Microstructural characterization of Inconel 713C superalloy after creep testing
|
|
|
- Amalia Pietrzyk
- 6 lat temu
- Przeglądów:
Transkrypt
1 Microstructural characterization of Inconel 713C superalloy after creep testing Charakterystyka mikrostruktury nadstopu Inconel 713C po badaniach pełzania Małgorzata Grudzień 1 *, Rafał Cygan 2, Zenon Pirowski 1, Łukasz Rakoczy 3 1 Foundry Research Institute, ul. Zakopianska 73, Krakow, Poland 2 Consolidated Precision Products, Investment Casting Division CPP-Poland, ul. Hetmanska 120, Rzeszow, Poland 3 AGH University of Science and Technology, Faculty of Metals Engineering and Industrial Computer Science, Department of Physical and Powder Metallurgy, al. A. Mickiewicza 30, Krakow, Poland 1 Instytut Odlewnictwa, ul. Zakopiańska 73, Kraków, Polska 2 Consolidated Precision Products, Investment Casting Division CPP-Poland, ul. Hetmańska 120, Rzeszów, Polska 3 AGH Akademia Górniczo-Hutnicza im. S. Staszica w Krakowie, Wydział Inżynierii Metali i Informatyki Przemysłowej, Katedra Metaloznawstwa i Metalurgii Proszków, al. A. Mickiewicza 30, Kraków, Polska *Corresponding author: malgorzata.grudzien@iod.krakow.pl Received: Accepted in revised form: Instytut Odlewnictwa. All rights reserved. DOI: /iod Abstract The main aim of this investigation was to determine the microstructural degradation of Inconel 713C superalloy during creep at high homologous temperature. The alloy in as cast condition was characterized by large microstructural heterogeneity. Inside equiaxed grains dendrite cores consisted of γ' precipitates surrounded by channels of matrix, whereas enrichment of interdendritic spaces in carbide formers, Zr and B resulted in the formation of additional constituents, namely M 3, Ni 7 Zr 2 and eutectic island γ/γ'. Directional coarsening of γ precipitates (rafting) under applied stress and decomposition of primary MCtype carbides accompanied by the formation of secondary carbides enriched in Cr and γ' phase was observed. Keywords: degradation, Inconel 713C, NbC, M 23 Streszczenie Głównym celem badania było określenie degradacji mikrostruktury nadstopu Inconel 713C zachodzącej podczas badania pełzania w wysokiej temperaturze homologicznej. Badany nadstop bezpośrednio w stanie lanym charakteryzuje się wysoką niejednorodnością mikrostrukturalną. Wewnątrz ziaren równoosiowych rdzenie dendrytów składają się z wydzieleń γ' otoczonych kanałami osnowy, natomiast wzbogacenie przestrzeni międzydendrytycznych w pierwiastki węglikotwórcze, a także Zr i B, prowadzi do tworzenia dodatkowych składników, mianowicie eutektyki γ/γ', węglików MC, borków M 3 oraz fazy międzymetalicznej Ni 7 Zr 2. W trakcie pełzania przy parametrach T = 982ºC i naprężeniu σ = 152 MPa zaobserwowano rafting typu N fazy międzymetalicznej γ'. W przestrzeniach międzydendrytycznych w wyniku częściowego rozpuszczenia węglików typu MC wydzieliły się węgliki M 23 bogate w Cr. Słowa kluczowe: degradacja, Inconel 713C, NbC, M 23 39
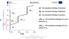
2 M. Grudzień, R. Cygan, Z. Pirowski, Ł. Rakoczy: Microstructural characterization of Inconel 713C superalloy after creep 1. Introduction Inconel 713C belongs to the group of nickel-based superalloys, strengthened primaly by the high volume fraction of intermetallic γ' phase, present to above 1000 C. Very good castability, creep resistance and microstructural stability make these superalloys suitable for manufacture of a low-pressure turbine (LPT) guide vanes in turbo-fan engines [1 4]. Polycrystalline turbine blades are typically manufactured by investment casting process known as the lost-wax process. These complex castings must meet all the extremely strict aerospace quality requirements. Ni-based superalloys are characterized by the ability of stressed γ precipitates to transformation into plates at the high temperature and normal to the axis of the applied stresses (Fig. 1). The phenomenon of a directional growth (coarsening) is usually called rafting [5,6], while N-type behaviour is associated with negative misfit alloys stressed in tension. Fig. 1. Scheme of N- and P-type rafting in superalloys strengthened by cubic-shaped γ' precipitates [5] Rys. 1. Rafting typu N oraz P w nadstopach niklu umacnianych fazą międzymetaliczną γ' [5] Lattice misfit is defined as: δ = 2(a γ' a γ )/(a γ' + a γ ), where a γ' and a γ are the lattice constant of the γ' phase and γ matrix respectively. During exposure to high temperature formation of continuous grain boundary carbide network, TCP phases and MC carbide degeneration can also occur. Most of these features are detrimental to properties of material such as tensile strength and creep resistance [7 10]. Usually, the nickel-based superalloys are heat treated (solution + ageing). However, Inconel 713C achieves sufficiently high strength directly in the casting in the as cast condition [11 13]. According to the AMS5391 the minimum time to rupture during creep of as cast Inconel 713C at 1800 F (~980 C) under 22 psi (~152 MPa) is 30 hours [14]. The tests are carried out at a temperature which significantly exceeds the in-service requirements of the Inconel 713C castings. To achieve the highest properties demand intensive research and testing in order to make correlations between mechanical properties and manufacturing parameters including the composition of shell mould. The aim of this work is to show all details about the parameters of investment casting and creep resistance at high homologous temperature under low stress with particular emphasis on change of primary (as cast) microstructure of Inconel 713C. 2. Experimental procedure Inconel 713C was provided by Canon Muskegon Company in the form of bar. Results of chemical composition obtained by optical emission spectroscopy (OES) are shown in Table 1. The wax pattern, similar in shape and dimensions to the required tensile specimen (Fig. 2) was injection moulded, and then a ceramic monolithic mould was built up around this pattern by a series of dip coatings. The casting was made in the Investment Casting Division of CPP Corp. Poland in Rzeszow and all technological conditions were as similar as possible to company standards. The prime coating of shell mould consisted of zircon filler, colloidal silica binder and 5% of cobalt aluminate (CoAl 2 O 4 ). Alumina grit was used as a primary stucco, and then several coats of ceramic slurries based on alumina silicate powders and colloidal silica binder and as a backup stucco aluminate silicate grit were applied. Master heat charge was melted in a zirconia crucible mounted in the vacuum Consarc furnace. During melting and subsequent pouring level of vacuum was mbar. The liquid metal at 1520 C was poured into a preheated (1000 C) mould. After the alloy has solidified and cooled, the mould was broken and then casting was cut out from the assembly. To obtain the required dimensions of the test specimen (Fig. 2) with optimal surface roughness and dimensions final machining was carried out. Creep resistance test was carried out in accordance with the requirements of ASTM E139 standard using the Walter + Bai AG LFMZ- 30 device at temperature 982 C and stress 152 MPa. Metallographic observations were preceded by standard metallographic preparation and chemical etching in 50 ml lactic acid, 30 ml nitric acid, 2 ml hydrofluoric acid: AG21. The observations at higher magnification before and after creep was carried out by light microscopy (LM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). For SEM, samples were etched in 50 ml water, 50 ml hydrochloric acid, 50 ml nitric acid, 1.5 g molybdic acid: no. 17 Etch (micro) reagent. Image analysis was used to calculate the number of equiaxed grains, mean area, mean perimeter, and number of precipitates per mm 2. For imaging and EDS analyses, a 15 kv accelerating voltage was used. 40 Prace IOd 1/2018
3 M. Grudzień, R. Cygan, Z. Pirowski, Ł. Rakoczy: Charakterystyka mikrostruktury nadstopu Inconel 713C po badaniach Element Table 1. Chemical composition of Inconel 713C Tabela 1. Skład chemiczny stopu Inconel 713C Cr Al Mo Nb Ti C Zr Co B S P Ni % wt Bal. growth and nucleation rate. The obtained structure was caused by the reaction between the Cr, Al and Ti consisted in Inconel 713C and cobalt aluminate (primary coat). Cobalt in the compound is displaced by these elements to form Co fine particles, which are considered to be the nucleants during solidification of casting [12]. Fig. 2. Geometry and dimensions of the specimen for creep test (mm) Rys. 2. Geometria próbki do badań pełzania (mm) 3. Results and discussion Fig. 4. Binary image of Inconel 713C macrostructure Rys. 4. Obraz binarny makrostruktury Inconel 713C Table 2. Stereological parameters of Inconel 713C casting Tabela 2. Parametry stereologiczne nadstopu Inconel 713C Number of grains Mean area, mm 2 Mean perimeter, mm Number of perimeter per mm 2 Value Standard deviation Fig. 3. Creep curve of Inconel 713C Rys. 3. Krzywa pełzania nadstopu Inconel 713C At high temperature/low stress (982 C/152 MPa), Inconel 713C showed short-term primary stage and then steady state creep ( % per h) and finally pronounced strain appearing at the tertiary stage (Fig. 3). Creep curve had the classical shape, while the time to rupture was almost 40 h, in accord with AMS5391 requirement of minimum 30 h. The macrostructure of Inconel 713C after binarization consisting of 18 equiaxed grains is shown in Figure 4. The generally unacceptable chill zone structure of the inner surface of casting was not present. The stereological parameters, presented in Table 2, indicate that relatively fine-grain structure was obtained. The mean area of detected grains was 4.08 mm 2, while the perimeter exceeded 20 mm. Standard deviations were relatively high due to irregular grains size and local condition of solidification process. Pouring temperature was relatively high, and so only 0.23 grain are per mm 2 was observed. The grain size in cast superalloys depends mainly on the velocity of The microstructure of as-cast Inconel 713C before mechanical testing at elevated temperature is shown in Figure 5. Dissimilarity between of dendrite core and interdendritic spaces microstructure originated from the change of solubility of alloying elements in γ-matrix during solidification and cooling (Fig. 5a). Dendrite cores consist of cubic-shaped γ precipitates surrounded by γ channels, while interdendritic spaces were strongly enriched in Nb, Zr and B which led to the creation of NbC (Fig. 5b), M 3 (Fig. 5c) and Ni 7 Z 2 (Fig. 5d) in the close vicinities of eutectic islands. More primary microstructure detail were presented in [15]. Fractographic observations revealed intergranular cracking with numerous faults resulting from the orientation of equiaxed grains (Fig. 6a). Cracks formed during creep were also observed inside the sample, which indicates a local weakening of grain boundaries (Fig. 6b). These crack length were of several dozen micrometers, less often more than 100 μm. In Figure 7 SEM micrograph of crept Inconel 713C is presented. A change in morphology, from the undeformed structure, of strengthening phases both in dendrite core and interdendritic spaces was evident. Inconel 713C is characterized by the Transactions of FRI 1/
4 M. Grudzień, R. Cygan, Z. Pirowski, Ł. Rakoczy: Microstructural characterization of Inconel 713C superalloy after creep Fig. 5. Microstructure of Inconel 713C before creep test: a) dendrite core and interdendritic space, b) Chinese script carbide, c) eutectic island and boride, d) Zr-rich intermetallic phase Rys. 5. Mikrostruktura Inconelu 713C przed testem pełzania: a) rdzeń dendrytu i przestrzeń międzydendrytyczna, b) węglik o morfologii chińskiego pisma, c) eutektyka γ/γ i borek, d) faza międzymetaliczna bogata w cyrkon Fig. 6. Microstructure of crept sample: a) fracture, b) small local voids along grain boundaries Rys. 6. Mikrostruktura próbki po pełzaniu: a) pęknięcia, b) lokalne pustki wzdłuż granic ziaren 42 Prace IOd 1/2018
5 M. Grudzień, R. Cygan, Z. Pirowski, Ł. Rakoczy: Charakterystyka mikrostruktury nadstopu Inconel 713C po badaniach Fig. 7. Microstructural changes after creep: a) dendrite core, b) interdendritic space, c) voids inside the material Rys. 7. Zmiany mikrostruktury po pełzaniu: a) rdzeń dendrytu, b) przestrzeń międzydendrytyczna, c) pustki wewnątrz materiału ability to γ precipitates to transform into plates under stress at high temperatures [16], rafting, as shown in Figure 7a. Significant microstructural changes resulting from the formation of precipitates was observed along grain boundaries (Fig. 7b). All these small precipitates were surrounded by coarsed precipitates with high angle grain boundaries. Locally, away from the fracture small voids were also detected (Fig. 7c). In order to characterize and indentify precipitates, a EDS linear analysis was performed. The line scan is shown in Figure 8, and the distribution of the main alloying elements in Figure 9. Small precipitates were strongly enriched in Cr and Mo and a high drop in content occured there for Ni and Al. Coarse precipitates observed in the vicinity of small precipitates were enriched especially in Al. After creep testing, the volume fraction of the MC (Nb-rich) carbides in the interdendritic areas was significantly decreased due to partial dissolution at the high homologous temperature. Usually in Ni-based superalloys most of the carbon below 982 C is in the form of MC-type carbide. During service or testing at elevated temperature, MC decomposes slowly to produce carbon that diffuses and triggers an important reactions The dominating reaction in the superalloys is the formation of M 23 -type carbide by the following reaction [16,17]: Fig. 8. Location of EDS line scan across grain boundary Rys. 8. Lokalizacja analizy liniowej EDS wzdłuż granicy ziaren MC + γ M 23 + γ' (Eqn. 1) Reaction occurs at about 982 C or even as low as 760 C. Our results indicate that, in accord with Equation 1, small M 23 carbide particles enriched mainly in Cr and Mo were surrounded by the intermetallic phase γ'. Transactions of FRI 1/
6 M. Grudzień, R. Cygan, Z. Pirowski, Ł. Rakoczy: Microstructural characterization of Inconel 713C superalloy after creep with the formation of platelet morphology, however, in their close vicinity, the smaller ones underwent such transformation. The results of the EDS analysis shown in Figure 11 indicated a strong enrichment in Cr, Mo and Nb in the area of the bright fine precipitate. The second commonly observed mechanism of MC-type carbide degradation is described by Equation 2 [17]: MC + γ M 6 C + γ' (Eqn. 2) Fig. 9. Distribution of the main alloying elements through grain boundary Rys. 9. Rozkład głównych pierwiastków stopowych wzdłuż granicy ziaren Microstructural degradation of MC carbides led to creation of M 6 C-type carbides which are most often rich in Mo, W, Co, Cr and Fe. The presence of these carbides was not detected, despite intensive observations. It was shown that the phase rich in Cr and Mo in the eutectic, was a M 3 boride. The presence of M 3 borides and M 23 Cr-rich secondary carbides observed after creep can be explained by the low solubility of B and C in the matrix. During exposure to high homologous temperature the MC-type carbides undergo a transformation, and thus, in the regions of their decomposition, the solid solution of matrix becomes enriched with C. Carbon due to larger atomic radius reduces the solubility of B in the matrix and leads to the creation of both borides and secondary carbides at room temperature. 4. Summary Fig. 10. Location of EDS line scan in the interdendritic space Rys. 10. Lokalizacja analizy liniowej EDS w przestrzeni międzydendrytycznej Fig. 11. Distribution of the main alloying elements in interdendritic space Rys. 11. Rozkład głównych pierwiastków stopowych w przestrzeni międzydendrytycznej Microstructural changes in the interdendritic space together with the EDS line scan are shown in Figure 10. Large eutectic γ' precipitates did not significantly deform At high temperature/low stress (982 C/152 MPa), Inconel 713C showed short-term primary stage and then steady-state creep ( % per h) and finally pronounced strain appearing at the tertiary stage. The time to rupture was almost 40 h. Microstructure in the as cast condition of Inconel 713C was characterized by dendritic structure with irregular distribution of phases. Dendrite cores consisted of high volume fraction of γ' phase surrounded by channels of the matrix, while segregation of Al, Nb, Zr, and C into interdendritic spaces led to the formation of eutectic islands, carbides, borides and Zr-rich intermetallic phase. Observation of degraded microstructure indicated significant changes that include N-type rafting (directional growth) of γ' precipitates. In interdendritic spaces, including grain boundaries, decomposition of MC-type into M 23 carbides was observed. Borides enriched in Cr and Mo were also present, so during creep their complete dissolution in the matrix does not occur. Formation of M 23 carbides can be accompanied by borides formation. Acknowledgements This research work was supported by National Centre for Research and Development, Grant No. LIDER/227/L-6/14/NCBR/2015. The authors declare no conflict of interest. 44 Prace IOd 1/2018
7 M. Grudzień, R. Cygan, Z. Pirowski, Ł. Rakoczy: Charakterystyka mikrostruktury nadstopu Inconel 713C po badaniach References 1. Reed R.C The Superalloys: Fundamentals and Applications. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 2. Benini E Advances in Gas Turbine Technology. London: IntechOpen. 3. Rakoczy Ł., M. Grudzień, A. Zielińska-Lipiec Contribution of microstructural constituents on hot cracking of MAR-M247 nickel based superalloy. Archives of Metallurgy and Materials 63 (1) : Rakoczy Ł., M. Grudzień, L. Tuz, K. Pańcikiewicz, A. Zielińska-Lipiec Microstructure and properties of a repair weld in a nickel based superalloy gas turbine component. Advances in Materials Science 17 (2) : Nguyen L., R. Shi, Y. Wang, M. De Graef Quantification of rafting of γ precipitates in Ni-based superalloys. Acta Materialia 103 (15 January 2016) : Nörtershäuser P., J. Frenzel, A. Ludwig, K. Neuking, G. Eggeler The effect of cast microstructure and crystallography on rafting, dislocation plasticity and creep anisotropy of single crystal Ni-base superalloys. Materials and Engineering: A 626 (25 February) : Cieśla M., F. Binczyk, G. Junak, M. Mańka, P. Gradoń Durability of MAR-247 and IN-713C nickel superalloys under cyclic creep conditions. Archives of Foundry Engineering 15 (4) : Cieśla M., F. Binczyk, M. Mańka Impact of surface and volume modification of nickel superalloys IN-713C and MAR-247 on high temperature creep resistance. Archives of Foundry Engineering 12 (4) : Azadi M., A. Marbout, S. Safarloo, M. Azadi, M. Shariat, M.H. Rizi Effects of solutioning and ageing treatments on properties of Inconel-713C nickel-based superalloy under creep loading. Materials Science and Engineering: A 711 (10 January 2018) : Matysiak H., M. Zagorska, A. Balkowiec, B. Adamczyk- -Cieslak, K. Dobkowski, M. Koralnik, R. Cygan, J. Nawrocki, J. Cwajna, K.J. Kurzydlowski The influence of the melt-pouring temperature and inoculant content on the macro and microstructure of the IN713C Ni-based superalloy. JOM 68 (1) : Zupanič F., T. Bončina, A. Križman, F.D. Tichelaar Structure of continuously cast Ni-based superalloy Inconel 713C. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 329 (1 2) : Standard AMS5391. Nickel Alloy, Corrosion and Heat Resistant, Investment Castings, 73ni 13cr 4.5mo 2.3cb 0.75ti 6.0al 0.010b 0.10zr Vacuum Cast, As-Cast. 15. Cieśla M., F. Binczyk, M. Mańka, R. Findziński The influence of macrostructure of nickel-based superalloys IN713C and MAR 247 on the characteristics of high-temperature creep. Archives of Foundry Engineering 14 (4) : Matysiak H., M. Zagorska, A. Balkowiec, B. Adamczyk- -Cieslak, R. Cygan, J. Cwajna, J. Nawrocki, K.J. Kurzydłowski The microstructure degradation of the IN713C nickel-based superalloy after stress rupture tests. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance 23 (9) : Bhambri A.K., T.Z. Kattamis, J.E. Morral Cast microstructure of Inconel 713C and its dependence on solidification variables. Metallurgical Transactions B 6 (4) : Desmorat R., A. Mattiello, J. Cormier A tensorial thermodynamic framework to account for the γ' rafting in nickel-based single crystal superalloys. International Journal of Plasticity 95 (August 2017) : Touratier F., E. Andrieu, D. Poquillon, B. Viguier Rafting microstructure during creep of the MC2 nickelbased superalloy at very high temperature. Materials and Engineering: A (15 June 2009) : Transactions of FRI 1/
8
Investment casting parameters impact on IN 713C nickel-based superalloy microstructure
 Inżynieria Materiałowa 2 (210) (2016) 59 64 DOI 10.15199/28.2016.2.2 Copyright SIGMA-NOT MATERIALS ENGINEERING Investment casting parameters impact on IN 713C nickel-based superalloy microstructure Stanisław
Inżynieria Materiałowa 2 (210) (2016) 59 64 DOI 10.15199/28.2016.2.2 Copyright SIGMA-NOT MATERIALS ENGINEERING Investment casting parameters impact on IN 713C nickel-based superalloy microstructure Stanisław
Tytuł pracy w języku angielskim: Microstructural characterization of Ag/X/Ag (X = Sn, In) joints obtained as the effect of diffusion soledering.
 Dr inż. Przemysław Skrzyniarz Kierownik pracy: Prof. dr hab. inż. Paweł Zięba Tytuł pracy w języku polskim: Charakterystyka mikrostruktury spoin Ag/X/Ag (X = Sn, In) uzyskanych w wyniku niskotemperaturowego
Dr inż. Przemysław Skrzyniarz Kierownik pracy: Prof. dr hab. inż. Paweł Zięba Tytuł pracy w języku polskim: Charakterystyka mikrostruktury spoin Ag/X/Ag (X = Sn, In) uzyskanych w wyniku niskotemperaturowego
IDENTYFIKACJA FAZ W MODYFIKOWANYCH CYRKONEM ŻAROWYTRZYMAŁYCH ODLEWNICZYCH STOPACH KOBALTU METODĄ DEBYEA-SCHERRERA
 44/14 Archives of Foundry, Year 2004, Volume 4, 14 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2004, Rocznik 4, Nr 14 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 IDENTYFIKACJA FAZ W MODYFIKOWANYCH CYRKONEM ŻAROWYTRZYMAŁYCH ODLEWNICZYCH
44/14 Archives of Foundry, Year 2004, Volume 4, 14 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2004, Rocznik 4, Nr 14 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 IDENTYFIKACJA FAZ W MODYFIKOWANYCH CYRKONEM ŻAROWYTRZYMAŁYCH ODLEWNICZYCH
Dr inż. Łukasz Rogal zatrudniony jest w Instytucie Metalurgii i Inżynierii Materiałowej Polskiej Akademii Nauk na stanowisku adiunkta
 e-mail: l.rogal@imim.pl tel. 12 2952826 Miejsce zatrudnienia i zajmowane stanowiska Dr inż. Łukasz Rogal zatrudniony jest w Instytucie Metalurgii i Inżynierii Materiałowej Polskiej Akademii Nauk na stanowisku
e-mail: l.rogal@imim.pl tel. 12 2952826 Miejsce zatrudnienia i zajmowane stanowiska Dr inż. Łukasz Rogal zatrudniony jest w Instytucie Metalurgii i Inżynierii Materiałowej Polskiej Akademii Nauk na stanowisku
STRUCTURE OF PHOSPHOR TIN BRONZE CuSn10P MODIFIED WITH MIXTURE OF MICROADDITIVES
 11/15 Archives of Foundry, Year 2005, Volume 5, 15 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2005, Rocznik 5, Nr 15 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 STRUCTURE OF PHOSPHOR TIN BRONZE CuSn10P MODIFIED WITH MIXTURE OF MICROADDITIVES
11/15 Archives of Foundry, Year 2005, Volume 5, 15 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2005, Rocznik 5, Nr 15 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 STRUCTURE OF PHOSPHOR TIN BRONZE CuSn10P MODIFIED WITH MIXTURE OF MICROADDITIVES
Międzynarodowa aktywność naukowa młodej kadry Wydziału Metali Nieżelaznych AGH na przykładzie współpracy z McMaster University w Kanadzie
 Międzynarodowa aktywność naukowa młodej kadry Wydziału Metali Nieżelaznych AGH na przykładzie współpracy z McMaster University w Kanadzie Anna Kula Akademia Górniczo-Hutnicza im. St. Staszica w Krakowie,
Międzynarodowa aktywność naukowa młodej kadry Wydziału Metali Nieżelaznych AGH na przykładzie współpracy z McMaster University w Kanadzie Anna Kula Akademia Górniczo-Hutnicza im. St. Staszica w Krakowie,
PRACE INSTYTUTU ODLEWNICTWA TRANSACTIONS OF FOUNDRY RESEARCH INSTITUTE
 PRACE INSTYTUTU ODLEWNICTWA TRANSACTIONS OF FOUNDRY RESEARCH INSTITUTE Volume LIII Year 2013 Number 3 DOI: 10.7356/iod.2013.15 Wpływ modyfikacji na strukturę i udarność mosiądzu aluminiowego CuZn30Al3
PRACE INSTYTUTU ODLEWNICTWA TRANSACTIONS OF FOUNDRY RESEARCH INSTITUTE Volume LIII Year 2013 Number 3 DOI: 10.7356/iod.2013.15 Wpływ modyfikacji na strukturę i udarność mosiądzu aluminiowego CuZn30Al3
Adres do korespondencji: Instytut Metalurgii i Inżynierii Materiałowej PAN, Kraków, ul. Reymonta 25
 Adres do korespondencji: Instytut Metalurgii i Inżynierii Materiałowej PAN, 30059 Kraków, ul. Reymonta 25 Tel.: (012) 295 28 70, pokój 104, fax: (012) 295 28 04, email: p.petrzak@imim.pl Miejsca zatrudnienia
Adres do korespondencji: Instytut Metalurgii i Inżynierii Materiałowej PAN, 30059 Kraków, ul. Reymonta 25 Tel.: (012) 295 28 70, pokój 104, fax: (012) 295 28 04, email: p.petrzak@imim.pl Miejsca zatrudnienia
WPŁYW TEMPERATURY WYGRZEWANIA NA UDZIAŁ FAZ PIERWOTNYCH W STRUKTURZE ŻAROWYTRZYMAŁEGO ODLEWNICZEGO STOPU KOBALTU
 50/22 Archives of Foundry, Year 2006, Volume 6, 22 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 22 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 WPŁYW TEMPERATURY WYGRZEWANIA NA UDZIAŁ FAZ PIERWOTNYCH W STRUKTURZE ŻAROWYTRZYMAŁEGO
50/22 Archives of Foundry, Year 2006, Volume 6, 22 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 22 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 WPŁYW TEMPERATURY WYGRZEWANIA NA UDZIAŁ FAZ PIERWOTNYCH W STRUKTURZE ŻAROWYTRZYMAŁEGO
ZMIANY MIKROSTRUKTURY I WYDZIELEŃ WĘGLIKÓW W STALIWIE Cr-Ni PO DŁUGOTRWAŁEJ EKSPLOATACJI
 25/8 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2003, Rocznik 3, Nr 8 Archives of Foundry Year 2003, Volume 3, Book 8 PAN - Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 ZMIANY MIKROSTRUKTURY I WYDZIELEŃ WĘGLIKÓW W STALIWIE Cr-Ni PO DŁUGOTRWAŁEJ
25/8 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2003, Rocznik 3, Nr 8 Archives of Foundry Year 2003, Volume 3, Book 8 PAN - Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 ZMIANY MIKROSTRUKTURY I WYDZIELEŃ WĘGLIKÓW W STALIWIE Cr-Ni PO DŁUGOTRWAŁEJ
WPŁYW WARUNKÓW PRZESYCANIA I STARZENIA STOPU C355 NA ZMIANY JEGO TWARDOŚCI
 40/15 Archives of Foundry, Year 2005, Volume 5, 15 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2005, Rocznik 5, Nr 15 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 WPŁYW WARUNKÓW PRZESYCANIA I STARZENIA STOPU C355 NA ZMIANY JEGO TWARDOŚCI
40/15 Archives of Foundry, Year 2005, Volume 5, 15 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2005, Rocznik 5, Nr 15 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 WPŁYW WARUNKÓW PRZESYCANIA I STARZENIA STOPU C355 NA ZMIANY JEGO TWARDOŚCI
WYSOKOTEMPERATUROWE WŁASNOŚCI TRIBOLOGICZNE STOPÓW Fe-Al
 3-2012 T R I B O L O G I A 209 Tomasz ŚLEBODA *, Janusz KRAWCZYK *, Sławomir ZIMOWSKI **, Marcin KOT ** WYSOKOTEMPERATUROWE WŁASNOŚCI TRIBOLOGICZNE STOPÓW Fe-Al HIGH TEMPERATURE TRIBOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
3-2012 T R I B O L O G I A 209 Tomasz ŚLEBODA *, Janusz KRAWCZYK *, Sławomir ZIMOWSKI **, Marcin KOT ** WYSOKOTEMPERATUROWE WŁASNOŚCI TRIBOLOGICZNE STOPÓW Fe-Al HIGH TEMPERATURE TRIBOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
ODLEWNICZY STOP MAGNEZU ELEKTRON 21 STRUKTURA I WŁAŚCIWOŚCI W STANIE LANYM
 26/18 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 18 (1/2) ARCHIVES OF FOUNDRY Year 2006, Volume 6, N o 18 (1/2) PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 ODLEWNICZY STOP MAGNEZU ELEKTRON 21 STRUKTURA I WŁAŚCIWOŚCI
26/18 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 18 (1/2) ARCHIVES OF FOUNDRY Year 2006, Volume 6, N o 18 (1/2) PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 ODLEWNICZY STOP MAGNEZU ELEKTRON 21 STRUKTURA I WŁAŚCIWOŚCI
Dr inż. Paulina Indyka
 Dr inż. Paulina Indyka Kierownik pracy: dr hab. Ewa BełtowskaLehman, prof. PAN Tytuł pracy w języku polskim: Optymalizacja mikrostruktury i właściwości powłok NiW osadzanych elektrochemicznie Tytuł pracy
Dr inż. Paulina Indyka Kierownik pracy: dr hab. Ewa BełtowskaLehman, prof. PAN Tytuł pracy w języku polskim: Optymalizacja mikrostruktury i właściwości powłok NiW osadzanych elektrochemicznie Tytuł pracy
The influence of the chosen welding technology on the microstructure and selected mechanical properties of welded magnesium alloy AZ91
 Paweł Bolanowski, Andrzej Dziadoń przeglad Welding Technology Review The influence of the chosen welding technology on the microstructure and selected mechanical properties of welded magnesium alloy AZ91
Paweł Bolanowski, Andrzej Dziadoń przeglad Welding Technology Review The influence of the chosen welding technology on the microstructure and selected mechanical properties of welded magnesium alloy AZ91
MIKROSTRUKTURA NADSTOPU KOBALTU MAR M509 W STANIE LANYM I PO OBRÓBCE CIEPLNEJ
 Prace IMŻ 1 (2010) 259 Piotr SKUPIEŃ, Krzysztof RADWAŃSKI, Jarosław GAZDOWICZ, Sebastian ARABASZ, Jerzy WIEDERMANN Instytut Metalurgii Żelaza im. St. Staszica Janusz SZALA Politechnika Śląska, Wydział
Prace IMŻ 1 (2010) 259 Piotr SKUPIEŃ, Krzysztof RADWAŃSKI, Jarosław GAZDOWICZ, Sebastian ARABASZ, Jerzy WIEDERMANN Instytut Metalurgii Żelaza im. St. Staszica Janusz SZALA Politechnika Śląska, Wydział
Akademia Górniczo-Hutnicza im. Stanisława Staszica Wydział: Inżynierii Metali i Informatyki Przemysłowej Katedra: Metaloznawstwa i Metalurgii Proszków
 Akademia Górniczo-Hutnicza im. Stanisława Staszica Wydział: Inżynierii Metali i Informatyki Przemysłowej Katedra: Metaloznawstwa i Metalurgii Proszków Rozprawa doktorska Microstructure stability of second
Akademia Górniczo-Hutnicza im. Stanisława Staszica Wydział: Inżynierii Metali i Informatyki Przemysłowej Katedra: Metaloznawstwa i Metalurgii Proszków Rozprawa doktorska Microstructure stability of second
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume Issue 2 DOI: /v x
 A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 57 2012 Issue 2 DOI: 10.2478/v10172-012-0056-x T. WĘGRZYN, J. PIWNIK LOW ALLOY STEEL WELDING WITH MICRO-JET COOLING SPAWANIE STALI
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 57 2012 Issue 2 DOI: 10.2478/v10172-012-0056-x T. WĘGRZYN, J. PIWNIK LOW ALLOY STEEL WELDING WITH MICRO-JET COOLING SPAWANIE STALI
WSKAŹNIK JAKOŚCI ODLEWÓW ZE STOPU Al-Si
 48/14 Archives of Foundry, Year 2004, Volume 4, 14 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2004, Rocznik 4, Nr 14 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 WSKAŹNIK JAKOŚCI ODLEWÓW ZE STOPU Al-Si A. W. ORŁOWICZ 1, M. MRÓZ 2 Zakład
48/14 Archives of Foundry, Year 2004, Volume 4, 14 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2004, Rocznik 4, Nr 14 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 WSKAŹNIK JAKOŚCI ODLEWÓW ZE STOPU Al-Si A. W. ORŁOWICZ 1, M. MRÓZ 2 Zakład
BADANIE WYDZIELEŃ W STALIWIE RUR KATALITYCZNYCH PRZY POMOCY MIKROSKOPU SKANINGOWEGO
 33/9 Archives of Foundry, Year 2003, Volume 3, 9 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2003, Rocznik 3, Nr 9 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 BADANIE WYDZIELEŃ W STALIWIE RUR KATALITYCZNYCH PRZY POMOCY MIKROSKOPU SKANINGOWEGO
33/9 Archives of Foundry, Year 2003, Volume 3, 9 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2003, Rocznik 3, Nr 9 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 BADANIE WYDZIELEŃ W STALIWIE RUR KATALITYCZNYCH PRZY POMOCY MIKROSKOPU SKANINGOWEGO
INSPECTION METHODS FOR QUALITY CONTROL OF FIBRE METAL LAMINATES IN AEROSPACE COMPONENTS
 Kompozyty 11: 2 (2011) 130-135 Krzysztof Dragan 1 * Jarosław Bieniaś 2, Michał Sałaciński 1, Piotr Synaszko 1 1 Air Force Institute of Technology, Non Destructive Testing Lab., ul. ks. Bolesława 6, 01-494
Kompozyty 11: 2 (2011) 130-135 Krzysztof Dragan 1 * Jarosław Bieniaś 2, Michał Sałaciński 1, Piotr Synaszko 1 1 Air Force Institute of Technology, Non Destructive Testing Lab., ul. ks. Bolesława 6, 01-494
BADANIE WYDZIELEŃ W STABILIZOWANYM STALIWIE ŻAROWYTRZYMAŁYM PRZY POMOCY MIKROSKOPU SKANINGOWEGO
 18/2 Archives of Foundry, Year 2001, Volume 1, 1 (2/2) Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2001, Rocznik 1, Nr 1 (2/2) PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 BADANIE WYDZIELEŃ W STABILIZOWANYM STALIWIE ŻAROWYTRZYMAŁYM PRZY
18/2 Archives of Foundry, Year 2001, Volume 1, 1 (2/2) Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2001, Rocznik 1, Nr 1 (2/2) PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 BADANIE WYDZIELEŃ W STABILIZOWANYM STALIWIE ŻAROWYTRZYMAŁYM PRZY
TYRE PYROLYSIS. REDUXCO GENERAL DISTRIBUTOR :: ::
 TYRE PYROLYSIS Installation for rubber waste pyrolysis designed for processing of used tyres and plastic waste (polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene), where the final product could be electricity,
TYRE PYROLYSIS Installation for rubber waste pyrolysis designed for processing of used tyres and plastic waste (polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene), where the final product could be electricity,
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume Issue 4 DOI: /amm
 A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 59 2014 Issue 4 DOI: 10.2478/amm-2014-0253 A. WINIOWSKI, M. RÓŻAŃSKI BRAZING OF ALLOY BASED ON Fe 3 Al ALUMINIDE LUTOWANIE TWARDE
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 59 2014 Issue 4 DOI: 10.2478/amm-2014-0253 A. WINIOWSKI, M. RÓŻAŃSKI BRAZING OF ALLOY BASED ON Fe 3 Al ALUMINIDE LUTOWANIE TWARDE
MODYFIKACJA BRĄZU CuSn8 I JEJ WPŁYW NA SEGREGACJĘ CYNY
 42/10 Archives of Foundry, Year 2003, Volume 3, 10 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2003, Rocznik 3, Nr 10 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 MODYFIKACJA BRĄZU CuSn8 I JEJ WPŁYW NA SEGREGACJĘ CYNY J. SZAJNAR 1, M.
42/10 Archives of Foundry, Year 2003, Volume 3, 10 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2003, Rocznik 3, Nr 10 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 MODYFIKACJA BRĄZU CuSn8 I JEJ WPŁYW NA SEGREGACJĘ CYNY J. SZAJNAR 1, M.
FABRICATION OF MAGNESIUM MATRIX COMPOSITE WITH GLASSY CARBON PARTICLES BY PRESSURE DIE CASTING
 14: 2 (2014) 101-105 Anita Olszówka-Myalska 1 * Jerzy Myalski 1, Konrad Wrzała 2 1 Silesian University of Technology, Department of Materials Science, ul. Krasińskiego 8, 40-019 Katowice, Poland 2 SILUM
14: 2 (2014) 101-105 Anita Olszówka-Myalska 1 * Jerzy Myalski 1, Konrad Wrzała 2 1 Silesian University of Technology, Department of Materials Science, ul. Krasińskiego 8, 40-019 Katowice, Poland 2 SILUM
Własności mechaniczne kompozytów odlewanych na osnowie stopu Al-Si zbrojonych fazami międzymetalicznymi
 A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 10 Special Issue 4/2010 9 14
A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 10 Special Issue 4/2010 9 14
OCENA WŁASNOŚCI TRIBOLOGICZNYCH NOWYCH MATERIAŁÓW NARZĘDZIOWYCH NA OSNOWIE NIKLU
 4-2011 T R I B O L O G I A 11 Piotr BAŁA *, Janusz KRAWCZYK *, Marcin MADEJ * OCENA WŁASNOŚCI TRIBOLOGICZNYCH NOWYCH MATERIAŁÓW NARZĘDZIOWYCH NA OSNOWIE NIKLU THE TRIBOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF NEW Ni-BASED
4-2011 T R I B O L O G I A 11 Piotr BAŁA *, Janusz KRAWCZYK *, Marcin MADEJ * OCENA WŁASNOŚCI TRIBOLOGICZNYCH NOWYCH MATERIAŁÓW NARZĘDZIOWYCH NA OSNOWIE NIKLU THE TRIBOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF NEW Ni-BASED
Przetapianie laserowe i łukiem plazmowym odlewów precyzyjnych ze stopu Inconel 713C
 Janusz Adamiec, Katarzyna Łyczkowska przeglad Welding Technology Review Przetapianie laserowe i łukiem plazmowym odlewów precyzyjnych ze stopu Inconel 713C Remelting of Inconel 713C alloy by laser and
Janusz Adamiec, Katarzyna Łyczkowska przeglad Welding Technology Review Przetapianie laserowe i łukiem plazmowym odlewów precyzyjnych ze stopu Inconel 713C Remelting of Inconel 713C alloy by laser and
WPŁYW PARAMETRÓW ODLEWANIA CIŚNIENIOWEGO NA STRUKTURĘ i WŁAŚCIWOŚCI STOPU MAGNEZU AM50
 28/18 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 18 (1/2) ARCHIVES OF FOUNDRY Year 2006, Volume 6, N o 18 (1/2) PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 WPŁYW PARAMETRÓW ODLEWANIA CIŚNIENIOWEGO NA STRUKTURĘ i
28/18 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 18 (1/2) ARCHIVES OF FOUNDRY Year 2006, Volume 6, N o 18 (1/2) PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 WPŁYW PARAMETRÓW ODLEWANIA CIŚNIENIOWEGO NA STRUKTURĘ i
MIKROSTRUKTURA ODLEWNICZEGO STOPU MAGNEZU GA8
 31/18 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 18 (1/2) ARCHIVES OF FOUNDRY Year 2006, Volume 6, N o 18 (1/2) PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 MIKROSTRUKTURA ODLEWNICZEGO STOPU MAGNEZU GA8 A. KIEŁBUS
31/18 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 18 (1/2) ARCHIVES OF FOUNDRY Year 2006, Volume 6, N o 18 (1/2) PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 MIKROSTRUKTURA ODLEWNICZEGO STOPU MAGNEZU GA8 A. KIEŁBUS
Adres do korespondencji:
 Adres do korespondencji: Instytut Metalurgii i Inżynierii Materiałowej PAN, 30-059 Kraków, ul. Reymonta 25 Tel.: (012) 2952826, pokój 001, fax: (012) 2952804 e-mail: kstan@imim.pl Miejsca zatrudnienia
Adres do korespondencji: Instytut Metalurgii i Inżynierii Materiałowej PAN, 30-059 Kraków, ul. Reymonta 25 Tel.: (012) 2952826, pokój 001, fax: (012) 2952804 e-mail: kstan@imim.pl Miejsca zatrudnienia
SILUMIN NADEUTEKTYCZNY Z DODATKAMI Cr, Mo, W i Co
 18/38 Solidification of Metals and Alloys, No. 38, 1998 Krzepnięcie Metali i Stopów, nr 38, 1998 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 0208-9386 SILUMIN NADEUTEKTYCZNY Z DODATKAMI Cr, Mo, W i Co PIETROWSKI Stanisław, Instytut
18/38 Solidification of Metals and Alloys, No. 38, 1998 Krzepnięcie Metali i Stopów, nr 38, 1998 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 0208-9386 SILUMIN NADEUTEKTYCZNY Z DODATKAMI Cr, Mo, W i Co PIETROWSKI Stanisław, Instytut
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume Issue 1 DOI: /v x
 A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 56 2011 Issue 1 DOI: 10.2478/v10172-011-0008-x A. PAWŁOWSKI, C. SENDEROWSKI, W. WOŁCZYŃSKI, J. MORGIEL, Ł. MAJOR DETONATION DEPOSITED
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 56 2011 Issue 1 DOI: 10.2478/v10172-011-0008-x A. PAWŁOWSKI, C. SENDEROWSKI, W. WOŁCZYŃSKI, J. MORGIEL, Ł. MAJOR DETONATION DEPOSITED
Metodyki projektowania i modelowania systemów Cyganek & Kasperek & Rajda 2013 Katedra Elektroniki AGH
 Kierunek Elektronika i Telekomunikacja, Studia II stopnia Specjalność: Systemy wbudowane Metodyki projektowania i modelowania systemów Cyganek & Kasperek & Rajda 2013 Katedra Elektroniki AGH Zagadnienia
Kierunek Elektronika i Telekomunikacja, Studia II stopnia Specjalność: Systemy wbudowane Metodyki projektowania i modelowania systemów Cyganek & Kasperek & Rajda 2013 Katedra Elektroniki AGH Zagadnienia
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume Issue 2 DOI: /amm
 A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 60 2015 Issue 2 DOI: 10.1515/amm-2015-0183 J. PEZDA, EFFECT OF THE T6 HEAT TREATMENT ON CHANGE OF MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF THE AlSi12CuNiMg
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 60 2015 Issue 2 DOI: 10.1515/amm-2015-0183 J. PEZDA, EFFECT OF THE T6 HEAT TREATMENT ON CHANGE OF MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF THE AlSi12CuNiMg
WPŁYW GRUBOŚCI ŚCIANKI ODLEWU NA MORFOLOGIĘ WĘGLIKÓW W STOPIE WYSOKOCHROMOWYM
 3/4 Archives of Foundry, Year 2002, Volume 2, 4 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2002, Rocznik 2, Nr 4 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 WPŁYW GRUBOŚCI ŚCIANKI ODLEWU NA MORFOLOGIĘ WĘGLIKÓW W STOPIE WYSOKOCHROMOWYM
3/4 Archives of Foundry, Year 2002, Volume 2, 4 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2002, Rocznik 2, Nr 4 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 WPŁYW GRUBOŚCI ŚCIANKI ODLEWU NA MORFOLOGIĘ WĘGLIKÓW W STOPIE WYSOKOCHROMOWYM
WPŁYW WARUNKÓW UTWARDZANIA I GRUBOŚCI UTWARDZONEJ WARSTEWKI NA WYTRZYMAŁOŚĆ NA ROZCIĄGANIE ŻYWICY SYNTETYCZNEJ
 61/2 Archives of Foundry, Year 21, Volume 1, 1 (2/2) Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 21, Rocznik 1, Nr 1 (2/2) PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-58 WPŁYW WARUNKÓW UTWARDZANIA I GRUBOŚCI UTWARDZONEJ WARSTEWKI NA WYTRZYMAŁOŚĆ
61/2 Archives of Foundry, Year 21, Volume 1, 1 (2/2) Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 21, Rocznik 1, Nr 1 (2/2) PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-58 WPŁYW WARUNKÓW UTWARDZANIA I GRUBOŚCI UTWARDZONEJ WARSTEWKI NA WYTRZYMAŁOŚĆ
ROZPRAWY NR 128. Stanis³aw Mroziñski
 UNIWERSYTET TECHNOLOGICZNO-PRZYRODNICZY IM. JANA I JÊDRZEJA ŒNIADECKICH W BYDGOSZCZY ROZPRAWY NR 128 Stanis³aw Mroziñski STABILIZACJA W ASNOŒCI CYKLICZNYCH METALI I JEJ WP YW NA TRWA OŒÆ ZMÊCZENIOW BYDGOSZCZ
UNIWERSYTET TECHNOLOGICZNO-PRZYRODNICZY IM. JANA I JÊDRZEJA ŒNIADECKICH W BYDGOSZCZY ROZPRAWY NR 128 Stanis³aw Mroziñski STABILIZACJA W ASNOŒCI CYKLICZNYCH METALI I JEJ WP YW NA TRWA OŒÆ ZMÊCZENIOW BYDGOSZCZ
Wpływ powłoki Al Si na proces wytwarzania i jakość zgrzewanych aluminiowanych rur stalowych
 Akademia Górniczo-Hutnicza im. Stanisława Staszica w Krakowie Wpływ powłoki Al Si na proces wytwarzania i jakość zgrzewanych aluminiowanych rur stalowych The influence of Al Si coating on the manufacturing
Akademia Górniczo-Hutnicza im. Stanisława Staszica w Krakowie Wpływ powłoki Al Si na proces wytwarzania i jakość zgrzewanych aluminiowanych rur stalowych The influence of Al Si coating on the manufacturing
THE INFLUENCE OF REMELTING PARAMETERS ON Mg ALLOY/GLASSY CARBON SUSPENSION STABILITY
 14: 2 (2014) 96-100 Anita Olszówka-Myalska Silesian University of Technology, Department of Materials Science, ul. Krasińskiego 8, 40-019 Katowice, Poland * Corresponding author. E-mail: anita.olszowka-myalska@polsl.pl
14: 2 (2014) 96-100 Anita Olszówka-Myalska Silesian University of Technology, Department of Materials Science, ul. Krasińskiego 8, 40-019 Katowice, Poland * Corresponding author. E-mail: anita.olszowka-myalska@polsl.pl
Cracow University of Economics Poland. Overview. Sources of Real GDP per Capita Growth: Polish Regional-Macroeconomic Dimensions 2000-2005
 Cracow University of Economics Sources of Real GDP per Capita Growth: Polish Regional-Macroeconomic Dimensions 2000-2005 - Key Note Speech - Presented by: Dr. David Clowes The Growth Research Unit CE Europe
Cracow University of Economics Sources of Real GDP per Capita Growth: Polish Regional-Macroeconomic Dimensions 2000-2005 - Key Note Speech - Presented by: Dr. David Clowes The Growth Research Unit CE Europe
Proposal of thesis topic for mgr in. (MSE) programme in Telecommunications and Computer Science
 Proposal of thesis topic for mgr in (MSE) programme 1 Topic: Monte Carlo Method used for a prognosis of a selected technological process 2 Supervisor: Dr in Małgorzata Langer 3 Auxiliary supervisor: 4
Proposal of thesis topic for mgr in (MSE) programme 1 Topic: Monte Carlo Method used for a prognosis of a selected technological process 2 Supervisor: Dr in Małgorzata Langer 3 Auxiliary supervisor: 4
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 11. Spectral Embedding + Clustering
 Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 11 Spectral Embedding + Clustering MOTIVATING EXAMPLE What can you say from this network? MOTIVATING EXAMPLE How about now? THOUGHT EXPERIMENT For each
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 11 Spectral Embedding + Clustering MOTIVATING EXAMPLE What can you say from this network? MOTIVATING EXAMPLE How about now? THOUGHT EXPERIMENT For each
WŁAŚCIWOŚCI TRIBOLOGICZNE POWŁOK ELEKTROLITYCZNYCH ZE STOPÓW NIKLU PO OBRÓBCE CIEPLNEJ
 4-2011 T R I B O L O G I A 43 Bogdan BOGDAŃSKI *, Ewa KASPRZYCKA *,**, Jerzy SMOLIK ***, Jan TACIKOWSKI *, Jan SENATORSKI *, Wiktor GRZELECKI * WŁAŚCIWOŚCI TRIBOLOGICZNE POWŁOK ELEKTROLITYCZNYCH ZE STOPÓW
4-2011 T R I B O L O G I A 43 Bogdan BOGDAŃSKI *, Ewa KASPRZYCKA *,**, Jerzy SMOLIK ***, Jan TACIKOWSKI *, Jan SENATORSKI *, Wiktor GRZELECKI * WŁAŚCIWOŚCI TRIBOLOGICZNE POWŁOK ELEKTROLITYCZNYCH ZE STOPÓW
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume Issue 2 DOI: /amm
 A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 60 2015 Issue 2 DOI: 10.1515/amm-2015-0200 K. LANKIEWICZ,, M. BARANOWSKI, T. BABUL, S. KOWALSKI THE STUDY OF THE IMPACT OF SURFACE
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 60 2015 Issue 2 DOI: 10.1515/amm-2015-0200 K. LANKIEWICZ,, M. BARANOWSKI, T. BABUL, S. KOWALSKI THE STUDY OF THE IMPACT OF SURFACE
Wtrącenia niemetaliczne w staliwie topionym w małym piecu indukcyjnym
 A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (897-0) Volume Special Issue /0 9 97 8/ Wtrącenia
A R C H I V E S of F O U N D R Y E N G I N E E R I N G Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (897-0) Volume Special Issue /0 9 97 8/ Wtrącenia
MIKROSTRUKTURA NADSTOPÓW IN 519 PO PRZESYCANIU. W. JASIŃSKI Instytut Inżynierii Materiałowej, Politechnika Szczecińska Al. Piastów 17, 70-310 Szczecin
 26/12 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2004, Rocznik 4, Nr 12 Archives of Foundry Year 2004, Volume 4, Book 12 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 MIKROSTRUKTURA NADSTOPÓW IN 519 PO PRZESYCANIU W. JASIŃSKI Instytut
26/12 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2004, Rocznik 4, Nr 12 Archives of Foundry Year 2004, Volume 4, Book 12 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 MIKROSTRUKTURA NADSTOPÓW IN 519 PO PRZESYCANIU W. JASIŃSKI Instytut
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume Issue 2 DOI: /amm
 A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 59 2014 Issue 2 DOI: 10.2478/amm-2014-0113 J. ZYCH, J. WRÓBEL INFLUENCE OF THE SELECTED FACTORS ON THERMAL FATIGUE OF THE ADI IN AN
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 59 2014 Issue 2 DOI: 10.2478/amm-2014-0113 J. ZYCH, J. WRÓBEL INFLUENCE OF THE SELECTED FACTORS ON THERMAL FATIGUE OF THE ADI IN AN
MODYFIKACJA SILUMINÓW AK7 i AK9. F. ROMANKIEWICZ 1 Uniwersytet Zielonogórski, ul. Podgórna 50, Zielona Góra
 23/6 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2002, Rocznik 2, Nr 6 Archives of Foundry Year 2002, Volume 2, Book 6 PAN - Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 MODYFIKACJA SILUMINÓW AK7 i AK9 F. ROMANKIEWICZ 1 Uniwersytet Zielonogórski,
23/6 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2002, Rocznik 2, Nr 6 Archives of Foundry Year 2002, Volume 2, Book 6 PAN - Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 MODYFIKACJA SILUMINÓW AK7 i AK9 F. ROMANKIEWICZ 1 Uniwersytet Zielonogórski,
ZMIANA WYTRZYMAŁOŚCI NA ROZCIĄGANIE STOPU AlSi12 PO OBRÓBCE MIESZANKĄ EGZOTERMICZNĄ ZŁOŻONĄ Z Na 2 B 4 O 7, NaNO 3 I Mg
 44/22 Archives of Foundry, Year 2006, Volume 6, 22 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 22 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-508 ZMIANA WYTRZYMAŁOŚCI NA ROZCIĄGANIE STOPU AlSi12 PO OBRÓBCE MIESZANKĄ EGZOTERMICZNĄ
44/22 Archives of Foundry, Year 2006, Volume 6, 22 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 22 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-508 ZMIANA WYTRZYMAŁOŚCI NA ROZCIĄGANIE STOPU AlSi12 PO OBRÓBCE MIESZANKĄ EGZOTERMICZNĄ
MICROSTRUCTURE AND WEAR RESISTANCE OF STELLITE-6/WC METAL MATRIX COMPOSITE COATINGS
 Dariusz BARTKOWSKI 1, Grzegorz KINAL 1, Bartłomiej DUDZIAK 2, Adam PIASECKI 1, Waldemar MATYSIAK 1 1 Poznan University of Technology Pl. Marii Skłodowskiej-Curie 5, Poznań, Poland e-mail: dariusz.bartkowski@put.poznan.pl
Dariusz BARTKOWSKI 1, Grzegorz KINAL 1, Bartłomiej DUDZIAK 2, Adam PIASECKI 1, Waldemar MATYSIAK 1 1 Poznan University of Technology Pl. Marii Skłodowskiej-Curie 5, Poznań, Poland e-mail: dariusz.bartkowski@put.poznan.pl
OBRÓBKA CIEPLNA SILUMINU AK132
 52/22 Archives of Foundry, Year 2006, Volume 6, 22 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 22 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 OBRÓBKA CIEPLNA SILUMINU AK132 J. PEZDA 1 Akademia Techniczno-Humanistyczna
52/22 Archives of Foundry, Year 2006, Volume 6, 22 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 22 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 OBRÓBKA CIEPLNA SILUMINU AK132 J. PEZDA 1 Akademia Techniczno-Humanistyczna
OKREŚLENIE TEMPERATURY I ENTALPII PRZEMIAN FAZOWYCH W STOPACH Al-Si
 8/22 Archives of Foundry, Year 2006, Volume 6, 22 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 22 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 OKREŚLENIE TEMPERATURY I ENTALPII PRZEMIAN FAZOWYCH W STOPACH Al-Si F.
8/22 Archives of Foundry, Year 2006, Volume 6, 22 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 22 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 OKREŚLENIE TEMPERATURY I ENTALPII PRZEMIAN FAZOWYCH W STOPACH Al-Si F.
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume Issue 3 DOI: /v
 A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 56 2011 Issue 3 DOI: 10.2478/v10172-011-0087-8 J. KARWAN-BACZEWSKA THE PROPERTIES OF Fe-Ni-Mo-Cu-B MATERIALS PRODUCED VIA LIQUID PHASE
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 56 2011 Issue 3 DOI: 10.2478/v10172-011-0087-8 J. KARWAN-BACZEWSKA THE PROPERTIES OF Fe-Ni-Mo-Cu-B MATERIALS PRODUCED VIA LIQUID PHASE
Has the heat wave frequency or intensity changed in Poland since 1950?
 Has the heat wave frequency or intensity changed in Poland since 1950? Joanna Wibig Department of Meteorology and Climatology, University of Lodz, Poland OUTLINE: Motivation Data Heat wave frequency measures
Has the heat wave frequency or intensity changed in Poland since 1950? Joanna Wibig Department of Meteorology and Climatology, University of Lodz, Poland OUTLINE: Motivation Data Heat wave frequency measures
NOWE ODLEWNICZE STOPY Mg-Al-RE
 25/18 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 18 (1/2) ARCHIVES OF FOUNDRY Year 2006, Volume 6, N o 18 (1/2) PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 NOWE ODLEWNICZE STOPY Mg-Al-RE T. RZYCHOŃ 1, A. KIEŁBUS
25/18 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 18 (1/2) ARCHIVES OF FOUNDRY Year 2006, Volume 6, N o 18 (1/2) PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 NOWE ODLEWNICZE STOPY Mg-Al-RE T. RZYCHOŃ 1, A. KIEŁBUS
 www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
Mikrostruktura, struktura magnetyczna oraz właściwości magnetyczne amorficznych i częściowo skrystalizowanych stopów Fe, Co i Ni
 mgr inż. Jakub Rzącki Praca doktorska p.t.: Mikrostruktura, struktura magnetyczna oraz właściwości magnetyczne amorficznych i częściowo skrystalizowanych stopów Fe, Co i Ni STRESZCZENIE W pracy przedstawiono
mgr inż. Jakub Rzącki Praca doktorska p.t.: Mikrostruktura, struktura magnetyczna oraz właściwości magnetyczne amorficznych i częściowo skrystalizowanych stopów Fe, Co i Ni STRESZCZENIE W pracy przedstawiono
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume Issue 1 DOI: /amm
 A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 59 2014 Issue 1 DOI: 10.2478/amm-2014-0066 S. DZIK, W. TARGOWSKI RESEARCH OF LIQUID ALUMINIUM ALLOYS AT PARTICULAR STAGES OF MANUFACTURING
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 59 2014 Issue 1 DOI: 10.2478/amm-2014-0066 S. DZIK, W. TARGOWSKI RESEARCH OF LIQUID ALUMINIUM ALLOYS AT PARTICULAR STAGES OF MANUFACTURING
INVESTIGATION OF SCREWS FOUND IN WILHELM ORE MINE
 Key words: cast steel, puddled steel, ore mine, steel screw Andrzej ŻAK * INVESTIGATION OF SCREWS FOUND IN WILHELM ORE MINE This article presents macro- and microscopic investigation of steel screws which
Key words: cast steel, puddled steel, ore mine, steel screw Andrzej ŻAK * INVESTIGATION OF SCREWS FOUND IN WILHELM ORE MINE This article presents macro- and microscopic investigation of steel screws which
PRACE INSTYTUTU ODLEWNICTWA TRANSACTIONS OF FOUNDRY RESEARCH INSTITUTE
 PRACE INSTYTUTU ODLEWNICTWA TRANSACTIONS OF FOUNDRY RESEARCH INSTITUTE Volume LIII Year 2013 Number 3 DOI: 10.7356/iod.2013.12 Korozja stali i żeliwa sferoidalnego ferrytycznego w ciekłej cynie Corrosion
PRACE INSTYTUTU ODLEWNICTWA TRANSACTIONS OF FOUNDRY RESEARCH INSTITUTE Volume LIII Year 2013 Number 3 DOI: 10.7356/iod.2013.12 Korozja stali i żeliwa sferoidalnego ferrytycznego w ciekłej cynie Corrosion
TECHNICAL CATALOGUE WHITEHEART MALLEABLE CAST IRON FITTINGS EE
 TECHNICAL CATALOGUE WHITEHEART MALLEABLE CAST IRON FITTINGS EE Poland GENERAL INFORMATION USE Whiteheart malleable cast iron fittings brand EE are used in threaded pipe joints, particularly in water, gas,
TECHNICAL CATALOGUE WHITEHEART MALLEABLE CAST IRON FITTINGS EE Poland GENERAL INFORMATION USE Whiteheart malleable cast iron fittings brand EE are used in threaded pipe joints, particularly in water, gas,
KRYSTALIZACJA I MIKROSTRUKTURA BRĄZU CuAl10Fe5Ni5 PO RAFINACJI
 55/17 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2005, Rocznik 5, Nr 17 Archives of Foundry Year 2005, Volume 5, Book 17 PAN - Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 KRYSTALIZACJA I MIKROSTRUKTURA BRĄZU CuAl10Fe5Ni5 PO RAFINACJI S.
55/17 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2005, Rocznik 5, Nr 17 Archives of Foundry Year 2005, Volume 5, Book 17 PAN - Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 KRYSTALIZACJA I MIKROSTRUKTURA BRĄZU CuAl10Fe5Ni5 PO RAFINACJI S.
SILUMIN OKOŁOEUTEKTYCZNY Z DODATKAMI Cr, Mo, W i Co
 17/38 Solidification of Metals and Alloys, No. 38, 1998 Krzepnięcie Metali i Stopów, nr 38, 1998 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 0208-9386 SILUMIN OKOŁOEUTEKTYCZNY Z DODATKAMI Cr, Mo, W i Co PIETROWSKI Stanisław,
17/38 Solidification of Metals and Alloys, No. 38, 1998 Krzepnięcie Metali i Stopów, nr 38, 1998 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 0208-9386 SILUMIN OKOŁOEUTEKTYCZNY Z DODATKAMI Cr, Mo, W i Co PIETROWSKI Stanisław,
Streszczenie rozprawy doktorskiej
 Doskonalenie pomiaru zawartości wody w produktach spożywczych z wykorzystaniem metody wagosuszarkowej bazującej na promieniowaniu IR mgr Sławomir Janas Streszczenie rozprawy doktorskiej Promotor pracy:
Doskonalenie pomiaru zawartości wody w produktach spożywczych z wykorzystaniem metody wagosuszarkowej bazującej na promieniowaniu IR mgr Sławomir Janas Streszczenie rozprawy doktorskiej Promotor pracy:
THE EFFECT OF THE METHOD OF POURING LIQUID METAL INTO MOULD ON MISRUN FORMATION IN THE CASTINGS MADE WITH LOST-WAX CASTING TECHNOLOGY
 A R C H I V E S O F M E C H A N I C A L T E C H N O L O G Y A N D A U T O M A T I O N Vol. 33 no. 4 2013 KRZYSZTOF GRZE KOWIAK, MARCIN WOJCIECHOWSKI KAMIL SYTEK THE EFFECT OF THE METHOD OF POURING LIQUID
A R C H I V E S O F M E C H A N I C A L T E C H N O L O G Y A N D A U T O M A T I O N Vol. 33 no. 4 2013 KRZYSZTOF GRZE KOWIAK, MARCIN WOJCIECHOWSKI KAMIL SYTEK THE EFFECT OF THE METHOD OF POURING LIQUID
FREZY PM; END MILLS PM
 FREZY PM; END MILLS PM DIN 327-B K, 844-A K-N www.fenes.com.pl DIN 327-B K D [e8] d [h8] I I 1 L 6 6 8 36 52 7 10 10 40 60 8 10 11 40 61 9 10 11 40 61 10 10 13 40 63 11 12 13 45 70 12 12 16 45 73 14 12
FREZY PM; END MILLS PM DIN 327-B K, 844-A K-N www.fenes.com.pl DIN 327-B K D [e8] d [h8] I I 1 L 6 6 8 36 52 7 10 10 40 60 8 10 11 40 61 9 10 11 40 61 10 10 13 40 63 11 12 13 45 70 12 12 16 45 73 14 12
OTRZYMYWANIE KOMPOZYTÓW METALOWO-CERAMICZNYCH METODAMI PLAZMOWYMI
 KOMPOZYTY (COMPOSITES) 1(21)1 Władysław Włosiński 1, Tomasz Chmielewski 2 Politechnika Warszawska, Instytut Technologii Materiałowych, ul. Narbutta 85, 2-542 Warszawa OTRZYMYWANIE KOMPOZYTÓW METALOWO-CERAMICZNYCH
KOMPOZYTY (COMPOSITES) 1(21)1 Władysław Włosiński 1, Tomasz Chmielewski 2 Politechnika Warszawska, Instytut Technologii Materiałowych, ul. Narbutta 85, 2-542 Warszawa OTRZYMYWANIE KOMPOZYTÓW METALOWO-CERAMICZNYCH
WPŁYW WANADU NA KSZTAŁTOWANIE STRUKTURY ŻELIWA
 93/18 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 18 (2/2) ARCHIVES OF FOUNDRY Year 2006, Volume 6, N o 18 (2/2) PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 WPŁYW WANADU NA KSZTAŁTOWANIE STRUKTURY ŻELIWA M. KAWALEC
93/18 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 18 (2/2) ARCHIVES OF FOUNDRY Year 2006, Volume 6, N o 18 (2/2) PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 WPŁYW WANADU NA KSZTAŁTOWANIE STRUKTURY ŻELIWA M. KAWALEC
BIOPHYSICS. Politechnika Łódzka, ul. Żeromskiego 116, Łódź, tel. (042)
 BIOPHYSICS Prezentacja multimedialna współfinansowana przez Unię Europejską w ramach Europejskiego Funduszu Społecznego w projekcie pt. Innowacyjna dydaktyka bez ograniczeń - zintegrowany rozwój Politechniki
BIOPHYSICS Prezentacja multimedialna współfinansowana przez Unię Europejską w ramach Europejskiego Funduszu Społecznego w projekcie pt. Innowacyjna dydaktyka bez ograniczeń - zintegrowany rozwój Politechniki
WARUNKI KRZEPNIĘCIA ODLEWÓW Z SILUMINÓW, A PARAMETRY MIKROSTRUKTURY
 /14 Archives of Foundry, Year 4, Volume 4, 14 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 4, Rocznik 4, Nr 14 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-58 WARUNKI KRZEPNIĘCIA ODLEWÓW Z SILUMINÓW, A PARAMETRY MIKROSTRUKTURY M. HAJKOWSKI
/14 Archives of Foundry, Year 4, Volume 4, 14 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 4, Rocznik 4, Nr 14 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-58 WARUNKI KRZEPNIĘCIA ODLEWÓW Z SILUMINÓW, A PARAMETRY MIKROSTRUKTURY M. HAJKOWSKI
 www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
PROCEEDINGS OF THE INSTITUTE OF VEHICLES 2(106)/2016 (12 pt)
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE INSTITUTE OF VEHICLES 2(106)/2016 Maciej Foremny 1, Szymon Gudowski 2, Michał Malesza 3, Henryk Bąkowski 4 TRIBOLOGICAL WEAR ESTIMATION OF THE ENGINE OILS USED IN DRIFTING 1. Introduction
PROCEEDINGS OF THE INSTITUTE OF VEHICLES 2(106)/2016 Maciej Foremny 1, Szymon Gudowski 2, Michał Malesza 3, Henryk Bąkowski 4 TRIBOLOGICAL WEAR ESTIMATION OF THE ENGINE OILS USED IN DRIFTING 1. Introduction
KONTROLA STALIWA GXCrNi72-32 METODĄ ATD
 54/14 Archives of Foundry, Year 2004, Volume 4, 14 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2004, Rocznik 4, Nr 14 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 KONTROLA STALIWA GXCrNi72-32 METODĄ ATD S. PIETROWSKI 1, G. GUMIENNY 2
54/14 Archives of Foundry, Year 2004, Volume 4, 14 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2004, Rocznik 4, Nr 14 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 KONTROLA STALIWA GXCrNi72-32 METODĄ ATD S. PIETROWSKI 1, G. GUMIENNY 2
Adres do korespondencji: Instytut Metalurgii i Inżynierii Materiałowej PAN, Kraków, ul. Reymonta 25
 Adres do korespondencji: Instytut Metalurgii i Inżynierii Materiałowej PAN, 30059 Kraków, ul. Reymonta 25 Tel.: (012) 295 28 86, pokój 10, fax: (012) 295 28 04 email: w.wajda@imim.pl Miejsca zatrudnienia
Adres do korespondencji: Instytut Metalurgii i Inżynierii Materiałowej PAN, 30059 Kraków, ul. Reymonta 25 Tel.: (012) 295 28 86, pokój 10, fax: (012) 295 28 04 email: w.wajda@imim.pl Miejsca zatrudnienia
MODYFIKACJA TYTANEM, BOREM I FOSFOREM SILUMINU AK20
 43/50 Solidification of Metais and Alloys, Year 2000, Volume 2. Book No. 43 Krzepnięcie Metali i Stopów, Rok 2000, Rocznik 2, Nr 43 PAN -Katowice PL ISSN 0208-9386 MODYFIKACJA TYTANEM, BOREM I FOSFOREM
43/50 Solidification of Metais and Alloys, Year 2000, Volume 2. Book No. 43 Krzepnięcie Metali i Stopów, Rok 2000, Rocznik 2, Nr 43 PAN -Katowice PL ISSN 0208-9386 MODYFIKACJA TYTANEM, BOREM I FOSFOREM
WPŁYW WANADU I MOLIBDENU ORAZ OBRÓBKI CIEPLNEJ STALIWA Mn-Ni DLA UZYSKANIA GRANICY PLASTYCZNOŚCI POWYŻEJ 850 MPa
 7/8 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2003, Rocznik 3, Nr 8 Archives of Foundry Year 2003, Volume 3, Book 8 PAN - Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 WPŁYW WANADU I MOLIBDENU ORAZ OBRÓBKI CIEPLNEJ STALIWA Mn-Ni DLA UZYSKANIA
7/8 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2003, Rocznik 3, Nr 8 Archives of Foundry Year 2003, Volume 3, Book 8 PAN - Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 WPŁYW WANADU I MOLIBDENU ORAZ OBRÓBKI CIEPLNEJ STALIWA Mn-Ni DLA UZYSKANIA
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume Issue 1 DOI: /v y
 A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 57 2012 Issue 1 DOI: 10.2478/v10172-011-0149-y G. BOCZKAL, P. MARECKI, M. PEREK-NOWAK THE INFLUENCE OF SOLDERING CONDITIONS ON CONDUCTIVITY,
A R C H I V E S O F M E T A L L U R G Y A N D M A T E R I A L S Volume 57 2012 Issue 1 DOI: 10.2478/v10172-011-0149-y G. BOCZKAL, P. MARECKI, M. PEREK-NOWAK THE INFLUENCE OF SOLDERING CONDITIONS ON CONDUCTIVITY,
LISTA PUBLIKACJI PAKIETU BADAWCZEGO KCM 1
 Projekt: Kompozyty i Nanokompozyty Ceramiczno-Metalowe dla Przemysłu Lotniczego i Samochodowego (akronim: KomCerMet) współfinansowany jest ze środków Europejskiego Funduszu Rozwoju Regionalnego w ramach
Projekt: Kompozyty i Nanokompozyty Ceramiczno-Metalowe dla Przemysłu Lotniczego i Samochodowego (akronim: KomCerMet) współfinansowany jest ze środków Europejskiego Funduszu Rozwoju Regionalnego w ramach
Characteristic of DTA curves for cast ferrous alloys
 ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 8 Issue 1/2008 183 197 37/1 Characteristic of DTA curves
ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 8 Issue 1/2008 183 197 37/1 Characteristic of DTA curves
STRUKTURA I POROWATOŚĆ ODLEWÓW ZE STOPU ALUMINIUM A WŁAŚCIWOŚCI MECHANICZNE
 4/22 Archives of Foundry, Year 26, Volume 6, 22 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 26, Rocznik 6, Nr 22 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-538 STRUKTURA I POROWATOŚĆ ODLEWÓW ZE STOPU ALUMINIUM A WŁAŚCIWOŚCI MECHANICZNE
4/22 Archives of Foundry, Year 26, Volume 6, 22 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 26, Rocznik 6, Nr 22 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-538 STRUKTURA I POROWATOŚĆ ODLEWÓW ZE STOPU ALUMINIUM A WŁAŚCIWOŚCI MECHANICZNE
KS-342 IKS-342 Pirometr monochromatyczny podczerwieni KS-342 KS-342 jest wyprodukowany by kontrolować i regulować temperaturę topnienia poprzez bezkon
 KS-342 IKS-342 Pirometr monochromatyczny podczerwieni KS-342 KS-342 jest wyprodukowany by kontrolować i regulować temperaturę topnienia poprzez bezkontaktowe mierzenie temperatury. Podwójny wyświetlacz
KS-342 IKS-342 Pirometr monochromatyczny podczerwieni KS-342 KS-342 jest wyprodukowany by kontrolować i regulować temperaturę topnienia poprzez bezkontaktowe mierzenie temperatury. Podwójny wyświetlacz
Fig 5 Spectrograms of the original signal (top) extracted shaft-related GAD components (middle) and
 Fig 4 Measured vibration signal (top). Blue original signal. Red component related to periodic excitation of resonances and noise. Green component related. Rotational speed profile used for experiment
Fig 4 Measured vibration signal (top). Blue original signal. Red component related to periodic excitation of resonances and noise. Green component related. Rotational speed profile used for experiment
Conception of reuse of the waste from onshore and offshore in the aspect of
 Conception of reuse of the waste from onshore and offshore in the aspect of environmental protection" Koncepcja zagospodarowania odpadów wiertniczych powstających podczas wierceń lądowych i morskich w
Conception of reuse of the waste from onshore and offshore in the aspect of environmental protection" Koncepcja zagospodarowania odpadów wiertniczych powstających podczas wierceń lądowych i morskich w
AFTER LONG-TERM OPERATION IN CREEP CONDITIONS FOR THE POWER INDUSTRY
 2 Prace Instytutu Metalurgii Żelaza 2018, 70 (2), s. 2 18 DOI: 10.32730/imz.0137-9941.18.2.01 Tadeusz JÓŹWIK EFFECT OF AUSTENITISING ON THE STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES OF LOW-ALLOY Cr-Mo-V STEELS AFTER LONG-TERM
2 Prace Instytutu Metalurgii Żelaza 2018, 70 (2), s. 2 18 DOI: 10.32730/imz.0137-9941.18.2.01 Tadeusz JÓŹWIK EFFECT OF AUSTENITISING ON THE STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES OF LOW-ALLOY Cr-Mo-V STEELS AFTER LONG-TERM
EKOLOGICZNA MODYFIKACJA STOPU AlSi7Mg
 13/18 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 18 (1/2) ARCHIVES OF FOUNDRY Year 2006, Volume 6, N o 18 (1/2) PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 EKOLOGICZNA MODYFIKACJA STOPU AlSi7Mg T. LIPIŃSKI 1 Uniwersytet
13/18 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 18 (1/2) ARCHIVES OF FOUNDRY Year 2006, Volume 6, N o 18 (1/2) PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 EKOLOGICZNA MODYFIKACJA STOPU AlSi7Mg T. LIPIŃSKI 1 Uniwersytet
GEOMETRIA NADTOPIEŃ I STRUKTURA USZLACHETNIONYCH POWIERZCHNIOWO ODLEWÓW Z NADEUTEKTYCZNEGO STOPU Al-Si
 25/17 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2005, Rocznik 5, Nr 17 Archives of Foundry Year 2005, Volume 5, Book 17 PAN - Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 GEOMETRIA NADTOPIEŃ I STRUKTURA USZLACHETNIONYCH POWIERZCHNIOWO ODLEWÓW
25/17 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 2005, Rocznik 5, Nr 17 Archives of Foundry Year 2005, Volume 5, Book 17 PAN - Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 GEOMETRIA NADTOPIEŃ I STRUKTURA USZLACHETNIONYCH POWIERZCHNIOWO ODLEWÓW
WŁAŚCIWOŚCI MECHANICZNE KOMPOZYTÓW AlSi13Cu2- WŁÓKNA WĘGLOWE WYTWARZANYCH METODĄ ODLEWANIA CIŚNIENIOWEGO
 31/14 Archives of Foundry, Year 2004, Volume 4, 14 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2004, Rocznik 4, Nr 14 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 WŁAŚCIWOŚCI MECHANICZNE KOMPOZYTÓW AlSi13Cu2- WŁÓKNA WĘGLOWE WYTWARZANYCH
31/14 Archives of Foundry, Year 2004, Volume 4, 14 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2004, Rocznik 4, Nr 14 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 WŁAŚCIWOŚCI MECHANICZNE KOMPOZYTÓW AlSi13Cu2- WŁÓKNA WĘGLOWE WYTWARZANYCH
MICROSTRUCTURE AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF A SIMILAR T24 STEEL WELDED JOINT AFTER SERVICE
 Prace Instytutu Metalurgii Żelaza 2018, 70 (2), s. 37 41 37 Agata MERDA, Grzegorz GOLAŃSKI, Paweł URBAŃCZYK, Klaudia KLIMASZEWSKA DOI: 10.32730/imz.0137-9941.18.2.04 MICROSTRUCTURE AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES
Prace Instytutu Metalurgii Żelaza 2018, 70 (2), s. 37 41 37 Agata MERDA, Grzegorz GOLAŃSKI, Paweł URBAŃCZYK, Klaudia KLIMASZEWSKA DOI: 10.32730/imz.0137-9941.18.2.04 MICROSTRUCTURE AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES
WŁASNOŚCI TRIBOLOGICZNE STOPÓW Z UKŁADU Ni-Ta-Al-M O DUŻEJ ZAWARTOŚCI WĘGLA
 3-2012 T R I B O L O G I A 21 Piotr BAŁA *, Janusz KRAWCZYK *, Marcin MADEJ * WŁASNOŚCI TRIBOLOGICZNE STOPÓW Z UKŁADU Ni-Ta-Al-M O DUŻEJ ZAWARTOŚCI WĘGLA THE TRIBOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF THE ALLOY FROM Ni-Ta-Al-M
3-2012 T R I B O L O G I A 21 Piotr BAŁA *, Janusz KRAWCZYK *, Marcin MADEJ * WŁASNOŚCI TRIBOLOGICZNE STOPÓW Z UKŁADU Ni-Ta-Al-M O DUŻEJ ZAWARTOŚCI WĘGLA THE TRIBOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF THE ALLOY FROM Ni-Ta-Al-M
SYMULACJA NUMERYCZNA KRZEPNIĘCIA KIEROWANEGO OCHŁADZALNIKAMI ZEWNĘTRZNYMI I WEWNĘTRZNYMI
 31/4 Archives of Foundry, Year 2002, Volume 2, 4 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2002, Rocznik 2, Nr 4 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 SYMULACJA NUMERYCZNA KRZEPNIĘCIA KIEROWANEGO OCHŁADZALNIKAMI ZEWNĘTRZNYMI
31/4 Archives of Foundry, Year 2002, Volume 2, 4 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2002, Rocznik 2, Nr 4 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 SYMULACJA NUMERYCZNA KRZEPNIĘCIA KIEROWANEGO OCHŁADZALNIKAMI ZEWNĘTRZNYMI
BADANIA MATERIAŁOWE ODLEWÓW GŁOWIC SILNIKÓW
 16/38 Solidification of Metals and Alloys, No. 38, 1998 Krzepnięcie Metali i Stopów, nr 38, 1998 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 0208-9386 BADANIA MATERIAŁOWE ODLEWÓW GŁOWIC SILNIKÓW ORŁOWICZ Władysław, OPIEKUN Zenon
16/38 Solidification of Metals and Alloys, No. 38, 1998 Krzepnięcie Metali i Stopów, nr 38, 1998 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 0208-9386 BADANIA MATERIAŁOWE ODLEWÓW GŁOWIC SILNIKÓW ORŁOWICZ Władysław, OPIEKUN Zenon
Mikrostruktura i właściwości mechaniczne nadstopu Inconel 625
 Obróbka Plastyczna Metali t. XXI nr 3 (2010) InŜynieria materiałowa w obróbce plastycznej Dr hab. inŝ. Zbigniew PAKIEŁA Politechnika Warszawska, Wydział InŜynierii Materiałowej, Warszawa Mikrostruktura
Obróbka Plastyczna Metali t. XXI nr 3 (2010) InŜynieria materiałowa w obróbce plastycznej Dr hab. inŝ. Zbigniew PAKIEŁA Politechnika Warszawska, Wydział InŜynierii Materiałowej, Warszawa Mikrostruktura
STRUKTURA WARSTWY WIERZCHNIEJ ODLEWU ZE STOPU KOBALTU KSZTAŁTOWANA PLAZMĄ ŁUKU ELEKTRYCZNEGO Z. A. OPIEKUN 1, S. GUT 2
 45/14 Archives of Foundry, Year 2004, Volume 4, 14 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2004, Rocznik 4, Nr 14 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 STRUKTURA WARSTWY WIERZCHNIEJ ODLEWU ZE STOPU KOBALTU KSZTAŁTOWANA PLAZMĄ
45/14 Archives of Foundry, Year 2004, Volume 4, 14 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2004, Rocznik 4, Nr 14 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 STRUKTURA WARSTWY WIERZCHNIEJ ODLEWU ZE STOPU KOBALTU KSZTAŁTOWANA PLAZMĄ
ANALIZA KRYSTALIZACJI STOPU AlMg (AG 51) METODĄ ATND
 18/22 Archives of Foundry, Year 2006, Volume 6, 22 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 22 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 ANALIZA KRYSTALIZACJI STOPU AlMg (AG 51) METODĄ ATND T. CIUĆKA 1 Katedra
18/22 Archives of Foundry, Year 2006, Volume 6, 22 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2006, Rocznik 6, Nr 22 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 ANALIZA KRYSTALIZACJI STOPU AlMg (AG 51) METODĄ ATND T. CIUĆKA 1 Katedra
H γ0 - the standard enthalpy of g phase. H β γ - the transition enthalpy of b to g
 H α0 - the standard enthalpy of a phase H β0 - the standard enthalpy of b phase H γ0 - the standard enthalpy of g phase H α β - the transition enthalpy of a to b phase at T t1 H β γ - the transition enthalpy
H α0 - the standard enthalpy of a phase H β0 - the standard enthalpy of b phase H γ0 - the standard enthalpy of g phase H α β - the transition enthalpy of a to b phase at T t1 H β γ - the transition enthalpy
P/M COMPOSITES OF Al-Si-Fe-Cu ALLOY WITH SiC PARTICLES HOT-EXTRUDED AFTER PRELIMINARY COMPACTION
 Kompozyty 11: 4 (211) 336-341 Marek Wojtaszek AGH University of Science and Technology, Faculty of Metals Engineering and Industrial Computer Science, al. Mickiewicza 3, 3-59 Kraków, Poland * Corresponding
Kompozyty 11: 4 (211) 336-341 Marek Wojtaszek AGH University of Science and Technology, Faculty of Metals Engineering and Industrial Computer Science, al. Mickiewicza 3, 3-59 Kraków, Poland * Corresponding
Krytyczne czynniki sukcesu w zarządzaniu projektami
 Seweryn SPAŁEK Krytyczne czynniki sukcesu w zarządzaniu projektami MONOGRAFIA Wydawnictwo Politechniki Śląskiej Gliwice 2004 SPIS TREŚCI WPROWADZENIE 5 1. ZARZĄDZANIE PROJEKTAMI W ORGANIZACJI 13 1.1. Zarządzanie
Seweryn SPAŁEK Krytyczne czynniki sukcesu w zarządzaniu projektami MONOGRAFIA Wydawnictwo Politechniki Śląskiej Gliwice 2004 SPIS TREŚCI WPROWADZENIE 5 1. ZARZĄDZANIE PROJEKTAMI W ORGANIZACJI 13 1.1. Zarządzanie
SEGREGATION REINFORCED PHASE IN AlSi/CrxCy COMPOSITE PRODUCED UNDER ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD
 Kompozyty 11: 4 (2011) 317-323 Anna Dulęba*, Mirosław Cholewa Silesian University of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Department of Foundry, ul. Towarowa 7, 44-100 Gliwice, Poland * Corresponding
Kompozyty 11: 4 (2011) 317-323 Anna Dulęba*, Mirosław Cholewa Silesian University of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Department of Foundry, ul. Towarowa 7, 44-100 Gliwice, Poland * Corresponding
