlin London Paris Barcelona Vienna Prague Krakow Zakopane Jan Witkowski ARTIST FROM
Fizyka Procesów Klimatycznych Wykład 11 Aktualne zmiany klimatu: atmosfera, hydrosfera, kriosfera
 Fizyka Procesów Klimatycznych Wykład 11 Aktualne zmiany klimatu: atmosfera, hydrosfera, kriosfera prof. dr hab. Szymon Malinowski Instytut Geofizyki, Wydział Fizyki Uniwersytet Warszawski malina@igf.fuw.edu.pl
Fizyka Procesów Klimatycznych Wykład 11 Aktualne zmiany klimatu: atmosfera, hydrosfera, kriosfera prof. dr hab. Szymon Malinowski Instytut Geofizyki, Wydział Fizyki Uniwersytet Warszawski malina@igf.fuw.edu.pl
DUAL SIMILARITY OF VOLTAGE TO CURRENT AND CURRENT TO VOLTAGE TRANSFER FUNCTION OF HYBRID ACTIVE TWO- PORTS WITH CONVERSION
 ELEKTRYKA 0 Zeszyt (9) Rok LX Andrzej KUKIEŁKA Politechnika Śląska w Gliwicach DUAL SIMILARITY OF VOLTAGE TO CURRENT AND CURRENT TO VOLTAGE TRANSFER FUNCTION OF HYBRID ACTIVE TWO- PORTS WITH CONVERSION
ELEKTRYKA 0 Zeszyt (9) Rok LX Andrzej KUKIEŁKA Politechnika Śląska w Gliwicach DUAL SIMILARITY OF VOLTAGE TO CURRENT AND CURRENT TO VOLTAGE TRANSFER FUNCTION OF HYBRID ACTIVE TWO- PORTS WITH CONVERSION
 www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
Few-fermion thermometry
 Few-fermion thermometry Phys. Rev. A 97, 063619 (2018) Tomasz Sowiński Institute of Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences Co-authors: Marcin Płodzień Rafał Demkowicz-Dobrzański FEW-BODY PROBLEMS FewBody.ifpan.edu.pl
Few-fermion thermometry Phys. Rev. A 97, 063619 (2018) Tomasz Sowiński Institute of Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences Co-authors: Marcin Płodzień Rafał Demkowicz-Dobrzański FEW-BODY PROBLEMS FewBody.ifpan.edu.pl
B IURO B ADAWCZE DS. J AKOŚCI
 ISO 9001 Q Ref. Certif. No. PL 2 IEC SYSTEM FOR MUTUAL RECOGNITION OF TEST CERTIFICATES FOR ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT (IECEE) CB SCHEME SYSTEME CEI D ACCEPTATION MUTUELLE DE CERTIFICATS D ESSAIS DES EQUIPEMENTS
ISO 9001 Q Ref. Certif. No. PL 2 IEC SYSTEM FOR MUTUAL RECOGNITION OF TEST CERTIFICATES FOR ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT (IECEE) CB SCHEME SYSTEME CEI D ACCEPTATION MUTUELLE DE CERTIFICATS D ESSAIS DES EQUIPEMENTS
Akademia Morska w Szczecinie. Wydział Mechaniczny
 Akademia Morska w Szczecinie Wydział Mechaniczny ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA mgr inż. Marcin Kołodziejski Analiza metody obsługiwania zarządzanego niezawodnością pędników azymutalnych platformy pływającej Promotor:
Akademia Morska w Szczecinie Wydział Mechaniczny ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA mgr inż. Marcin Kołodziejski Analiza metody obsługiwania zarządzanego niezawodnością pędników azymutalnych platformy pływającej Promotor:
POLISH PARASITOLOGY AT THE TURN OF THE 21 st CENTURY
 POLISH PARASITOLOGICAL SOCIETY COMMITTEE ON PARASITOLOGY OF THE POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES W. STEFAŃSKI INSTITUTE OF PARASITOLOGY PAS POLISH PARASITOLOGY AT THE TURN OF THE 21 st CENTURY Book of Abstracts
POLISH PARASITOLOGICAL SOCIETY COMMITTEE ON PARASITOLOGY OF THE POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES W. STEFAŃSKI INSTITUTE OF PARASITOLOGY PAS POLISH PARASITOLOGY AT THE TURN OF THE 21 st CENTURY Book of Abstracts
EPS. Erasmus Policy Statement
 Wyższa Szkoła Biznesu i Przedsiębiorczości Ostrowiec Świętokrzyski College of Business and Entrepreneurship EPS Erasmus Policy Statement Deklaracja Polityki Erasmusa 2014-2020 EN The institution is located
Wyższa Szkoła Biznesu i Przedsiębiorczości Ostrowiec Świętokrzyski College of Business and Entrepreneurship EPS Erasmus Policy Statement Deklaracja Polityki Erasmusa 2014-2020 EN The institution is located
OCENA MECHANIZMÓW POWSTAWANIA PĘKNIĘĆ WĄTROBY W URAZACH DECELERACYJNYCH ZE SZCZEGÓLNYM UWZGLĘDNIENIEM ROLI WIĘZADEŁ WĄTROBY
 Lek. Piotr Arkuszewski OCENA MECHANIZMÓW POWSTAWANIA PĘKNIĘĆ WĄTROBY W URAZACH DECELERACYJNYCH ZE SZCZEGÓLNYM UWZGLĘDNIENIEM ROLI WIĘZADEŁ WĄTROBY Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych Promotor:
Lek. Piotr Arkuszewski OCENA MECHANIZMÓW POWSTAWANIA PĘKNIĘĆ WĄTROBY W URAZACH DECELERACYJNYCH ZE SZCZEGÓLNYM UWZGLĘDNIENIEM ROLI WIĘZADEŁ WĄTROBY Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych Promotor:
