Einstein s Theory of Gravity. Kostas Kokkotas December 11, 2018
|
|
|
- Ludwika Ciesielska
- 6 lat temu
- Przeglądów:
Transkrypt
1 Einstein s Theory of Gravity Kostas Kokkotas December 11,
2 Newtonian Gravity Poisson equation 2 U( x) = 4πGρ( x) U( x) = G For a spherically symmetric mass distribution of radius R U(r) = 1 r U(r) = 1 r R 0 r 0 r 2 ρ(r )dr for r > R r 2 ρ(r )dr R r ρ( x) x x d 3 x r ρ(r )dr for r < R 2
3 For a non-spherical distribution the term 1/ x x can be expanded as 1 x x = 1 r + k U( x) = GM r Gravitational Multipoles M = D k = Q kl = ρ( x )d 3 x x k x k r k ( 3x k x l r 2 δk) l x k x l +... r 5 k l G x k D k G Q kl x k x l +... r 3 2 r 5 Mass x k ρ( x )d 3 x Mass Dipole moment 1 ( ) 3x k x l r 2 δk l ρ( x )d 3 x Mass Quadrupole tensor 2 kl 1 If the center of mas is chosen to coincide with the origin of the coordinates then D k = 0 (no mass dipole). 2 If Q kl 0 the potential will contain a term proportional to 1/r 3 and the gravitational force will deviate from the inverse square law by a term 1/r 4. 3
4 The Earth s polar and equatorial diameters differ by 3/1000, while for the Sun we measure This deviation produces a quadrupole term in the gravitational potential, which causes perturbations in the elliptical Kepler orbits of satellites. Usually, we define the dimensionless parameter Q33 J 2 = 2M R 2 (1) as a convenient measure of the oblateness of a nearly spherical body. For the Sun the oblateness due to rotation (if uniform) would be J The most recent measurements (based on helioseismology) suggest J The main perturbation is the precession of Kepler s ellipse and this can be used for precise determinations of the multipole moments and the mass distribution in the Earth. 4
5 Equivalence Principle i In GR gravitational phenomena arise not from forces and fields, but from the curvature of the 4-dim spacetime. The starting point for this consideration is the Equivalence Principle which states that the Gravitational and the Inertial masses are equal. The equality m G = m I is one of the most accurately tested principles in physics! Now it is known experimentally that: γ = m G m I m G <
6 Equivalence Principle ii Experimental verification Galileo (1610) γ < 10 3 Newton (1680) γ < 10 3 Bessel (19th century) γ < Eötvös (1890) & (1908) γ < Dicke et al. (1964) γ < Braginsky et al. (1971) γ < , Kuroda and Mio (1989) γ < , Adelberger et al. (1990) γ < Su et al. (1994) γ < (torsional) Williams et al. ( 96), Anderson & Williams ( 01) γ < Schlamminger et al. (2008) γ <
7 Equivalence Principle iii MICROSCOPE: On 4 December 2017, the first results were published. The equivalence principle was measured to hold true within a precision of 10?15, improving prior measurements by an order of magnitude. Weak Equivalence Principle : The motion of a neutral test body released at a given point in space-time is independent of its composition Strong Equivalence Principle : The results of all local experiments in a frame in free fall are independent of the motion The results are the same for all such frames at all places and all times The results of local experiments in free fall are consistent with STR 7
8 Equivalence Principle : Dicke s Experiment The experiment is based on measuring the effect of the gravitational field on two masses of different material in a torsional pendulum. GMm (E) G R 2 = m(e) I v 2 R The forces acting on both masses are: F (j) + GMm(j) G R 2 = m(j) I v 2 R v 2 = GM R F (j) = GMm(j) I R 2 ( mg m I ) (E) [ ( mg m I ) (E) ( mg m I ) (j) ] and the total torque applied is: L = ( F (1) F (2)) [ l = GM m (1) R 2 G m(2) G ] l here we assumed that : m (1) I = m (2) I = m. 8
9 Towards a New Theory for Gravity Because of the success of Newton s theory of gravity, we should demand from our new theory : In an appropriate first approximation (weak field) the new theory should reduce to the newtonian one. Beyond this approximation the new theory should predict small deviations from newtonian theory which must be verified by experiments/observations Einstein s equivalence principle: Gravitational and Inertial forces/accelerations are equivalent and they cannot be distinguished by any physical experiment. This statement has 3 implications: 1. Gravitational forces/accelerations are described in the same way as the inertial ones. 2. When gravitational accelerations are present the space cannot be flat. 3. Consequence: if gravity is present there cannot exist inertial frames. 9
10 1. Gravitational forces/accelerations are described in the same way as the inertial ones. This means that the motion of a freely moving particle, observed from an inertial frame, will be described by d 2 x µ = 0 dt 2 while from a non-inertial frame its movement will be described by the geodesic equation d 2 x µ + Γ µ dx ρ dx σ ds 2 ρσ = 0. ds ds The 2nd term appeared due to the use of a non-inertial frame, i.e. the inertial accelerations will be described by the Christoffel symbols. But according to Einstein the gravitational accelerations as well will be described by the Christoffel symbols. This leads to the following conclusion: The metric tensor should play the role of the gravitational potential since Γ µ ρσ is a function of the metric tensor and its derivatives. 10
11 2. When gravitational accelerations are present the space cannot be flat since the Christoffel symbols are non-zero and the Riemann tensor is not zero as well. In other words, the presence of the gravitational field forces the space to be curved, i.e. there is a direct link between the presence of a gravitational field and the geometry of the space. 3. Consequence: if gravity is present there cannot exist inertial frames. If it was possible then one would have been able to discriminate among inertial and gravitational accelerations which against the generalized equivalence principle of Einstein. The absence of special coordinate frames (like the inertial) and their substitution from general (non-inertial) coordinate systems lead in naming Einstein s theory for gravity General Theory of Relativity. 11
12 Einstein s Equations Since the source of the gravitational field is a tensor (T µν) the field should be also described by a 2nd order tensor e.g. F µν. Since the role of the gravitational potential is played by the metric tensor then F µν should be a function of the metric tensor g µν and its 1st and 2nd order derivatives. Moreover, the law of energy-momenum conservation implies that T µν ;µ = 0 which suggests that F µν ;µ = 0. Then, since F µν should be a linear function of the 2nd derivative of g µν we come to the following form of the field equations (how & why?): F µν = R µν + ag µν R + bg µν = κt µν (2) where κ = 8πG. Then since F µν c 4 ;µ = 0 there should be which is possible only for a = 1/2. (R µν + ag µν R + bg µν ) ;µ = 0 (3) 12
13 Einstein s Equations Thus the final form of Einstein s equations is: R µν 1 2 g µν R + Λg µν = κt µν, (4) where Λ = 8πG ρ c 2 vac is the so called cosmological constant. 13
14 Example: Another writing of Einstein Equations We will show that Einstein s equations can be written as R µν = κ (T µν 1 ) 2 gµνt (5) This is true because if we multiply with g ρν they can be written as: R µν 1 gµνr = κtµν 2 2R ρ ν δ ρ νr = 2κT ρ ν and by contracting ρ and ν we get 2R 4R = 2κT i.e. R = κt. Thus: R µν = κt µν + 1 ( 2 gµνr = κ T µν 1 ) 2 gµνt. (6) 14
15 A few words about the cosmological-constant term i In eqn (3) there exists the term bg µν. There is freedom in adding constant multiples of g µν since we know from equation (74) (1st Chapter) that g µν ;µ = 0. This is the reason that we kept this term in (4) and we wrote it as Λ and named it as cosmological constant. In the spirit of the previous example, Einstein s equations (5) can be written as R µν = κ (T µν 1 ) 2 gµνt + Λg µν. (7) which in the Newtonian limit, eqn (33), will be written in the form 2 U = 4πGρ Λc 2 (8) and for a spherically symmetric mass M the gravitational field strength will be written as g = U = GM c ˆ r 2 Λr + r 2 3 ˆ r (9) 15
16 A few words about the cosmological-constant term ii Thus, if Λ is positive corresponds to a gravitational repulsion whose strengh increases linearly with r. The energy-momentum tensor of a perfect fluid as defined earlier is: T µν = ( ρ + p/c 2) u µ u ν pg µν (10) If we consider some strange form of something with equation of state p = ρc 2 (negative pressure!!!) its energy momentum tensor will be written as Notice that: T µν = ρc 2 g µν (11) Its energy-momentum tensor depends only on the metric tensor. This means that it is property of the vacuum itself and can be called the energy density of the vacuum. Its T µν is similar to the cosmological-constant term in eqn (4). 16
17 A few words about the cosmological-constant term iii Thus we can view the cosmological constant as a universal constant that fixes the energy density of the vacuum ρ vacc 2 = Λc4 8πG (12) 17
18 The Scalar Theory of Gravity It is the simplest generalization of Newton s gravity. Matter relativistically is described by the energy-momentum tensor T µν, the only scalar with the dimensions of mass density is T µ µ. Thus a consistent scalar relativistic theory of gravity will be given by the field equation 2 U = 4πG c 2 T µ µ (13) This theory cannot be accepted because: Predicts a retardation of the perihelion of Mercury in contradiction to observations It does not allow one to couple gravity to electromagnetism since (EM) T µ µ = 0. Does not predict gravitational redshift. Does not predict deflection of light by matter. NOTE: A gravitational theory based on a vector field cannot be accepted since such a theory predicts that two massive particles would repel and not attract one another. 18
19 The Scalar-Tensor Theory of Gravity (Jordan-Brans-Dicke) i It is possible to construct theories which combine tensor, vector and scalar fields. Brans-Dicke assumed equivalence principle and also that gravity is described as spacetime curvature. BUT they introduced a scalar field φ that determines the strength of gravitational constant G. The key ingredients of the theory are: matter is represented by the energy-momentum tensor (M) T µν, and a coupling constant λ fix the scalar field φ The scalar field φ fixes the value of G. The gravitational field equations relate the curvature to the energy momentum tensors of the scalar field and matter. 19
20 The Scalar-Tensor Theory of Gravity (Jordan-Brans-Dicke) ii The field equations are: φ = 4πλ (M) T µ µ (14) R µν 1 8π [ gµνr = (M) ] T 2 c 4 µν + (φ) T µν (15) φ (φ) T αβ = ω φ 2 ( φ,αφ,β 1 2 g αβφ,γφ,γ ) + 1 φ (φ ;αβ g αβ φ) (16) Typically the coupling constant is written as: λ = ω In the limit ω, λ 0 so the scalar field is not affected by the matter distribution and can be set equal to a constant φ = 1/G (!). In this case (φ) T µν = 0 and Brans-Dicke theory reduces to Einstein s in the limit ω 0. (17) 20
21 The Scalar-Tensor Theory of Gravity (Jordan-Brans-Dicke) iii One of the key features of Brans-Dicke theory is that the effective gravitational constant G varies with time and is determined by the scalar field φ. Brans-Dicke theory predicts light deflection and the precession of perihelia of planets orbiting the Sun but the formulae depend on ω. A variation of the G affects the orbits of planets e.g. altering the dates of eclipses. The experiments as for today predict that ω 40, 000 (Cassini-Huygens experiment, 2003). In 1973 ω 5, in 1981 ω 30! 21
22 Newtonian Limit In the absence of strong gravitational fields and for small velocities both Einstein & geodesic equations reduce to the Newtonian ones. Geodesic equations: d 2 x µ dt 2 + Γ µ dx α dx β αβ dt dt = d 2 t/ds 2 dx µ (dt/ds) 2 dt d 2 x j dt 2 g 00,j (18) If g 00 η 00 + h 00 = 1 + h 00 = 1 + 2U c 2 Einstein equations R µν = κ (T µν 1 ) 2 gµνt where κ = 8πG or κ = 8πG/c 4. then d2 x k dt 2 Here we have used the following approximations: U x k Γ j g00,j and R00 Γj 00,j 2 U 2 U = 1 κρ (19) 2 22
23 Newtonian Limit: The geodesic equations i The geodesic equations are typically written with respect to the proper time τ or the proper length s. In Newtonian theory the absolute time and the proper time are identical thus the equations need to be written with respect to the coordinate time t, which is not an affine parameter! Thus we will use the form of the geodesic equations (for non affine parameters) presented in Chapter 1 i.e. eqn (76) d 2 x µ dσ 2 + dx α dx β Γµ αβ dσ dσ = d 2 σ/ds 2 dx µ (dσ/ds) 2 dσ. (20) and if we select σ = x 0 = ct the above relation will be written: d 2 x µ c 2 dt + dx α dx β 2 Γµ αβ cdt cdt = cd2 t/ds 2 dx µ (cdt/ds) 2 cdt. (21) 23
24 Newtonian Limit: The geodesic equations ii The 1st of the above equations (the one for x 0 ) simplified because dx 0 /cdt = d(ct)/cdt = 1 and d 2 x 0 /c 2 dt 2 = 0 and thus Γ 0 dx α dx β αβ cdt cdt = cd2 t/ds 2 1 (cdt/ds) 2 c. (22) This can be substituted in (21) and the remaining 3 equations will have the form for the coordinates x k for (k = 1, 2, 3) become: ( ) d 2 x k c 2 dt + Γ k 2 αβ Γ 0 dx k dx α dx β αβ cdt cdt cdt = 0. (23) Then we will use the approximation that all velocities are much smaller than the speed of light i.e. u k = dx k /cdt << 1. Thus Γ k αβ >> Γ 0 αβ dxk and the previous equation will be approximately (...) cdt written as: 1 d 2 x k Γ k c 2 dt 2 00 (24) 24
25 Newtonian Limit: The geodesic equations iii In other words the Christoffel symbol Γ k 00 corresponds to the Newtonian force per unit of mass. Let s assume that the space is slightly curved i.e. g µν η µν + h µν with η µν >> h µν. (25) Under this assumption the Christoffel Γ k 00, gets the form Γ k 00 = 1 ( 2 g kλ 2 g ) λ0 x g x λ 2 ηkλ g 00,λ = 1 2 δkj g 00,j = 1 2 g 00,k (26) Thus in the Newtonian limit the geodesic equations reduced to: 1 d 2 x k c 2 dt 2 Which reminds the Newtonian relation 1 d 2 x k c 2 dt 2 g 00,k g00 x k. (27) U x k (28) 25
26 Newtonian Limit: The geodesic equations iv which suggests that g 00 has the form here we set h 00 = 2U c 2. g 00 η 00 + h 00 = 1 + h 00 = 1 + 2U c 2 (29) 26
27 Newtonian Limit: Einstein equations i We will show that Einstein s equations in the Newtonian limit reduce to the well known Poisson equation of Newtonian gravity. For small concentrations of masses the dominant component of the energy momentum tensor is the T 00. Thus the dominant component of the Einstein s equations is R 00 = κ (T 00 1 ) 2 g00t κ (T 00 1 ) 2 η00t 1 2 κt00 = 1 2 κρc2. (30) where we assumed that T = g µν T µν η µν T µν η 00 T 00 = T 00. The 00 component of the Ricci tensor is given by the relation R 00 = Γ µ 00,µ Γµ 0µ,0 + Γµ 00 Γν νµ Γ µ 0ν Γν 0µ Γ µ 00,µ Γj 00,j. (31) 27
28 Newtonian Limit: Einstein equations ii But as we have shown Γ j 00 g00,j/2 and thus: leading to: R 00 Γ j 00,j 1 2 g 00 = 1 2 x j x j 2 2 g 00 1 c 2 2 U. (32) 2 U = 1 2 κc4 ρ (33) From which by comparing with Poisson s equation (1) we get the value of the coupling constant κ that is: κ = 8πG c 4. (34) 28
29 Solutions of Einstein s Equations i A static spacetime is one for which a timelike coordinate x 0 has the following properties: (I) all metric components g µν are independent of x 0 (II) the line element ds 2 is invariant under the transformation x 0 x 0. Note that the 1st property does not imply the 2nd (e.g. the time reversal on a rotating star changes the sense of rotation, but the metric components are constant in time). A spacetime that satisfies (I) but not (II) is called stationary. The line element ds 2 of a static metric depends only on rotational invariants of the spacelike coordinates x i and their differentials, i.e. the metric is isotropic. 29
30 Solutions of Einstein s Equations ii The only rotational invariants of the spacelike coordinates x i and their differentials are x x r 2, x d x rdr, d x d x dr 2 + r 2 dθ 2 + r 2 sin 2 θdφ 2 Thus the more general form of a spatially isotropic metric is: ds 2 = A(t, r)dt 2 B(t, r)dt ( x d x) C(t, r)( x d x) 2 D(t, r)d x 2 = A(t, r)dt 2 B(t, r)r dt dr C(t, r)r 2 dr 2 D(t, r) ( dr 2 + r 2 dθ 2 + r 2 sin 2 θdφ 2) (35) = A(t, r)dt 2 B(t, r)dt dr C(t, r)dr 2 D(t, r) ( dθ 2 + sin 2 θdφ 2) = A (t, r)dt 2 B (t, r)dt d r C (t, r)d r 2 r 2 ( dθ 2 + sin 2 θdφ 2) (36) where we have set r 2 = D(t, r) and redefined the A, B and C. The next step will be to introduce a new timelike coordinate t as [ d t = Φ(t, r) A (t, r)dt 1 ] 2 B (t, r)d r 30
31 Solutions of Einstein s Equations iii where Φ(t, r) is an integrating factor that makes the right-hand side an exact differential. By squaring we obtain from which we find d t 2 = Φ 2 ( A 2 dt 2 A B dtd r B 2 d r 2 ) A dt 2 B dtd r = 1 A Φ 2 d t 2 B 2 4A d r 2 Thus by defining the new functions  = 1/(A Φ) 2 and ˆB = C + B 2 /(4A ) the metric (36) becomes diagonal ds 2 = Â( t, r)d t 2 ˆB( t, r)d r 2 r 2 ( dθ 2 + sin 2 θdφ 2) (37) or by dropping the hats and tildes ds 2 = A(t, r)dt 2 B(t, r)dr 2 r 2 ( dθ 2 + sin 2 θdφ 2) (38) 31
32 Solutions of Einstein s Equations iv Thus the general isotropic metric is specified by two functions of t and r, namely A(t, r) and B(t, r). Also, surfaces for t and r constant are 2-spheres (isotropy of the metric). Since B(t, r) is not unity we cannot assume that r is the radial distance. The metric tensor in matrix form is: A(t, r) g µν = 0 B(t, r) r r 2 sin 2 θ (39) 32
33 Schwarzschild Solution i A typical solution of Einstein s equations describing spherically symmetric spacetimes has the form: ds 2 = e ν(t,r) dt 2 e λ(t,r) dr 2 r 2 ( dθ 2 + sin 2 θdφ 2) (40) We next calculate the components of the Ricci tensor R µν = 0. (41) Then the Christoffel symbols for the metric (40) ( = / t) & ( = / r) are Γ 0 00 = ν 2, Γ1 00 = ν 2 eν λ, Γ 0 01 = ν 2, (42) Γ 1 01 = λ 2, Γ0 11 = λ 2 eλ ν, Γ 1 11 = λ 2, (43) Γ 1 12 = 1 Γ 3 13 = 1 r r, Γ1 22 = re λ, (44) Γ 3 23 = cot θ, Γ 1 33 = re λ sin 2 θ, Γ 2 33 = sin θ cos θ. (45) 33
34 Schwarzschild Solution ii Then the components of the Ricci tensor will be: [ R 11 = ν 2 ν ν λ λ 4 + λ r + eλ ν 2 + λ 2 4 λ ] ν 4 [ ] R 00 = e ν λ ν 2 + ν 2 4 ν λ 4 + ν λ r 2 λ λ ν 4 (46) (47) R 10 = λ (48) r R 22 = = e [1 λ + r ] 2 (ν λ ) + 1 (49) R 33 = sin 2 θr 22 (50) in the absence of matter (outside the source) R µν = 0 we can prove that λ(r) = ν(r), i.e. the solution is independent of time (how and why?). 34
35 Schwarzschild Solution iii We will use the above relations to find the functional form of ν(t, r) and λ(t, r) in an empty space i.e. when R µν = 0. Then from the sum: R 11 + e λ ν R 00 = 0 we get: ν + λ = 0 (51) while from we conclude that λ = λ(r). R 10 = λ r = 0 (52) From R 22 = 0 (eq. 49) we get: ν λ = 2 r (eλ 1) (53) Thus ν = 1 r (eλ 1) (54) λ = 1 r (eλ 1) (55) 35
36 Schwarzschild Solution iv Since the right side of the above differential equation (54) for ν is function only of r the function ν = ν(t, r) can be written as: which leads to a redefinition of the time coordinate t, ν(t, r) = α(t) + ν(r) (56) d t = e α/2 dt (57) i.e the time dependence of ν(t, r) is absorbed by the change of variable from t to t. Thus from (51) we lead to the relation: λ(r) = ν(r) (58) i.e. both unknown components of the metric tensor are independent of time and for simplicity we will write ν(r) instead of ν(r). 36
37 Schwarzschild Solution v BIRKOFF s THEOREM If the geometry of a spacetime is spherically symmetric and solution of the Einstein s equations, then it is described by the Schwarzschild solution. OR The spacetime geometry outside a general spherically symmetric matter distribution is the Schwarzschild geometry. The solution of equation (55) provides the function λ(r). We can get it by substituting f = e λ then eqn (55) will be written as: with obvious solution: rf + f = 1 (59) f = 1 k r = e λ = e ν (60) where k and will be determined by the boundary conditions. 37
38 Schwarzschild Solution vi In the present case for r our solutions should lead to Newton s solution that is g 00 = U(r) (61) c2 where U(r) is the Newtonian potential and for the case of spherical symmetry is U(r) = GM r (62) which leads to k = 2GM (63) c 2 and Schwarzschild solutions gets the form: ( ds 2 = 1 2 c 2 GM r ) ( c 2 dt c 2 GM r ) 1 dr 2 r 2 ( dθ 2 + sin 2 θdφ 2) 38
39 Schwarzschild Solution vii Sun: M gr and R = km 2GM rc Neutron star : M 1.4M and R 10 15km 2GM rc Newtonian limit: g 00 η 00 + h 00 = 1 + 2U c 2 U = GM r (64) 39
Helena Boguta, klasa 8W, rok szkolny 2018/2019
 Poniższy zbiór zadań został wykonany w ramach projektu Mazowiecki program stypendialny dla uczniów szczególnie uzdolnionych - najlepsza inwestycja w człowieka w roku szkolnym 2018/2019. Składają się na
Poniższy zbiór zadań został wykonany w ramach projektu Mazowiecki program stypendialny dla uczniów szczególnie uzdolnionych - najlepsza inwestycja w człowieka w roku szkolnym 2018/2019. Składają się na
Aerodynamics I Compressible flow past an airfoil
 Aerodynamics I Compressible flow past an airfoil transonic flow past the RAE-8 airfoil (M = 0.73, Re = 6.5 10 6, α = 3.19 ) Potential equation in compressible flows Full potential theory Let us introduce
Aerodynamics I Compressible flow past an airfoil transonic flow past the RAE-8 airfoil (M = 0.73, Re = 6.5 10 6, α = 3.19 ) Potential equation in compressible flows Full potential theory Let us introduce
Convolution semigroups with linear Jacobi parameters
 Convolution semigroups with linear Jacobi parameters Michael Anshelevich; Wojciech Młotkowski Texas A&M University; University of Wrocław February 14, 2011 Jacobi parameters. µ = measure with finite moments,
Convolution semigroups with linear Jacobi parameters Michael Anshelevich; Wojciech Młotkowski Texas A&M University; University of Wrocław February 14, 2011 Jacobi parameters. µ = measure with finite moments,
Few-fermion thermometry
 Few-fermion thermometry Phys. Rev. A 97, 063619 (2018) Tomasz Sowiński Institute of Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences Co-authors: Marcin Płodzień Rafał Demkowicz-Dobrzański FEW-BODY PROBLEMS FewBody.ifpan.edu.pl
Few-fermion thermometry Phys. Rev. A 97, 063619 (2018) Tomasz Sowiński Institute of Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences Co-authors: Marcin Płodzień Rafał Demkowicz-Dobrzański FEW-BODY PROBLEMS FewBody.ifpan.edu.pl
Weronika Mysliwiec, klasa 8W, rok szkolny 2018/2019
 Poniższy zbiór zadań został wykonany w ramach projektu Mazowiecki program stypendialny dla uczniów szczególnie uzdolnionych - najlepsza inwestycja w człowieka w roku szkolnym 2018/2019. Tresci zadań rozwiązanych
Poniższy zbiór zadań został wykonany w ramach projektu Mazowiecki program stypendialny dla uczniów szczególnie uzdolnionych - najlepsza inwestycja w człowieka w roku szkolnym 2018/2019. Tresci zadań rozwiązanych
Relaxation of the Cosmological Constant
 Relaxation of the Cosmological Constant with Peter Graham and David E. Kaplan The Born Again Universe + Work in preparation + Work in progress aaab7nicdvbns8nafhypx7v+vt16wsycp5kioseifw8ekthwaepzbf7apztn2n0ipfrhepggifd/jzf/jzs2brudwbhm5rhvtzakro3rfjqlpewv1bxyemvjc2t7p7q719zjphi2wcisdr9qjyjlbblubn6ncmkccoweo6vc7zyg0jyrd2acoh/tgeqrz9ryqdo7sdgq9qs1t37m5ibu3v2qqvekpqyfmv3qry9mwbajnexqrbuemxp/qpxhtoc00ss0ppsn6ac7lkoao/yns3wn5mgqiykszz80zkz+n5jqwotxhnhktm1q//zy8s+vm5nowp9wmwygjzt/fgwcmitkt5oqk2rgjc2hthg7k2fdqigztqgklwfxkfmfte/qnuw3p7xgzvfhgq7gei7bg3nowdu0oqumrvaiz/dipm6t8+q8zamlp5jzhx9w3r8agjmpzw==
Relaxation of the Cosmological Constant with Peter Graham and David E. Kaplan The Born Again Universe + Work in preparation + Work in progress aaab7nicdvbns8nafhypx7v+vt16wsycp5kioseifw8ekthwaepzbf7apztn2n0ipfrhepggifd/jzf/jzs2brudwbhm5rhvtzakro3rfjqlpewv1bxyemvjc2t7p7q719zjphi2wcisdr9qjyjlbblubn6ncmkccoweo6vc7zyg0jyrd2acoh/tgeqrz9ryqdo7sdgq9qs1t37m5ibu3v2qqvekpqyfmv3qry9mwbajnexqrbuemxp/qpxhtoc00ss0ppsn6ac7lkoao/yns3wn5mgqiykszz80zkz+n5jqwotxhnhktm1q//zy8s+vm5nowp9wmwygjzt/fgwcmitkt5oqk2rgjc2hthg7k2fdqigztqgklwfxkfmfte/qnuw3p7xgzvfhgq7gei7bg3nowdu0oqumrvaiz/dipm6t8+q8zamlp5jzhx9w3r8agjmpzw==
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 11. Spectral Embedding + Clustering
 Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 11 Spectral Embedding + Clustering MOTIVATING EXAMPLE What can you say from this network? MOTIVATING EXAMPLE How about now? THOUGHT EXPERIMENT For each
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 11 Spectral Embedding + Clustering MOTIVATING EXAMPLE What can you say from this network? MOTIVATING EXAMPLE How about now? THOUGHT EXPERIMENT For each
Hard-Margin Support Vector Machines
 Hard-Margin Support Vector Machines aaacaxicbzdlssnafiyn9vbjlepk3ay2gicupasvu4iblxuaw2hjmuwn7ddjjmxm1bkcg1/fjqsvt76fo9/gazqfvn8y+pjpozw5vx8zkpvtfxmlhcwl5zxyqrm2vrg5zw3vxmsoezi4ogkr6phieky5crvvjhriqvdom9l2xxftevuwcekj3lktmhghgniauiyutvrwxtvme34a77kbvg73gtygpjsrfati1+xc8c84bvraowbf+uwnipyehcvmkjrdx46vlykhkgykm3ujjdhcyzqkxy0chur6ax5cbg+1m4bbjptjcubuz4kuhvjoql93hkin5hxtav5x6yyqopnsyuneey5ni4keqrxbar5wqaxbik00icyo/iveiyqqvjo1u4fgzj/8f9x67bzmxnurjzmijtlybwfgcdjgfdtajwgcf2dwaj7ac3g1ho1n4814n7wwjgjmf/ys8fenfycuzq==
Hard-Margin Support Vector Machines aaacaxicbzdlssnafiyn9vbjlepk3ay2gicupasvu4iblxuaw2hjmuwn7ddjjmxm1bkcg1/fjqsvt76fo9/gazqfvn8y+pjpozw5vx8zkpvtfxmlhcwl5zxyqrm2vrg5zw3vxmsoezi4ogkr6phieky5crvvjhriqvdom9l2xxftevuwcekj3lktmhghgniauiyutvrwxtvme34a77kbvg73gtygpjsrfati1+xc8c84bvraowbf+uwnipyehcvmkjrdx46vlykhkgykm3ujjdhcyzqkxy0chur6ax5cbg+1m4bbjptjcubuz4kuhvjoql93hkin5hxtav5x6yyqopnsyuneey5ni4keqrxbar5wqaxbik00icyo/iveiyqqvjo1u4fgzj/8f9x67bzmxnurjzmijtlybwfgcdjgfdtajwgcf2dwaj7ac3g1ho1n4814n7wwjgjmf/ys8fenfycuzq==
A sufficient condition of regularity for axially symmetric solutions to the Navier-Stokes equations
 A sufficient condition of regularity for axially symmetric solutions to the Navier-Stokes equations G. Seregin & W. Zajaczkowski A sufficient condition of regularity for axially symmetric solutions to
A sufficient condition of regularity for axially symmetric solutions to the Navier-Stokes equations G. Seregin & W. Zajaczkowski A sufficient condition of regularity for axially symmetric solutions to
Revenue Maximization. Sept. 25, 2018
 Revenue Maximization Sept. 25, 2018 Goal So Far: Ideal Auctions Dominant-Strategy Incentive Compatible (DSIC) b i = v i is a dominant strategy u i 0 x is welfare-maximizing x and p run in polynomial time
Revenue Maximization Sept. 25, 2018 Goal So Far: Ideal Auctions Dominant-Strategy Incentive Compatible (DSIC) b i = v i is a dominant strategy u i 0 x is welfare-maximizing x and p run in polynomial time
Rozpoznawanie twarzy metodą PCA Michał Bereta 1. Testowanie statystycznej istotności różnic między jakością klasyfikatorów
 Rozpoznawanie twarzy metodą PCA Michał Bereta www.michalbereta.pl 1. Testowanie statystycznej istotności różnic między jakością klasyfikatorów Wiemy, że możemy porównywad klasyfikatory np. za pomocą kroswalidacji.
Rozpoznawanie twarzy metodą PCA Michał Bereta www.michalbereta.pl 1. Testowanie statystycznej istotności różnic między jakością klasyfikatorów Wiemy, że możemy porównywad klasyfikatory np. za pomocą kroswalidacji.
Lecture 18 Review for Exam 1
 Spring, 2019 ME 323 Mechanics of Materials Lecture 18 Review for Exam 1 Reading assignment: HW1-HW5 News: Ready for the exam? Instructor: Prof. Marcial Gonzalez Announcements Exam 1 - Wednesday February
Spring, 2019 ME 323 Mechanics of Materials Lecture 18 Review for Exam 1 Reading assignment: HW1-HW5 News: Ready for the exam? Instructor: Prof. Marcial Gonzalez Announcements Exam 1 - Wednesday February
Rachunek lambda, zima
 Rachunek lambda, zima 2015-16 Wykład 2 12 października 2015 Tydzień temu: Własność Churcha-Rossera (CR) Jeśli a b i a c, to istnieje takie d, że b d i c d. Tydzień temu: Własność Churcha-Rossera (CR) Jeśli
Rachunek lambda, zima 2015-16 Wykład 2 12 października 2015 Tydzień temu: Własność Churcha-Rossera (CR) Jeśli a b i a c, to istnieje takie d, że b d i c d. Tydzień temu: Własność Churcha-Rossera (CR) Jeśli
SSW1.1, HFW Fry #20, Zeno #25 Benchmark: Qtr.1. Fry #65, Zeno #67. like
 SSW1.1, HFW Fry #20, Zeno #25 Benchmark: Qtr.1 I SSW1.1, HFW Fry #65, Zeno #67 Benchmark: Qtr.1 like SSW1.2, HFW Fry #47, Zeno #59 Benchmark: Qtr.1 do SSW1.2, HFW Fry #5, Zeno #4 Benchmark: Qtr.1 to SSW1.2,
SSW1.1, HFW Fry #20, Zeno #25 Benchmark: Qtr.1 I SSW1.1, HFW Fry #65, Zeno #67 Benchmark: Qtr.1 like SSW1.2, HFW Fry #47, Zeno #59 Benchmark: Qtr.1 do SSW1.2, HFW Fry #5, Zeno #4 Benchmark: Qtr.1 to SSW1.2,
ver grawitacja
 ver-7.11.11 grawitacja początki Galileusz 1564-164 układ słoneczny http://www.arachnoid.com/gravitation/small.html prawa Keplera 1. orbity planet krążących wokół słońca są elipsami ze słońcem w ognisku
ver-7.11.11 grawitacja początki Galileusz 1564-164 układ słoneczny http://www.arachnoid.com/gravitation/small.html prawa Keplera 1. orbity planet krążących wokół słońca są elipsami ze słońcem w ognisku
y = The Chain Rule Show all work. No calculator unless otherwise stated. If asked to Explain your answer, write in complete sentences.
 The Chain Rule Show all work. No calculator unless otherwise stated. If asked to Eplain your answer, write in complete sentences. 1. Find the derivative of the functions y 7 (b) (a) ( ) y t 1 + t 1 (c)
The Chain Rule Show all work. No calculator unless otherwise stated. If asked to Eplain your answer, write in complete sentences. 1. Find the derivative of the functions y 7 (b) (a) ( ) y t 1 + t 1 (c)
Zakopane, plan miasta: Skala ok. 1: = City map (Polish Edition)
 Zakopane, plan miasta: Skala ok. 1:15 000 = City map (Polish Edition) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Zakopane, plan miasta: Skala ok. 1:15 000 = City map (Polish Edition) Zakopane,
Zakopane, plan miasta: Skala ok. 1:15 000 = City map (Polish Edition) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Zakopane, plan miasta: Skala ok. 1:15 000 = City map (Polish Edition) Zakopane,
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition)
 Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
Proposal of thesis topic for mgr in. (MSE) programme in Telecommunications and Computer Science
 Proposal of thesis topic for mgr in (MSE) programme 1 Topic: Monte Carlo Method used for a prognosis of a selected technological process 2 Supervisor: Dr in Małgorzata Langer 3 Auxiliary supervisor: 4
Proposal of thesis topic for mgr in (MSE) programme 1 Topic: Monte Carlo Method used for a prognosis of a selected technological process 2 Supervisor: Dr in Małgorzata Langer 3 Auxiliary supervisor: 4
Stability of Tikhonov Regularization Class 07, March 2003 Alex Rakhlin
 Stability of Tikhonov Regularization 9.520 Class 07, March 2003 Alex Rakhlin Plan Review of Stability Bounds Stability of Tikhonov Regularization Algorithms Uniform Stability Review notation: S = {z 1,...,
Stability of Tikhonov Regularization 9.520 Class 07, March 2003 Alex Rakhlin Plan Review of Stability Bounds Stability of Tikhonov Regularization Algorithms Uniform Stability Review notation: S = {z 1,...,
DUAL SIMILARITY OF VOLTAGE TO CURRENT AND CURRENT TO VOLTAGE TRANSFER FUNCTION OF HYBRID ACTIVE TWO- PORTS WITH CONVERSION
 ELEKTRYKA 0 Zeszyt (9) Rok LX Andrzej KUKIEŁKA Politechnika Śląska w Gliwicach DUAL SIMILARITY OF VOLTAGE TO CURRENT AND CURRENT TO VOLTAGE TRANSFER FUNCTION OF HYBRID ACTIVE TWO- PORTS WITH CONVERSION
ELEKTRYKA 0 Zeszyt (9) Rok LX Andrzej KUKIEŁKA Politechnika Śląska w Gliwicach DUAL SIMILARITY OF VOLTAGE TO CURRENT AND CURRENT TO VOLTAGE TRANSFER FUNCTION OF HYBRID ACTIVE TWO- PORTS WITH CONVERSION
Copyright 2013 Zbigniew Płotnicki. Licence allows only a publication on arxiv.org and vixra.org. Beside it all rights reserved.
 Copyright 2013 Zbigniew Płotnicki Licence allows only a publication on arxiv.org and vixra.org. Beside it all rights reserved. Very simple proof that theory of special relativity is false Author: Zbigniew
Copyright 2013 Zbigniew Płotnicki Licence allows only a publication on arxiv.org and vixra.org. Beside it all rights reserved. Very simple proof that theory of special relativity is false Author: Zbigniew
Analysis of Movie Profitability STAT 469 IN CLASS ANALYSIS #2
 Analysis of Movie Profitability STAT 469 IN CLASS ANALYSIS #2 aaaklnictzzjb9tgfmcnadpg7oy0lxa9edva9kkapdarhyk2k7gourinlwsweyzikuyiigvyleiv/cv767fpf/5crc1xt9va5mx7w3m/ecuqw1kuztpx/rl3/70h73/w4cog9dhhn3z62d6jzy+yzj766txpoir9nzszisjynetqr+rvlfvyoozu5xbybpsxb1wahul8phczdt2v4zgchb7uecwphlyigrgkjcyiflfyci0kxnmr4z6kw0jsokvot8isntpa3gbknlcufiv/h+hh+eur4fomd417rvtfjoit5pfju6yxiab2fmwk0y/feuybobqk+axnke8xzjjhfyd8kkpl9zdoddkazd5j6bzpemjb64smjb6vb4xmehysu08lsrszopxftlzee130jcb0zjxy7r5wa2f1s2off2+dyatrughnrtpkuprlcpu55zlxpss/yqe2eamjkcf0jye8w8yas0paf6t0t2i9stmcua+inbi2rt01tz22tubbqwidypvgz6piynkpobirkxgu54ibzoti4pkw2i5ow9lnuaoabhuxfxqhvnrj6w15tb3furnbm+scyxobjhr5pmj5j/w5ix9wsa2tlwx9alpshlunzjgnrwvqbpwzjl9wes+ptyn+ypy/jgskavtl8j0hz1djdhzwtpjbbvpr1zj7jpg6ve7zxfngj75zee0vmp9qm2uvgu/9zdofq6r+g8l4xctvo+v+xdrfr8oxiwutycu0qgyf8icuyvp/sixfi9zxe11vp6mrjjovpmxm6acrtbia+wjr9bevlgjwlz5xd3rfna9g06qytaoofk8olxbxc7xby2evqjmmk6pjvvzxmpbnct6+036xp5vdbrnbdqph8brlfn/n/khnfumhf6z1v7h/80yieukkd5j0un82t9mynxzmk0s/bzn4tacdziszdhwrl8x5ako8qp1n1zn0k6w2em0km9zj1i4yt1pt3xiprw85jmc2m1ut2geum6y6es2fwx6c+wlrpykblopbuj5nnr2byygfy5opllv4+jmm7s6u+tvhywbnb0kv2lt5th4xipmiij+y1toiyo7bo0d+vzvovjkp6aoejsubhj3qrp3fjd/m23pay8h218ibvx3nicofvd1xi86+kh6nb/b+hgsjp5+qwpurzlir15np66vmdehh6tyazdm1k/5ejtuvurgcqux6yc+qw/sbsaj7lkt4x9qmtp7euk6zbdedyuzu6ptsu2eeu3rxcz06uf6g8wyuveznhkbzynajbb7r7cbmla+jbtrst0ow2v6ntkwv8svnwqnu5pa3oxfeexf93739p93chq/fv+jr8r0d9brhpcxr2w88bvqbr41j6wvrb+u5dzjpvx+veoaxwptzp/8cen+xbg==
Analysis of Movie Profitability STAT 469 IN CLASS ANALYSIS #2 aaaklnictzzjb9tgfmcnadpg7oy0lxa9edva9kkapdarhyk2k7gourinlwsweyzikuyiigvyleiv/cv767fpf/5crc1xt9va5mx7w3m/ecuqw1kuztpx/rl3/70h73/w4cog9dhhn3z62d6jzy+yzj766txpoir9nzszisjynetqr+rvlfvyoozu5xbybpsxb1wahul8phczdt2v4zgchb7uecwphlyigrgkjcyiflfyci0kxnmr4z6kw0jsokvot8isntpa3gbknlcufiv/h+hh+eur4fomd417rvtfjoit5pfju6yxiab2fmwk0y/feuybobqk+axnke8xzjjhfyd8kkpl9zdoddkazd5j6bzpemjb64smjb6vb4xmehysu08lsrszopxftlzee130jcb0zjxy7r5wa2f1s2off2+dyatrughnrtpkuprlcpu55zlxpss/yqe2eamjkcf0jye8w8yas0paf6t0t2i9stmcua+inbi2rt01tz22tubbqwidypvgz6piynkpobirkxgu54ibzoti4pkw2i5ow9lnuaoabhuxfxqhvnrj6w15tb3furnbm+scyxobjhr5pmj5j/w5ix9wsa2tlwx9alpshlunzjgnrwvqbpwzjl9wes+ptyn+ypy/jgskavtl8j0hz1djdhzwtpjbbvpr1zj7jpg6ve7zxfngj75zee0vmp9qm2uvgu/9zdofq6r+g8l4xctvo+v+xdrfr8oxiwutycu0qgyf8icuyvp/sixfi9zxe11vp6mrjjovpmxm6acrtbia+wjr9bevlgjwlz5xd3rfna9g06qytaoofk8olxbxc7xby2evqjmmk6pjvvzxmpbnct6+036xp5vdbrnbdqph8brlfn/n/khnfumhf6z1v7h/80yieukkd5j0un82t9mynxzmk0s/bzn4tacdziszdhwrl8x5ako8qp1n1zn0k6w2em0km9zj1i4yt1pt3xiprw85jmc2m1ut2geum6y6es2fwx6c+wlrpykblopbuj5nnr2byygfy5opllv4+jmm7s6u+tvhywbnb0kv2lt5th4xipmiij+y1toiyo7bo0d+vzvovjkp6aoejsubhj3qrp3fjd/m23pay8h218ibvx3nicofvd1xi86+kh6nb/b+hgsjp5+qwpurzlir15np66vmdehh6tyazdm1k/5ejtuvurgcqux6yc+qw/sbsaj7lkt4x9qmtp7euk6zbdedyuzu6ptsu2eeu3rxcz06uf6g8wyuveznhkbzynajbb7r7cbmla+jbtrst0ow2v6ntkwv8svnwqnu5pa3oxfeexf93739p93chq/fv+jr8r0d9brhpcxr2w88bvqbr41j6wvrb+u5dzjpvx+veoaxwptzp/8cen+xbg==
Knovel Math: Jakość produktu
 Knovel Math: Jakość produktu Knovel jest agregatorem materiałów pełnotekstowych dostępnych w formacie PDF i interaktywnym. Narzędzia interaktywne Knovel nie są stworzone wokół specjalnych algorytmów wymagających
Knovel Math: Jakość produktu Knovel jest agregatorem materiałów pełnotekstowych dostępnych w formacie PDF i interaktywnym. Narzędzia interaktywne Knovel nie są stworzone wokół specjalnych algorytmów wymagających
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture11. Random Projections & Canonical Correlation Analysis
 Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture11 5 Random Projections & Canonical Correlation Analysis The Tall, THE FAT AND THE UGLY n X d The Tall, THE FAT AND THE UGLY d X > n X d n = n d d The
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture11 5 Random Projections & Canonical Correlation Analysis The Tall, THE FAT AND THE UGLY n X d The Tall, THE FAT AND THE UGLY d X > n X d n = n d d The
OpenPoland.net API Documentation
 OpenPoland.net API Documentation Release 1.0 Michał Gryczka July 11, 2014 Contents 1 REST API tokens: 3 1.1 How to get a token............................................ 3 2 REST API : search for assets
OpenPoland.net API Documentation Release 1.0 Michał Gryczka July 11, 2014 Contents 1 REST API tokens: 3 1.1 How to get a token............................................ 3 2 REST API : search for assets
Tychy, plan miasta: Skala 1: (Polish Edition)
 Tychy, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000 (Polish Edition) Poland) Przedsiebiorstwo Geodezyjno-Kartograficzne (Katowice Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Tychy, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000
Tychy, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000 (Polish Edition) Poland) Przedsiebiorstwo Geodezyjno-Kartograficzne (Katowice Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Tychy, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000
Towards Stability Analysis of Data Transport Mechanisms: a Fluid Model and an Application
 Towards Stability Analysis of Data Transport Mechanisms: a Fluid Model and an Application Gayane Vardoyan *, C. V. Hollot, Don Towsley* * College of Information and Computer Sciences, Department of Electrical
Towards Stability Analysis of Data Transport Mechanisms: a Fluid Model and an Application Gayane Vardoyan *, C. V. Hollot, Don Towsley* * College of Information and Computer Sciences, Department of Electrical
MaPlan Sp. z O.O. Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically
 Mierzeja Wislana, mapa turystyczna 1:50 000: Mikoszewo, Jantar, Stegna, Sztutowo, Katy Rybackie, Przebrno, Krynica Morska, Piaski, Frombork =... = Carte touristique (Polish Edition) MaPlan Sp. z O.O Click
Mierzeja Wislana, mapa turystyczna 1:50 000: Mikoszewo, Jantar, Stegna, Sztutowo, Katy Rybackie, Przebrno, Krynica Morska, Piaski, Frombork =... = Carte touristique (Polish Edition) MaPlan Sp. z O.O Click
ARNOLD. EDUKACJA KULTURYSTY (POLSKA WERSJA JEZYKOWA) BY DOUGLAS KENT HALL
 Read Online and Download Ebook ARNOLD. EDUKACJA KULTURYSTY (POLSKA WERSJA JEZYKOWA) BY DOUGLAS KENT HALL DOWNLOAD EBOOK : ARNOLD. EDUKACJA KULTURYSTY (POLSKA WERSJA Click link bellow and free register
Read Online and Download Ebook ARNOLD. EDUKACJA KULTURYSTY (POLSKA WERSJA JEZYKOWA) BY DOUGLAS KENT HALL DOWNLOAD EBOOK : ARNOLD. EDUKACJA KULTURYSTY (POLSKA WERSJA Click link bellow and free register
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 24. Differential Privacy and Re-useable Holdout
 Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 24 Differential Privacy and Re-useable Holdout Defining Privacy Defining Privacy Dataset + Defining Privacy Dataset + Learning Algorithm Distribution
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 24 Differential Privacy and Re-useable Holdout Defining Privacy Defining Privacy Dataset + Defining Privacy Dataset + Learning Algorithm Distribution
HOW MASSIVE ARE PROTOPLANETARY/ PLANET HOSTING/PLANET FORMING DISCS?
 GREAT BARRIERS IN PLANET FORMATION, PALM COVE 26/07/2019 HOW MASSIVE ARE PROTOPLANETARY/ PLANET HOSTING/PLANET FORMING DISCS? CAN ALL THESE STRUCTURES TELL US SOMETHING ABOUT THE (GAS) DISC MASS? BENEDETTA
GREAT BARRIERS IN PLANET FORMATION, PALM COVE 26/07/2019 HOW MASSIVE ARE PROTOPLANETARY/ PLANET HOSTING/PLANET FORMING DISCS? CAN ALL THESE STRUCTURES TELL US SOMETHING ABOUT THE (GAS) DISC MASS? BENEDETTA
Eksperymenty reaktorowe drugiej generacji wyznaczenie ϑ 13
 Eksperymenty reaktorowe drugiej generacji wyznaczenie ϑ 13 v Przypomnienie wyniku eksperymentu KamLAND - weryfikującego oscylacje neutrin słonecznych v Formuły na prawdopodobieństwo disappearance antyneutrin
Eksperymenty reaktorowe drugiej generacji wyznaczenie ϑ 13 v Przypomnienie wyniku eksperymentu KamLAND - weryfikującego oscylacje neutrin słonecznych v Formuły na prawdopodobieństwo disappearance antyneutrin
Karpacz, plan miasta 1:10 000: Panorama Karkonoszy, mapa szlakow turystycznych (Polish Edition)
 Karpacz, plan miasta 1:10 000: Panorama Karkonoszy, mapa szlakow turystycznych (Polish Edition) J Krupski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Karpacz, plan miasta 1:10 000: Panorama
Karpacz, plan miasta 1:10 000: Panorama Karkonoszy, mapa szlakow turystycznych (Polish Edition) J Krupski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Karpacz, plan miasta 1:10 000: Panorama
RESONANCE OF TORSIONAL VIBRATION OF SHAFTS COUPLED BY MECHANISMS
 SCIENTIFIC BULLETIN OF LOZ TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY Nr 78, TEXTILES 55, 997 ZESZYTY NAUKOWE POLITECHNIKI ŁÓZKIEJ Nr 78, WŁÓKIENNICTWO z. 55, 997 Pages: 8- http://bhp-k4.p.loz.pl/ JERZY ZAJACZKOWSKI Loz Technical
SCIENTIFIC BULLETIN OF LOZ TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY Nr 78, TEXTILES 55, 997 ZESZYTY NAUKOWE POLITECHNIKI ŁÓZKIEJ Nr 78, WŁÓKIENNICTWO z. 55, 997 Pages: 8- http://bhp-k4.p.loz.pl/ JERZY ZAJACZKOWSKI Loz Technical
Linear Classification and Logistic Regression. Pascal Fua IC-CVLab
 Linear Classification and Logistic Regression Pascal Fua IC-CVLab 1 aaagcxicbdtdbtmwfafwdgxlhk8orha31ibqycvkdgpshdqxtwotng2pxtvqujmok1qlky5xllzrnobbediegwcap4votk2kqkf+/y/tnphdschtadu/giv3vtea99cfma8fpx7ytlxx7ckns4sylo3doom7jguhj1hxchmy/irhrlgh67lxb5x3blis8jjqynmedqujiu5zsqqagrx+yjcfpcrydusshmzeluzsg7tttiew5khhcuzm5rv0gn1unw6zl3gbzlpr3liwncyr6aaqinx4wnc/rpg6ix5szd86agoftuu0g/krjxdarph62enthdey3zn/+mi5zknou2ap+tclvhob9sxhwvhaqketnde7geqjp21zvjsfrcnkfhtejoz23vq97elxjlpbtmxpl6qxtl1sgfv1ptpy/yq9mgacrzkgje0hjj2rq7vtywnishnnkzsqekucnlblrarlh8x8szxolrrxkb8n6o4kmo/e7siisnozcfvsedlol60a/j8nmul/gby8mmssrfr2it8lkyxr9dirxxngzthtbaejv
Linear Classification and Logistic Regression Pascal Fua IC-CVLab 1 aaagcxicbdtdbtmwfafwdgxlhk8orha31ibqycvkdgpshdqxtwotng2pxtvqujmok1qlky5xllzrnobbediegwcap4votk2kqkf+/y/tnphdschtadu/giv3vtea99cfma8fpx7ytlxx7ckns4sylo3doom7jguhj1hxchmy/irhrlgh67lxb5x3blis8jjqynmedqujiu5zsqqagrx+yjcfpcrydusshmzeluzsg7tttiew5khhcuzm5rv0gn1unw6zl3gbzlpr3liwncyr6aaqinx4wnc/rpg6ix5szd86agoftuu0g/krjxdarph62enthdey3zn/+mi5zknou2ap+tclvhob9sxhwvhaqketnde7geqjp21zvjsfrcnkfhtejoz23vq97elxjlpbtmxpl6qxtl1sgfv1ptpy/yq9mgacrzkgje0hjj2rq7vtywnishnnkzsqekucnlblrarlh8x8szxolrrxkb8n6o4kmo/e7siisnozcfvsedlol60a/j8nmul/gby8mmssrfr2it8lkyxr9dirxxngzthtbaejv
deep learning for NLP (5 lectures)
 TTIC 31210: Advanced Natural Language Processing Kevin Gimpel Spring 2019 Lecture 6: Finish Transformers; Sequence- to- Sequence Modeling and AJenKon 1 Roadmap intro (1 lecture) deep learning for NLP (5
TTIC 31210: Advanced Natural Language Processing Kevin Gimpel Spring 2019 Lecture 6: Finish Transformers; Sequence- to- Sequence Modeling and AJenKon 1 Roadmap intro (1 lecture) deep learning for NLP (5
General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS 4037/12
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level www.xtremepapers.com *6378719168* ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS 4037/12 Paper 1 May/June 2013 2 hours Candidates
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level www.xtremepapers.com *6378719168* ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS 4037/12 Paper 1 May/June 2013 2 hours Candidates
Stargard Szczecinski i okolice (Polish Edition)
 Stargard Szczecinski i okolice (Polish Edition) Janusz Leszek Jurkiewicz Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Stargard Szczecinski i okolice (Polish Edition) Janusz Leszek Jurkiewicz
Stargard Szczecinski i okolice (Polish Edition) Janusz Leszek Jurkiewicz Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Stargard Szczecinski i okolice (Polish Edition) Janusz Leszek Jurkiewicz
EXAMPLES OF CABRI GEOMETRE II APPLICATION IN GEOMETRIC SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH
 Anna BŁACH Centre of Geometry and Engineering Graphics Silesian University of Technology in Gliwice EXAMPLES OF CABRI GEOMETRE II APPLICATION IN GEOMETRIC SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH Introduction Computer techniques
Anna BŁACH Centre of Geometry and Engineering Graphics Silesian University of Technology in Gliwice EXAMPLES OF CABRI GEOMETRE II APPLICATION IN GEOMETRIC SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH Introduction Computer techniques
Zmiany techniczne wprowadzone w wersji Comarch ERP Altum
 Zmiany techniczne wprowadzone w wersji 2018.2 Copyright 2016 COMARCH SA Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone Nieautoryzowane rozpowszechnianie całości lub fragmentu niniejszej publikacji w jakiejkolwiek postaci
Zmiany techniczne wprowadzone w wersji 2018.2 Copyright 2016 COMARCH SA Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone Nieautoryzowane rozpowszechnianie całości lub fragmentu niniejszej publikacji w jakiejkolwiek postaci
Miedzy legenda a historia: Szlakiem piastowskim z Poznania do Gniezna (Biblioteka Kroniki Wielkopolski) (Polish Edition)
 Miedzy legenda a historia: Szlakiem piastowskim z Poznania do Gniezna (Biblioteka Kroniki Wielkopolski) (Polish Edition) Piotr Maluskiewicz Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Miedzy
Miedzy legenda a historia: Szlakiem piastowskim z Poznania do Gniezna (Biblioteka Kroniki Wielkopolski) (Polish Edition) Piotr Maluskiewicz Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Miedzy
Sargent Opens Sonairte Farmers' Market
 Sargent Opens Sonairte Farmers' Market 31 March, 2008 1V8VIZSV7EVKIRX8(1MRMWXIVSJ7XEXIEXXLI(ITEVXQIRXSJ%KVMGYPXYVI *MWLIVMIWERH*SSHTIVJSVQIHXLISJJMGMEPSTIRMRKSJXLI7SREMVXI*EVQIVW 1EVOIXMR0E]XS[R'S1IEXL
Sargent Opens Sonairte Farmers' Market 31 March, 2008 1V8VIZSV7EVKIRX8(1MRMWXIVSJ7XEXIEXXLI(ITEVXQIRXSJ%KVMGYPXYVI *MWLIVMIWERH*SSHTIVJSVQIHXLISJJMGMEPSTIRMRKSJXLI7SREMVXI*EVQIVW 1EVOIXMR0E]XS[R'S1IEXL
Physics-Based Animation 4 Mass-spring systems
 COL865: Special Topics in Computer Applications Physics-Based Animation 4 Mass-spring systems Particle systems Consider n point masses in R 3 ith particle has mass m i, position x i, velocity v i External
COL865: Special Topics in Computer Applications Physics-Based Animation 4 Mass-spring systems Particle systems Consider n point masses in R 3 ith particle has mass m i, position x i, velocity v i External
Strangeness in nuclei and neutron stars: many-body forces and the hyperon puzzle
 Strangeness in nuclei and neutron stars: many-body forces and the hyperon puzzle Diego Lonardoni FRIB Theory Fellow In collaboration with: S. Gandolfi, LAL J. A. Carlson, LAL A. Lovato, AL & IF F. Pederiva,
Strangeness in nuclei and neutron stars: many-body forces and the hyperon puzzle Diego Lonardoni FRIB Theory Fellow In collaboration with: S. Gandolfi, LAL J. A. Carlson, LAL A. Lovato, AL & IF F. Pederiva,
POLITECHNIKA ŚLĄSKA INSTYTUT AUTOMATYKI ZAKŁAD SYSTEMÓW POMIAROWYCH
 POLITECHNIKA ŚLĄSKA INSTYTUT AUTOMATYKI ZAKŁAD SYSTEMÓW POMIAROWYCH Gliwice, wrzesień 2005 Pomiar napięcia przemiennego Cel ćwiczenia Celem ćwiczenia jest zbadanie dokładności woltomierza cyfrowego dla
POLITECHNIKA ŚLĄSKA INSTYTUT AUTOMATYKI ZAKŁAD SYSTEMÓW POMIAROWYCH Gliwice, wrzesień 2005 Pomiar napięcia przemiennego Cel ćwiczenia Celem ćwiczenia jest zbadanie dokładności woltomierza cyfrowego dla
Previously on CSCI 4622
 More Naïve Bayes aaace3icbvfba9rafj7ew423vr998obg2gpzkojyh4rcx3ys4lafzbjmjifdototmhoilml+hf/mn3+kl+jkdwtr64gbj+8yl2/ywklhsfircg/dvnp33s796mhdr4+fdj4+o3fvywvorkuqe5zzh0oanjakhwe1ra5zhaf5xvgvn35f62rlvtcyxpnm50awundy1hzwi46jbmgprbtrrvidrg4jre4g07kak+picee6xfgiwvfaltorirucni64eeigkqhpegbwaxglabftpyq4gjbls/hw2ci7tr2xj5ddfmfzwtazj6ubmyddgchbzpf88dmrktfonct6vazputos5zakunhfweow5ukcn+puq8m1ulm7kq+d154pokysx4zgxw4nwq6dw+rcozwnhbuu9et/tgld5cgslazuci1yh1q2ynca/u9ais0kukspulds3xxegvtyfycu8iwk1598e0z2xx/g6ef94ehbpo0d9ok9yiowsvfskh1ix2zcbpsdvaxgww7wj4zdn+he2hogm8xz9s+e7/4cuf/ata==
More Naïve Bayes aaace3icbvfba9rafj7ew423vr998obg2gpzkojyh4rcx3ys4lafzbjmjifdototmhoilml+hf/mn3+kl+jkdwtr64gbj+8yl2/ywklhsfircg/dvnp33s796mhdr4+fdj4+o3fvywvorkuqe5zzh0oanjakhwe1ra5zhaf5xvgvn35f62rlvtcyxpnm50awundy1hzwi46jbmgprbtrrvidrg4jre4g07kak+picee6xfgiwvfaltorirucni64eeigkqhpegbwaxglabftpyq4gjbls/hw2ci7tr2xj5ddfmfzwtazj6ubmyddgchbzpf88dmrktfonct6vazputos5zakunhfweow5ukcn+puq8m1ulm7kq+d154pokysx4zgxw4nwq6dw+rcozwnhbuu9et/tgld5cgslazuci1yh1q2ynca/u9ais0kukspulds3xxegvtyfycu8iwk1598e0z2xx/g6ef94ehbpo0d9ok9yiowsvfskh1ix2zcbpsdvaxgww7wj4zdn+he2hogm8xz9s+e7/4cuf/ata==
tum.de/fall2018/ in2357
 https://piazza.com/ tum.de/fall2018/ in2357 Prof. Daniel Cremers From to Classification Categories of Learning (Rep.) Learning Unsupervised Learning clustering, density estimation Supervised Learning learning
https://piazza.com/ tum.de/fall2018/ in2357 Prof. Daniel Cremers From to Classification Categories of Learning (Rep.) Learning Unsupervised Learning clustering, density estimation Supervised Learning learning
Inverse problems - Introduction - Probabilistic approach
 Inverse problems - Introduction - Probabilistic approach Wojciech Dȩbski Instytut Geofizyki PAN debski@igf.edu.pl Wydział Fizyki UW, 13.10.2004 Wydział Fizyki UW Warszawa, 13.10.2004 (1) Plan of the talk
Inverse problems - Introduction - Probabilistic approach Wojciech Dȩbski Instytut Geofizyki PAN debski@igf.edu.pl Wydział Fizyki UW, 13.10.2004 Wydział Fizyki UW Warszawa, 13.10.2004 (1) Plan of the talk
Model standardowy i stabilność próżni
 Model standardowy i stabilność próżni Marek Lewicki Instytut Fizyki teoretycznej, Wydzia l Fizyki, Uniwersytet Warszawski Sympozjum Doktoranckie Warszawa-Fizyka-Kraków, 4 Marca 2016, Kraków Na podstawie:
Model standardowy i stabilność próżni Marek Lewicki Instytut Fizyki teoretycznej, Wydzia l Fizyki, Uniwersytet Warszawski Sympozjum Doktoranckie Warszawa-Fizyka-Kraków, 4 Marca 2016, Kraków Na podstawie:
Fig 5 Spectrograms of the original signal (top) extracted shaft-related GAD components (middle) and
 Fig 4 Measured vibration signal (top). Blue original signal. Red component related to periodic excitation of resonances and noise. Green component related. Rotational speed profile used for experiment
Fig 4 Measured vibration signal (top). Blue original signal. Red component related to periodic excitation of resonances and noise. Green component related. Rotational speed profile used for experiment
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition)
 Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
Title: On the curl of singular completely continous vector fields in Banach spaces
 Title: On the curl of singular completely continous vector fields in Banach spaces Author: Adam Bielecki, Tadeusz Dłotko Citation style: Bielecki Adam, Dłotko Tadeusz. (1973). On the curl of singular completely
Title: On the curl of singular completely continous vector fields in Banach spaces Author: Adam Bielecki, Tadeusz Dłotko Citation style: Bielecki Adam, Dłotko Tadeusz. (1973). On the curl of singular completely
Katowice, plan miasta: Skala 1: = City map = Stadtplan (Polish Edition)
 Katowice, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000 = City map = Stadtplan (Polish Edition) Polskie Przedsiebiorstwo Wydawnictw Kartograficznych im. Eugeniusza Romera Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically
Katowice, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000 = City map = Stadtplan (Polish Edition) Polskie Przedsiebiorstwo Wydawnictw Kartograficznych im. Eugeniusza Romera Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically
Camspot 4.4 Camspot 4.5
 User manual (addition) Dodatek do instrukcji obsługi Camspot 4.4 Camspot 4.5 1. WiFi configuration 2. Configuration of sending pictures to e-mail/ftp after motion detection 1. Konfiguracja WiFi 2. Konfiguracja
User manual (addition) Dodatek do instrukcji obsługi Camspot 4.4 Camspot 4.5 1. WiFi configuration 2. Configuration of sending pictures to e-mail/ftp after motion detection 1. Konfiguracja WiFi 2. Konfiguracja
Jak działa grawitacja?
 Nazwa projektu: Kreatywni i innowacyjni uczniowie konkurencyjni na rynku pracy DZIAŁANIE 3.2 EDUKACJA OGÓLNA PODDZIAŁANIE 3.2.1 JAKOŚĆ EDUKACJI OGÓLNEJ Projekt współfinansowany przez Unię Europejską w
Nazwa projektu: Kreatywni i innowacyjni uczniowie konkurencyjni na rynku pracy DZIAŁANIE 3.2 EDUKACJA OGÓLNA PODDZIAŁANIE 3.2.1 JAKOŚĆ EDUKACJI OGÓLNEJ Projekt współfinansowany przez Unię Europejską w
Walyeldeen Godah Małgorzata Szelachowska Jan Kryński. Instytut Geodezji i Kartografii (IGiK), Warszawa Centrum Geodezji i Geodynamiki
 Porównanie globalnych modeli geopotencjału opracowanych na podstawie danych z misji GRACE oraz GOCE/GRACE z przyspieszeniem siły ciężkości pomierzonym w Obserwatorium Geodezyjno-Geofizycznym Borowa Góra
Porównanie globalnych modeli geopotencjału opracowanych na podstawie danych z misji GRACE oraz GOCE/GRACE z przyspieszeniem siły ciężkości pomierzonym w Obserwatorium Geodezyjno-Geofizycznym Borowa Góra
Medical electronics part 10 Physiological transducers
 Medical electronics part 10 Prezentacja multimedialna współfinansowana przez Unię Europejską w ramach Europejskiego Funduszu Społecznego w projekcie pt. Innowacyjna dydaktyka bez ograniczeń - zintegrowany
Medical electronics part 10 Prezentacja multimedialna współfinansowana przez Unię Europejską w ramach Europejskiego Funduszu Społecznego w projekcie pt. Innowacyjna dydaktyka bez ograniczeń - zintegrowany
DODATKOWE ĆWICZENIA EGZAMINACYJNE
 I.1. X Have a nice day! Y a) Good idea b) See you soon c) The same to you I.2. X: This is my new computer. Y: Wow! Can I have a look at the Internet? X: a) Thank you b) Go ahead c) Let me try I.3. X: What
I.1. X Have a nice day! Y a) Good idea b) See you soon c) The same to you I.2. X: This is my new computer. Y: Wow! Can I have a look at the Internet? X: a) Thank you b) Go ahead c) Let me try I.3. X: What
Electromagnetism Q =) E I =) B E B. ! Q! I B t =) E E t =) B. 05/06/2018 Physics 0
 lectromagnetism lectromagnetic interaction is one of four fundamental interactions in Nature. lectromagnetism is the theory of electromagnetic interactions or of electromagnetic forces. lectric charge
lectromagnetism lectromagnetic interaction is one of four fundamental interactions in Nature. lectromagnetism is the theory of electromagnetic interactions or of electromagnetic forces. lectric charge
ERASMUS + : Trail of extinct and active volcanoes, earthquakes through Europe. SURVEY TO STUDENTS.
 ERASMUS + : Trail of extinct and active volcanoes, earthquakes through Europe. SURVEY TO STUDENTS. Strona 1 1. Please give one answer. I am: Students involved in project 69% 18 Student not involved in
ERASMUS + : Trail of extinct and active volcanoes, earthquakes through Europe. SURVEY TO STUDENTS. Strona 1 1. Please give one answer. I am: Students involved in project 69% 18 Student not involved in
TTIC 31210: Advanced Natural Language Processing. Kevin Gimpel Spring Lecture 9: Inference in Structured Prediction
 TTIC 31210: Advanced Natural Language Processing Kevin Gimpel Spring 2019 Lecture 9: Inference in Structured Prediction 1 intro (1 lecture) Roadmap deep learning for NLP (5 lectures) structured prediction
TTIC 31210: Advanced Natural Language Processing Kevin Gimpel Spring 2019 Lecture 9: Inference in Structured Prediction 1 intro (1 lecture) Roadmap deep learning for NLP (5 lectures) structured prediction
Nonlinear data assimilation for ocean applications
 Nonlinear data assimilation for ocean applications Peter Jan van Leeuwen, Manuel Pulido, Jacob Skauvold, Javier Amezcua, Polly Smith, Met Ades, Mengbin Zhu Comparing observations and models Ensure they
Nonlinear data assimilation for ocean applications Peter Jan van Leeuwen, Manuel Pulido, Jacob Skauvold, Javier Amezcua, Polly Smith, Met Ades, Mengbin Zhu Comparing observations and models Ensure they
Some Linear Algebra. Vectors operations = =(,, ) =( 1 + 2, 1 + 2, ) λ =(λ,λ,λ ) Addition. Scalar multiplication.
 Basic Geometry Vectors operations Some Linear Algebra Addition + 2 =( 1 + 2, 1 + 2, 1 + 2 ) =(,, ) + Scalar multiplication λ =(λ,λ,λ ) Norm = 2 + 2 + 2 2 Scalar Product Commutative Linear Orthogonally
Basic Geometry Vectors operations Some Linear Algebra Addition + 2 =( 1 + 2, 1 + 2, 1 + 2 ) =(,, ) + Scalar multiplication λ =(λ,λ,λ ) Norm = 2 + 2 + 2 2 Scalar Product Commutative Linear Orthogonally
Cracow University of Economics Poland
 Cracow University of Economics Poland Sources of Real GDP per Capita Growth: Polish Regional-Macroeconomic Dimensions 2000-2005 - Keynote Speech - Presented by: Dr. David Clowes The Growth Research Unit,
Cracow University of Economics Poland Sources of Real GDP per Capita Growth: Polish Regional-Macroeconomic Dimensions 2000-2005 - Keynote Speech - Presented by: Dr. David Clowes The Growth Research Unit,
 www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
Karpacz, plan miasta 1:10 000: Panorama Karkonoszy, mapa szlakow turystycznych (Polish Edition)
 Karpacz, plan miasta 1:10 000: Panorama Karkonoszy, mapa szlakow turystycznych (Polish Edition) J Krupski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Karpacz, plan miasta 1:10 000: Panorama
Karpacz, plan miasta 1:10 000: Panorama Karkonoszy, mapa szlakow turystycznych (Polish Edition) J Krupski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Karpacz, plan miasta 1:10 000: Panorama
Symmetry and Geometry of Generalized Higgs Sectors
 Symmetry and Geometry of Generalized Higgs Sectors Ryo Nagai Tohoku University in collaboration with M. Tanabashi (Nagoya U.), Y. Uchida (Nagoya U.), and K. Tsumura (Kyoto U.) PPP2018 @ YITP, Aug. 6-10,
Symmetry and Geometry of Generalized Higgs Sectors Ryo Nagai Tohoku University in collaboration with M. Tanabashi (Nagoya U.), Y. Uchida (Nagoya U.), and K. Tsumura (Kyoto U.) PPP2018 @ YITP, Aug. 6-10,
Egzamin maturalny z języka angielskiego na poziomie dwujęzycznym Rozmowa wstępna (wyłącznie dla egzaminującego)
 112 Informator o egzaminie maturalnym z języka angielskiego od roku szkolnego 2014/2015 2.6.4. Część ustna. Przykładowe zestawy zadań Przykładowe pytania do rozmowy wstępnej Rozmowa wstępna (wyłącznie
112 Informator o egzaminie maturalnym z języka angielskiego od roku szkolnego 2014/2015 2.6.4. Część ustna. Przykładowe zestawy zadań Przykładowe pytania do rozmowy wstępnej Rozmowa wstępna (wyłącznie
ver teoria względności
 ver-7.11.11 teoria względności interferometr Michelsona eter? Albert Michelson 1852 Strzelno, Kujawy 1931 Pasadena, Kalifornia Nobel - 1907 http://galileoandeinstein.physics.virginia.edu/more_stuff/flashlets/mmexpt6.htm
ver-7.11.11 teoria względności interferometr Michelsona eter? Albert Michelson 1852 Strzelno, Kujawy 1931 Pasadena, Kalifornia Nobel - 1907 http://galileoandeinstein.physics.virginia.edu/more_stuff/flashlets/mmexpt6.htm
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition)
 Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
H γ0 - the standard enthalpy of g phase. H β γ - the transition enthalpy of b to g
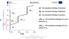 H α0 - the standard enthalpy of a phase H β0 - the standard enthalpy of b phase H γ0 - the standard enthalpy of g phase H α β - the transition enthalpy of a to b phase at T t1 H β γ - the transition enthalpy
H α0 - the standard enthalpy of a phase H β0 - the standard enthalpy of b phase H γ0 - the standard enthalpy of g phase H α β - the transition enthalpy of a to b phase at T t1 H β γ - the transition enthalpy
Polski Krok Po Kroku: Tablice Gramatyczne (Polish Edition) By Anna Stelmach
 Polski Krok Po Kroku: Tablice Gramatyczne (Polish Edition) By Anna Stelmach If you are looking for the ebook by Anna Stelmach Polski krok po kroku: Tablice gramatyczne (Polish Edition) in pdf form, in
Polski Krok Po Kroku: Tablice Gramatyczne (Polish Edition) By Anna Stelmach If you are looking for the ebook by Anna Stelmach Polski krok po kroku: Tablice gramatyczne (Polish Edition) in pdf form, in
1A. Which of the following five units is NOT the same as the other four? A) joule B) erg C) watt D) foot pound E) newton meter
 1P. Cząstka startuje ze stanu spoczynku w chwili t=0 i porusza wzdłuż osi x. Jeżeli siła wypadkowa działająca na cząstkę jest wprost proporcjonalna do t 2, gdzie t jest czasem liczonym od chwili początkowej,
1P. Cząstka startuje ze stanu spoczynku w chwili t=0 i porusza wzdłuż osi x. Jeżeli siła wypadkowa działająca na cząstkę jest wprost proporcjonalna do t 2, gdzie t jest czasem liczonym od chwili początkowej,
Jak zasada Pareto może pomóc Ci w nauce języków obcych?
 Jak zasada Pareto może pomóc Ci w nauce języków obcych? Artykuł pobrano ze strony eioba.pl Pokazuje, jak zastosowanie zasady Pareto może usprawnić Twoją naukę angielskiego. Słynna zasada Pareto mówi o
Jak zasada Pareto może pomóc Ci w nauce języków obcych? Artykuł pobrano ze strony eioba.pl Pokazuje, jak zastosowanie zasady Pareto może usprawnić Twoją naukę angielskiego. Słynna zasada Pareto mówi o
Matematyka 3. Suma szeregu. Promień zbieżności szeregu. Przykład 1: Przykład 2: GenerateConditions
 Matematyka 3 Suma szeregu? Sum i max Sum[f, {i, i max }] evaluates the sum f. Sum[f, {i, i min, i max }] starts with i = i min. Sum[f, {i, i min, i max, di}] uses steps di. Sum[f, {i, {i 1, i 2, }}] uses
Matematyka 3 Suma szeregu? Sum i max Sum[f, {i, i max }] evaluates the sum f. Sum[f, {i, i min, i max }] starts with i = i min. Sum[f, {i, i min, i max, di}] uses steps di. Sum[f, {i, {i 1, i 2, }}] uses
Gradient Coding using the Stochastic Block Model
 Gradient Coding using the Stochastic Block Model Zachary Charles (UW-Madison) Joint work with Dimitris Papailiopoulos (UW-Madison) aaacaxicbvdlssnafj3uv62vqbvbzwarxjsqikaboelgzux7gcaeywtsdp1mwsxeaepd+ctuxcji1r9w5984bbpq1gmxdufcy733bcmjutn2t1fawl5zxsuvvzy2t7z3zn29lkwyguktjywrnqbjwigntuuvi51uebqhjlsdwfxebz8qiwnc79uwjv6mepxgfcoljd88uiox0m1hvlnzwzgowymjn7tjyzertmvpareju5aqkndwzs83thawe64wq1j2httvxo6eopirccxnjekrhqae6wrkuuykl08/gmnjryqwsoqurubu/t2ro1jkyrzozhipvpz3juj/xjdt0ywxu55mina8wxrldkoetukairuekzbubgfb9a0q95fawonqkjoez/7lrdi6trzbcm7pqvwrio4yoarh4aq44bzuwq1ogcba4be8g1fwzjwzl8a78tfrlrnfzd74a+pzb2h+lzm=
Gradient Coding using the Stochastic Block Model Zachary Charles (UW-Madison) Joint work with Dimitris Papailiopoulos (UW-Madison) aaacaxicbvdlssnafj3uv62vqbvbzwarxjsqikaboelgzux7gcaeywtsdp1mwsxeaepd+ctuxcji1r9w5984bbpq1gmxdufcy733bcmjutn2t1fawl5zxsuvvzy2t7z3zn29lkwyguktjywrnqbjwigntuuvi51uebqhjlsdwfxebz8qiwnc79uwjv6mepxgfcoljd88uiox0m1hvlnzwzgowymjn7tjyzertmvpareju5aqkndwzs83thawe64wq1j2httvxo6eopirccxnjekrhqae6wrkuuykl08/gmnjryqwsoqurubu/t2ro1jkyrzozhipvpz3juj/xjdt0ywxu55mina8wxrldkoetukairuekzbubgfb9a0q95fawonqkjoez/7lrdi6trzbcm7pqvwrio4yoarh4aq44bzuwq1ogcba4be8g1fwzjwzl8a78tfrlrnfzd74a+pzb2h+lzm=
The Lorenz System and Chaos in Nonlinear DEs
 The Lorenz System and Chaos in Nonlinear DEs April 30, 2019 Math 333 p. 71 in Chaos: Making a New Science by James Gleick Adding a dimension adds new possible layers of complexity in the phase space of
The Lorenz System and Chaos in Nonlinear DEs April 30, 2019 Math 333 p. 71 in Chaos: Making a New Science by James Gleick Adding a dimension adds new possible layers of complexity in the phase space of
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition)
 Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
 www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
Cracow University of Economics Poland. Overview. Sources of Real GDP per Capita Growth: Polish Regional-Macroeconomic Dimensions 2000-2005
 Cracow University of Economics Sources of Real GDP per Capita Growth: Polish Regional-Macroeconomic Dimensions 2000-2005 - Key Note Speech - Presented by: Dr. David Clowes The Growth Research Unit CE Europe
Cracow University of Economics Sources of Real GDP per Capita Growth: Polish Regional-Macroeconomic Dimensions 2000-2005 - Key Note Speech - Presented by: Dr. David Clowes The Growth Research Unit CE Europe
WENTYLATORY PROMIENIOWE SINGLE-INLET DRUM BĘBNOWE JEDNOSTRUMIENIOWE CENTRIFUGAL FAN
 WENTYLATORY PROMIENIOWE SINGLE-INLET DRUM BĘBNOWE JEDNOSTRUMIENIOWE CENTRIFUGAL FAN TYP WPB TYPE WPB Wentylatory promieniowe jednostrumieniowe bębnowe (z wirnikiem typu Single-inlet centrifugal fans (with
WENTYLATORY PROMIENIOWE SINGLE-INLET DRUM BĘBNOWE JEDNOSTRUMIENIOWE CENTRIFUGAL FAN TYP WPB TYPE WPB Wentylatory promieniowe jednostrumieniowe bębnowe (z wirnikiem typu Single-inlet centrifugal fans (with
METHOD 2 -DIAGNOSTIC OUTSIDE
 VW MOTOMETER BOSCH METHOD 1 - OBD 2 METHOD 2 -DIAGNOSTIC OUTSIDE AFTER OPERATION YOU MUST DISCONECT ACU OR REMOVE FUSE FOR RESTART ODOMETER PO ZROBIENIU LICZNIKA ZDJĄĆ KLEMĘ LUB WYJĄĆ 2 BEZPIECZNIKI OD
VW MOTOMETER BOSCH METHOD 1 - OBD 2 METHOD 2 -DIAGNOSTIC OUTSIDE AFTER OPERATION YOU MUST DISCONECT ACU OR REMOVE FUSE FOR RESTART ODOMETER PO ZROBIENIU LICZNIKA ZDJĄĆ KLEMĘ LUB WYJĄĆ 2 BEZPIECZNIKI OD
Installation of EuroCert software for qualified electronic signature
 Installation of EuroCert software for qualified electronic signature for Microsoft Windows systems Warsaw 28.08.2019 Content 1. Downloading and running the software for the e-signature... 3 a) Installer
Installation of EuroCert software for qualified electronic signature for Microsoft Windows systems Warsaw 28.08.2019 Content 1. Downloading and running the software for the e-signature... 3 a) Installer
Emilka szuka swojej gwiazdy / Emily Climbs (Emily, #2)
 Emilka szuka swojej gwiazdy / Emily Climbs (Emily, #2) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Emilka szuka swojej gwiazdy / Emily Climbs (Emily, #2) Emilka szuka swojej gwiazdy / Emily
Emilka szuka swojej gwiazdy / Emily Climbs (Emily, #2) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Emilka szuka swojej gwiazdy / Emily Climbs (Emily, #2) Emilka szuka swojej gwiazdy / Emily
Dupin cyclides osculating surfaces
 Paweł Walczak, Uniwersytet Łódzki, Dijon, 25 stycznia 2012 Colaborators: Remi Langevin (UdeB), Adam Bartoszek, Szymon Walczak (UŁ) What is extrinsic conformal geometry? Conformal transformations = transformations
Paweł Walczak, Uniwersytet Łódzki, Dijon, 25 stycznia 2012 Colaborators: Remi Langevin (UdeB), Adam Bartoszek, Szymon Walczak (UŁ) What is extrinsic conformal geometry? Conformal transformations = transformations
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition)
 Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
Poland) Wydawnictwo "Gea" (Warsaw. Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically
 Suwalski Park Krajobrazowy i okolice 1:50 000, mapa turystyczno-krajoznawcza =: Suwalki Landscape Park, tourist map = Suwalki Naturpark,... narodowe i krajobrazowe) (Polish Edition) Click here if your
Suwalski Park Krajobrazowy i okolice 1:50 000, mapa turystyczno-krajoznawcza =: Suwalki Landscape Park, tourist map = Suwalki Naturpark,... narodowe i krajobrazowe) (Polish Edition) Click here if your
Pielgrzymka do Ojczyzny: Przemowienia i homilie Ojca Swietego Jana Pawla II (Jan Pawel II-- pierwszy Polak na Stolicy Piotrowej) (Polish Edition)
 Pielgrzymka do Ojczyzny: Przemowienia i homilie Ojca Swietego Jana Pawla II (Jan Pawel II-- pierwszy Polak na Stolicy Piotrowej) (Polish Edition) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically
Pielgrzymka do Ojczyzny: Przemowienia i homilie Ojca Swietego Jana Pawla II (Jan Pawel II-- pierwszy Polak na Stolicy Piotrowej) (Polish Edition) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically
Prices and Volumes on the Stock Market
 Prices and Volumes on the Stock Market Krzysztof Karpio Piotr Łukasiewicz Arkadiusz Orłowski Warszawa, 25-27 listopada 2010 1 Data selection Warsaw Stock Exchange WIG index assets most important for investors
Prices and Volumes on the Stock Market Krzysztof Karpio Piotr Łukasiewicz Arkadiusz Orłowski Warszawa, 25-27 listopada 2010 1 Data selection Warsaw Stock Exchange WIG index assets most important for investors
THE RATE OF GW CAPTURE OF STELLAR-MASS BHS IN NUCLEAR STAR CLUSTERS. Alexander Rasskazov & Bence Kocsis Eotvos University
 THE RATE OF GW CAPTURE OF STELLAR-MASS BHS IN NUCLEAR STAR CLUSTERS Alexander Rasskazov & Bence Kocsis Eotvos University Merger rate density of events with e>0.1 in the LIGO band (>10 Hz), Gpc -3 yr -1
THE RATE OF GW CAPTURE OF STELLAR-MASS BHS IN NUCLEAR STAR CLUSTERS Alexander Rasskazov & Bence Kocsis Eotvos University Merger rate density of events with e>0.1 in the LIGO band (>10 Hz), Gpc -3 yr -1
Extraclass. Football Men. Season 2009/10 - Autumn round
 Extraclass Football Men Season 2009/10 - Autumn round Invitation Dear All, On the date of 29th July starts the new season of Polish Extraclass. There will be live coverage form all the matches on Canal+
Extraclass Football Men Season 2009/10 - Autumn round Invitation Dear All, On the date of 29th July starts the new season of Polish Extraclass. There will be live coverage form all the matches on Canal+
Unitary representations of SL(2, R)
 Unitary representations of SL(, R) Katarzyna Budzik 8 czerwca 018 1/6 Plan 1 Schroedinger operators with inverse square potential Universal cover of SL(, R) x + (m 1 4) 1 x 3 Integrating sl(, R) representations
Unitary representations of SL(, R) Katarzyna Budzik 8 czerwca 018 1/6 Plan 1 Schroedinger operators with inverse square potential Universal cover of SL(, R) x + (m 1 4) 1 x 3 Integrating sl(, R) representations
Raport bieżący: 44/2018 Data: g. 21:03 Skrócona nazwa emitenta: SERINUS ENERGY plc
 Raport bieżący: 44/2018 Data: 2018-05-23 g. 21:03 Skrócona nazwa emitenta: SERINUS ENERGY plc Temat: Zawiadomienie o zmianie udziału w ogólnej liczbie głosów w Serinus Energy plc Podstawa prawna: Inne
Raport bieżący: 44/2018 Data: 2018-05-23 g. 21:03 Skrócona nazwa emitenta: SERINUS ENERGY plc Temat: Zawiadomienie o zmianie udziału w ogólnej liczbie głosów w Serinus Energy plc Podstawa prawna: Inne
Blow-Up: Photographs in the Time of Tumult; Black and White Photography Festival Zakopane Warszawa 2002 / Powiekszenie: Fotografie w czasach zgielku
 Blow-Up: Photographs in the Time of Tumult; Black and White Photography Festival Zakopane Warszawa 2002 / Powiekszenie: Fotografie w czasach zgielku Juliusz and Maciej Zalewski eds. and A. D. Coleman et
Blow-Up: Photographs in the Time of Tumult; Black and White Photography Festival Zakopane Warszawa 2002 / Powiekszenie: Fotografie w czasach zgielku Juliusz and Maciej Zalewski eds. and A. D. Coleman et
SubVersion. Piotr Mikulski. SubVersion. P. Mikulski. Co to jest subversion? Zalety SubVersion. Wady SubVersion. Inne różnice SubVersion i CVS
 Piotr Mikulski 2006 Subversion is a free/open-source version control system. That is, Subversion manages files and directories over time. A tree of files is placed into a central repository. The repository
Piotr Mikulski 2006 Subversion is a free/open-source version control system. That is, Subversion manages files and directories over time. A tree of files is placed into a central repository. The repository
PORTS AS LOGISTICS CENTERS FOR CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION OF THE OFFSHORE WIND FARMS - CASE OF SASSNITZ
 Part-financed by EU South Baltic Programme w w w. p t m e w. p l PROSPECTS OF THE OFFSHORE WIND ENERGY DEVELOPMENT IN POLAND - OFFSHORE WIND INDUSTRY IN THE COASTAL CITIES AND PORT AREAS PORTS AS LOGISTICS
Part-financed by EU South Baltic Programme w w w. p t m e w. p l PROSPECTS OF THE OFFSHORE WIND ENERGY DEVELOPMENT IN POLAND - OFFSHORE WIND INDUSTRY IN THE COASTAL CITIES AND PORT AREAS PORTS AS LOGISTICS
New method for the conformal bootstrap with OPE truncations
 New method for the conformal bootstrap with OPE truncations Wenliang LI Kyung Hee University, Seoul, South Korea Symposium: "Bootstrap Approach to Conformal Field Theories and Applications, OIST, March19-23,
New method for the conformal bootstrap with OPE truncations Wenliang LI Kyung Hee University, Seoul, South Korea Symposium: "Bootstrap Approach to Conformal Field Theories and Applications, OIST, March19-23,
Wprowadzenie do programu RapidMiner, część 2 Michał Bereta 1. Wykorzystanie wykresu ROC do porównania modeli klasyfikatorów
 Wprowadzenie do programu RapidMiner, część 2 Michał Bereta www.michalbereta.pl 1. Wykorzystanie wykresu ROC do porównania modeli klasyfikatorów Zaimportuj dane pima-indians-diabetes.csv. (Baza danych poświęcona
Wprowadzenie do programu RapidMiner, część 2 Michał Bereta www.michalbereta.pl 1. Wykorzystanie wykresu ROC do porównania modeli klasyfikatorów Zaimportuj dane pima-indians-diabetes.csv. (Baza danych poświęcona
Has the heat wave frequency or intensity changed in Poland since 1950?
 Has the heat wave frequency or intensity changed in Poland since 1950? Joanna Wibig Department of Meteorology and Climatology, University of Lodz, Poland OUTLINE: Motivation Data Heat wave frequency measures
Has the heat wave frequency or intensity changed in Poland since 1950? Joanna Wibig Department of Meteorology and Climatology, University of Lodz, Poland OUTLINE: Motivation Data Heat wave frequency measures
