ON DELAMINATION THRESHOLD LOADS IN LOW VELOCITY IMPACT ON GLASS-CARBON/EPOXY COMPOSITES
|
|
|
- Alicja Beata Ciesielska
- 8 lat temu
- Przeglądów:
Transkrypt
1 KOMPOZYTY (COMPOSITES) 5(25)1 Krystyna Imielińska 1 Politechnika Gdańska, Wydział Mechaniczny, Katedra Inżynierii Materiałowej, ul. Narutowicza 11/12, Gdańsk Rafał Wojtyra 2 Politechnika Gdańska, Wydział Oceanotechniki i Okrętownictwa, Katedra Technik Głębinowych, ul. Narutowicza 11/12, Gdańsk Marek Kozłowski 3 Politechnika Wrocławska, Instytut Inżynierii Ochrony Środowiska, Wybrzeże Wyspiańskiego 27, 5-37 Wrocław ON DELAMINATION THRESHOLD LOADS IN LOW VELOCITY IMPACT ON GLASS-CARBON/EPOXY COMPOSITES When a structure is accidentally impacted by an object, (e.g. by dropping a tool) it may be important to know if the impact is likely to cause serious damage in the structure. The easiest way to solve this is to compare the impact energy with the threshold impact energy of the structure. Thus, it is necessary to find the threshold impact energy of the structure which depends on the properties of the material and boundary conditions. In the present work the problem of delamination threshold load assessment was studied for epoxy laminates reinforced with woven glass-carbon laminates. The behaviour of symmetrical and unsymmetrical glass E/carbon C laminate was studied (E/C/E/C/E and E/E/C/E/C). Instrumented impact and static indentation tests were used. The rebound impact tests were conducted on the 1 mm square specimens in standard instrumented dropping weight tower Ceast Dartester. Indentation tests were performed using the same samples and supports geometry as in impact tests. The acoustic signal was used to assess the load and deflection corresponding to the first damage in the laminate. Damaged samples were examined using SEM. The approximate projected maximum delamination area was assessed and plotted against impact energy and maximum load (Fig. 6). The experimental results obtained in this work show (Figs 5, 6) that, similar to quasi-isotropic fibre reinforcement, for woven glass/carbon/epoxy laminates there exists a threshold impact load corresponding to a sudden jump of the area of delaminations from zero to a certain value (1 mm 2 ). The threshold impact energy was found 1.5 J independent of the glass fibre stacking sequence. The near-thethreshold damage in woven glass-carbon/epoxy laminates consists of delaminations and fibre/matrix debonding. Good correlation of the projected damage area obtained in this work for static (indentation) and impact measurements confirm that prediction of the threshold impact damage by quasi static tests instead of instrumented impact test is practical and useful. Key words: laminates, impact resistance, polymer composites BADANIA WARUNKÓW POWSTAWANIA DELAMINACJI W KOMPOZYTACH EPOKSYDOWYCH WZMOCNIONYCH WŁÓKNAMI SZKLANYMI I WĘGLOWYMI POD WPŁYWEM NISKOENERGETYCZNEGO UDARU Przedstawiono badania charakteru i rozmiaru zniszczeń w laminatach epoksydowych wzmocnionych włóknami węglowymi oraz szklanymi i węglowymi wywołanych przez udary o małej energii. Na podstawie dynamicznych charakterystyk obciążeń w funkcji czasu i odkształcenia płytek określano zależność pola delaminacji w funkcji obciążenia wywołującego te zniszczenia. Ze względu na konieczność posiadania młota spadowego z oprzyrządowaniem do prób dynamicznych badania takie są kłopotliwe. Jednak wyniki prób prowadzonych w zaawansowanych laboratoriach kompozytowych w Wlk. Brytanii i USA wskazują na możliwość wykorzystania badań przy obciążeniach quasi-statycznych o analogicznym układzie podpór i geometrii próbki do oceny progowych obciążeń wywołujących inicjację delaminacji w laminacie. Korzystając z takiej możliwości, porównano zniszczenia powstałe przy obciążeniach quasi-statycznych i udarowych (określonych przez maksymalne obciążenie P max). Posiadane dane z pomiarów dynamicznych o energii udaru wyższej od progowej umożliwiły identyfikację obciążenia wywołującego skokową inicjację delaminacji w laminacie epoksydowym o wzmocnieniu szklano-węglowym. Badania stanowią wprowadzenie do prognozowania obciążeń i energii wywołujących inicjację delaminacji w kompozytach warstwowych. Słowa kluczowe: laminaty, odporność udarowa, kompozyty polimerowe INTRODUCTION Impact induced damage, which may be undetectable by visual inspection, can have a significant effect on the strength, durability and stability of the structure. Much attention has been directed towards understanding the causes and failure mechanisms of delamination and towards developing techniques to improve the issue of delamination and impact damage. Numerous analytical and numerical methods have been proposed to predict 1 dr inż., 2 mgr inż., 3 prof. dr hab.
2 7 K. Imielińska, R. Wojtyra, M. Kozłowski damage development [1-4]. However, due to the complexity of the stress state in the vicinity of impact a general approach for predicting the initiation and propagation of damage during an impact event is absent. The load history for an impact event can yield important information concerning damage initiation and growth. It has been documented by several investigators that damage initiation is manifested in the load-time history as a sudden load drop due to loss of stiffness from unstable damage development [5, 6]. Subsequently, damage growth will arrest, the composite laminate will reload and a cycle of damage propagation and arrest occurs until the impactor begins to rebound and the laminate is unloaded. Several investigators [4, 6, 7] used load-displacement histories to compare structural responses from impact tests and incremental static test with equal maximum load. They found that although the dynamic load-displacement curves contain oscillations, both the dynamic and static responses had corresponding load drops due to failures in the laminates. Although the limits of the equivalence regime between static and impact tests remain to be determined [8] the loaddisplacement curves for static loading have been used to represent low velocity impact loading [5, 7, 9-11]. For a composite structure in engineering it is important to know what impact energy the structure can sustain without resulting in significant damage. On the other hand, when a structure is accidentally impacted by an object, e.g. by dropping a tool it may be important to know if the impact is likely to cause serious damage in the structure. The easiest way to solve this is to compare the impact energy with the threshold impact energy of the structure. Thus, it is necessary to find the threshold impact energy of the structure which depends on the properties of the material and boundary conditions. In research, in order to study the post-impact behaviour of a composite specimen at different levels of impact energy, the threshold impact energy for the onset of delaminations needs to be known [8, 12-14]. In the present work the problem of assessment of the threshold impact damage energy and load was studied for epoxy laminates reinforced with woven glass-carbon laminates using dynamic and static tests. suppliers. Laminates consisted of 5 plies of fabric impregnated with epoxy resin by hand lay-up. The resin was Epidian 52 (Organica-Sarzyna), typical Diglycidyl Ether of Bisphenol - A (DGEBA) cured with amine hardener ET (2 wt.%). The approximate fibre volume fraction was V f = 5%. The thickness was t = 2,3 2,9 mm. The following reinforcement architecture was used: 1) symmetrical - glass E/carbon C: E/C/E/C/E, 2) unsymmetrical E/E/C/E/C. The rebound impact tests were conducted on the 1 mm square specimens in standard instrumented dropping weight tower Ceast Dartester at three energy levels: 2.7, 5 and 9 J. The square laminate samples were clamped horizontally between the two plates with an inner diameter of 38 mm. The impactor tip was hemispherical type with a 12 mm diameter. The three specimens were tested for each material and impact energy. The load-time and load-displacement traces were recorded [15]. Alternatively, static indentation tests were performed using the same samples and supports geometry as in impact test. The acoustic signal was used to estimate the load and deflection corresponding to the first damage in the laminate. In order to estimate the impact damage size, in the absence of the instruments for non-destructive techniques (demonstrated by the authors in ref [18]), the simple (though time consuming) technique of microscopic examination of sample sections was used. Damaged samples were sectioned throughout the contact zone, polished and examined using SEM. The size of the most extensive delamination was assessed. Since the damage zone was circular the area of projected damage was estimated [16-18]. Figure 1 illustrates typical load-time plot for carbon/ epoxy laminate at impact energy 9 J showing change in the laminate stiffness (inflexion of the curve) due to the onset of impact damage. Arrow points to the load 35 N corresponding to the first crack (acoustic signal) found in the static indentation test (Fig. 2). However, no indentation or damage was observed on front or back face of the plate (Fig. 3a). 7 6 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS Materials used in this study were epoxy laminates reinforced with simple carbon and hybrid interlayer glass/carbon fibres. Laminates were fabricated from woven orthogonal balanced fibre fabrics: carbon (RC66T), E glass (STR 66-11). Carbon fibre fabric was supplied by SP Systems (UK) and glass fibre fabric - by Krosno, Poland. Standard pro-adhesive treatment of the fibres for use with epoxy resins was provided by the Load, N N,,5 1, 1,5 2, 2,5 3, Time, ms Fig. 1. Load-time plot for woven carbon/epoxy laminate
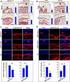
3 On delamination threshold loads in low velocity impact on glass-carbon/epoxy composites 71 Rys. 1. Wykres obciążenie-czas dla laminatu epoksydowego wzmocnionego tkaniną węglową load, N acoustic signal (cracking) impact 9JJ Similar tests were performed for two 5-ply glasse/ carbonc/epoxy laminates: symmetrical E/C/E/C/E and unsymmetrical E/E/C/E/C. Figures 4 and 5 show the dynamic and quasi static load-deflection plots corresponding to the impact 2.5 J for symmetrical laminate and 9 or 2.5 J (unsymmetrical laminate). Figures 4 and 5 show that, similar to carbon fibre composite (Fig. 2), the acoustic signal corresponding to the first laminate damage (arrow) points to the load at inflection in impact load deflection plot. 2 quasi-static deflection,mm Fig. 2. Load-deflection plots for impact and quasi static indentation tests on woven carbon fibre/epoxy laminate Rys. 2. Wykres obciążenie-odkształcenie dla laminatu epoksydowego wzmocnionego tkaniną węglową - obciążenie udarowe i quasi- -statyczne a) b) Load, N inflexion (damage onset) impact 9J indentation 2 4 Deflection, mm acoustic signal (cracking) Point of impact Point of impact Fig. 5. Load-deflection plots for dynamic and quasi static tests on unsymmetrical (E/E/C/E/C carbon-glass fibre/epoxy laminate Rys. 5. Wykres obciążenie-odkształcenie dla laminatu epoksydowego wzmocnionego tkaniną szklaną i węglową (układ niesymetryczny E/E/C/E/C), pomiar dynamiczny i quasi-statyczny Fig. 3. Front face of the carbon (a), glass/carbon/epoxy (b) plates, impact energy 2,5 J Rys. 3. Płaszczyzna uderzenia laminatu epoksydowego wzmocnionego tkaniną węglową (a), szklaną i węglową (b). Energia udaru 2,5 J Load, N carbon C/glass E E/C/E/C/E Deflection, mm acoustic signal(cracking) static Fig. 4. Load-deflection plots for dynamic and quasi static tests on symmetrical (E/C/E/C/E carbon-glass fibre/epoxy laminate. The plot is shifted to the left, due to delay in data acquisition Rys. 4. Wykres obciążenie-odkształcenie dla laminatu epoksydowego wzmocnionego tkaniną szklaną i węglową (układ symetryczny E/C/E/C/E), pomiar dynamiczny i quasi-statyczny. Wykres jest przesunięty w lewo na skutek opóźnienia w zapisie danych a) b) Impact damage area, mm 2 Projected impact damage area, mm threshold damage 1mm 2 1,5J impact damage indentation damage carbon C/glass E E/C/E/C/E Impact energy, J glass Threshold damage area 1mm 2 P threshold no perforation Maximum impact load, Pmax. N perforation
4 72 K. Imielińska, R. Wojtyra, M. Kozłowski Fig. 6. Projected damage area as a function of impact energy (a), maximum impact load (b) in carbon/glass/epoxy laminate Rys. 6. Wykres pola powierzchni zniszczeń w funkcji energii udaru (a), największego obciążenia (b) (próba dynamiczna i statyczna) w laminacie epoksydowym wzmocnionym włóknami szklanymi i węglowymi In static tests the machine was stopped and the sample removed when the first acoustic signal (corresponding to sample cracking) was registered. Damaged samples were sectioned at two perpendicular directions throughout the contact zone, polished and examined using SEM, similar to the impacted specimens. The approximate projected maximum delamination area was assessed [16-18]. The extension of the damage zone was measured and the projected damage area was plotted against impact energy (Fig. 6a). showing the extent of delamination formed under very low and high indentation load. It is evident that both the results of static and dynamic tests correlate well. Based on the experiments obtained in this work and of other investigators it may be concluded that static indentation tests may be the source of information about the threshold impact damage load. The morphology of the damaged sample was examined for impacted and statically loaded samples. Figure 7 shows typical features of undamaged and impact damaged (9 J) samples. For near-the-threshold impact loads the prevailing failure modes were the same: delaminations and matrix/fibre debonding (Fig. 8a). At higher impact (Figs 7b, 8b) energy delaminations were more extensive and numerous fibre breakage and ply cracks were observed. b) Carbon plies a) Transverse cracks delamination Glass plies Fig. 7. SEM images of undamaged (a), impact damaged (b) (9 J) carbon/ glass/epoxy sample Rys. 7. Obrazy SEM próbek laminatu epoksydowego o wzmocnieniu szklano-węglowym w stanie: nieuszkodzonym (a), po udarze o energii 9 J (b) Extensive delaminations a) 2,5J, P=23N Transverse cracks 9J, 5N Fibre fracture b) delaminations Fig. 8. Schematic of impact damage zone in carbon-glass/epoxy sample following impact 2.5 J (a), 9 J (b) Rys. 8. Schemat strefy zniszczeń udarowych w laminacie epoksydowym wzmocnionym tkaniną szklaną i węglową Figure 6b shows the relationship of impact damage and the peak impact load (found from dynamic load-time or deflection curves) which caused such a damage. In parallel the results of static (indentation) tests are plotted DISCUSSION The experimental results obtained in this work show (Fig. 6) that in woven glass/carbon/epoxy laminates
5 On delamination threshold loads in low velocity impact on glass-carbon/epoxy composites 73 studied under impact loading, there exists a threshold impact load 8 N (corresponding to the threshold impact energy 1,5 J). When the impact energy is above the threshold level, the delamination takes place instantaneously. This is by a sudden jump of the area of delaminations from zero to a certain value. When the impact energy is above the threshold level, the delamination area seems to increase continuously with the increase in the impact energy. However, the subsequent increase in delamination size with the increase in the impact energy is relatively slow. At high impact energies the considerable jump in damage area is observed. The same has been observed in glass and aramid- -glass/epoxy laminates subjected to impact [19]. Since the plates were transparent in the backlighting the internal delaminations were easily identified. Similar results were found in [9, 2]. For example for simply supported 125 mmx75 mm 2 mm quasi-isotropic laminate [1] the delamination size jumps to about 125 mm 2 at the threshold impact energy, whereas when the energy increases to twice the threshold level the damage area is about 175 mm 2. Jang-Kyo Kim [21] studied woven carbon fibre/epoxy laminates and found that the effect of threshold impact energy is also found in woven fibre reinforced laminate. These experiments demonstrated that the initial delamination corresponding to the threshold impact energy plays a vital role in the impact--induced damage an thus the threshold impact energy is an important parameter determining the resistance of a composite structure to impact [8]. The quasi static analysis gives a very accurate prediction of the maximum impact force for the considered laminates under low velocity impacts [8]. Based on this observation, for a given laboratory specimen of composite laminate or part made of a composite laminate in a real structure, the threshold impact energy for the onset of delamination can be predicted using a force driven, semi-empirical model proposed by Davies and Zhang [9, 12]. The model uses the Mode II strain energy release rate G IIC. The authors manufactured the ENF samples with artificial crack for glass and aramidglass fibre/epoxy laminates and assessed the G IIC [22] The prediction of the critical load for the onset of delamination based on these results and Davies s model is currently studied. CONCLUSIONS 1. The experimental results obtained in this work show that, similar to quasi-isotropic fibre reinforcement [1], for woven glass/carbon/epoxy laminates studied under impact loading there exists a threshold impact load (8 N) corresponding to a sudden jump of the area of delaminations from zero to a certain value (85 mm 2 ). 2. The threshold impact energy was found 1.5 J independent of the glass/carbon fibre stacking sequence. 3. The near-the-threshold damage in woven glass- -carbon/epoxy laminates consists of delaminations and fibre/matrix debonding. 4. The good correlation of the projected damage area obtained in this work for static (indentation) and impact measurements confirm that the prediction of the threshold impact damage by quasi static tests instead of instrumented impact is practical and useful. REFERENCES [1] Abrate S., Impact on laminated composite materials, Applied Mechanics Reviews 1991, 44, 4, [2] Abrate S., Impact on laminated composites: recent advances, Applied Mechanics Reviews 1994, 47(11), [3] Abrate S., Impact on composite structures, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge [4] Dear J.P., Brown S.A., Impact damage processes in reinforced polymeric materials, Composites: Part A 23, 34, [5] Lee S.M., Zahuta P., Instrumented impact and static indentation of composites, Journal of Composite Materials 1991, 25(2), 24. [6] Schoeppner G.A., Abrate S., Delamination threshold loads for low velocity impact on composite materials, Composites 2, 31, 9. [7] Kwon Y.S., Sankar B.V., Indentation-flexure and low velocity impact damage in graphite/epoxy laminates, Journal of Composites Technology and Research 1993, 15(2), [8] Davies G.A.O., Hitchings D., Wang J., Prediction of threshold impact energy for onset of delamination in quasiisotropic carbon/epoxy composite laminates under lowvelocity impact, Composites Science and Technology 2, 6, 1-7. [9] Davies G.A.O., Zhang X., Impact damage prediction in carbon composite structures, International Journal of Impact Engineering 1995, 16(1), [1] Wardle B.L., Lagace P.A., On the use of quasi-static test to asses impact damage resistance of composite shell structures, Mechanics of Composite Materials and Structures 1998, 5(1), [11] Legace P.A., Williamson J.E., Tsang P.H.W., Wolf E., Thomas S., A preliminary proposition for a test method to measure (impact)damage resistance, Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites 1993, 12(5), [12] Davies G.A.O., Zhang X., Zhou G., Watson S., Numerical modeling of impact damage, Composites 1994, 25(5), [13] Pavier M.J., Clarke M.P., Experimental techniques for the investigation of the effects of impact damage on carbonfibre composites, Composites Science and Technology 1995, 55(1), [14] Soutis C., Curtis P.T., Prediction of the post-impact compressive strength of CFRP laminated composites, Composites Science and Technology 1996, 56,
6 74 K. Imielińska, R. Wojtyra, M. Kozłowski [15] Imielińska K., Wojtyra R., Advanced laminate composites of improved impact tolerance, Kompozyty (Composites) 24, 4, 9, [16] Imielińska K, Wojtyra R., Udarowe pękanie hybrydowych kompozytów epoksydowych zbrojonych włóknami szklanymi, węglowymi i aramidowymi, Inżynieria Materiałowa 23, 3(134), [17] Bełzowski A., Degradacja mechaniczna kompozytów polimerowych metody oceny wytrzymałości długotrwałej i stopnia uszkodzenia, Oficyna Wydawnicza Politechniki Wrocławskiej, Wrocław 22. [18] Imielińska K., Castaings M., Wojtyra R., Haras J., Le Clezio E., Hosten B., Air-coupled ultrasonic C-scan technique in impact response testing of carbon fibre and hybrid: glass, carbon and Kevlar / epoxy composites, Journal of Materials Processing Technology 24, , [19] Imielińska K., Guillaumat L., The effect of water immersion ageing on low-velocity impact behaviour of woven aramid- -glass fibre/epoxy composites, Composites Science and Technology 24, 64, [2] Choi H.Y., Chang R-K., A model for predicting damage in graphite/epoxy laminated composites resulting from lowvelocity impact, Journal of Composite Materials 1992, 26, [21] Jang-Kyo Kim, Yiu-Wing Mai, High strength, high fracture toughness fibre composites with interface control - a review, Composites Science and Technology 1991, [22] Imielińska K., Badania energii oporu pękania interlaminarnego G IIC kompozytów polimerowych zbrojonych włóknem szklanym i aramidowym, Materiały i Technologie, Roczniki Naukowe Pomorskiego Oddzialu PTM 23, Nr 1(1), Recenzent Marian Klasztorny
INSPECTION METHODS FOR QUALITY CONTROL OF FIBRE METAL LAMINATES IN AEROSPACE COMPONENTS
 Kompozyty 11: 2 (2011) 130-135 Krzysztof Dragan 1 * Jarosław Bieniaś 2, Michał Sałaciński 1, Piotr Synaszko 1 1 Air Force Institute of Technology, Non Destructive Testing Lab., ul. ks. Bolesława 6, 01-494
Kompozyty 11: 2 (2011) 130-135 Krzysztof Dragan 1 * Jarosław Bieniaś 2, Michał Sałaciński 1, Piotr Synaszko 1 1 Air Force Institute of Technology, Non Destructive Testing Lab., ul. ks. Bolesława 6, 01-494
ENVIRONMENTAL STRESS CRACKING IN E-GLASS AND ARAMID/GLASS EPOXY COMPOSITES
 KOMPOZYTY (COMPOSITES) 6(2006)4 Krystyna Imielińska Politechnika Gdańska, Wydział Mechaniczny, Katedra Inżynierii Materiałowej, Narutowicza /2, 80-952 Gdańsk, e-mail: kimielin@pg.gda.pl ENVIRONMENTAL STRESS
KOMPOZYTY (COMPOSITES) 6(2006)4 Krystyna Imielińska Politechnika Gdańska, Wydział Mechaniczny, Katedra Inżynierii Materiałowej, Narutowicza /2, 80-952 Gdańsk, e-mail: kimielin@pg.gda.pl ENVIRONMENTAL STRESS
EFFECT OF TYPE OF REINFORCEMENT AND STACKING SEQUENCE ON LOW VELOCITY IMPACT DAMAGE TOLERANCE FOR HYBRID WOVEN CARBON, GLASS, KEVLAR-EPOXY LAMINATES
 KOMPOZYTY (COMPOSITES) 2(22)5 Krystyna Imielińska 1, Rafał Wojtyra 2 Politechnika Gdańska, ul. Narutowicza 11/12, 8-952 Gdańsk WPŁYW RODZAJU ZBROJENIA I KOLEJNOŚCI UŁOŻENIA WARSTW NA TOLERANCJĘ ZNISZCZEŃ
KOMPOZYTY (COMPOSITES) 2(22)5 Krystyna Imielińska 1, Rafał Wojtyra 2 Politechnika Gdańska, ul. Narutowicza 11/12, 8-952 Gdańsk WPŁYW RODZAJU ZBROJENIA I KOLEJNOŚCI UŁOŻENIA WARSTW NA TOLERANCJĘ ZNISZCZEŃ
Porównanie zdolności pochłaniania energii kompozytów winyloestrowych z epoksydowymi
 BIULETYN WAT VOL. LVII, NR 2, 2008 Porównanie zdolności pochłaniania energii kompozytów winyloestrowych z epoksydowymi STANISŁAW OCHELSKI, PAWEŁ GOTOWICKI Wojskowa Akademia Techniczna, Wydział Mechaniczny,
BIULETYN WAT VOL. LVII, NR 2, 2008 Porównanie zdolności pochłaniania energii kompozytów winyloestrowych z epoksydowymi STANISŁAW OCHELSKI, PAWEŁ GOTOWICKI Wojskowa Akademia Techniczna, Wydział Mechaniczny,
DETECTION OF MATERIAL INTEGRATED CONDUCTORS FOR CONNECTIVE RIVETING OF FUNCTION-INTEGRATIVE TEXTILE-REINFORCED THERMOPLASTIC COMPOSITES
 Kompozyty 11: 2 (2011) 152-156 Werner A. Hufenbach, Frank Adam, Maik Gude, Ivonne Körner, Thomas Heber*, Anja Winkler Technische Universität Dresden, Institute of Lightweight Engineering and Polymer Technology
Kompozyty 11: 2 (2011) 152-156 Werner A. Hufenbach, Frank Adam, Maik Gude, Ivonne Körner, Thomas Heber*, Anja Winkler Technische Universität Dresden, Institute of Lightweight Engineering and Polymer Technology
 aforementioned device she also has to estimate the time when the patients need the infusion to be replaced and/or disconnected. Meanwhile, however, she must cope with many other tasks. If the department
aforementioned device she also has to estimate the time when the patients need the infusion to be replaced and/or disconnected. Meanwhile, however, she must cope with many other tasks. If the department
WPŁYW ABSORPCJI WODY NA WŁAŚCIWOŚCI LAMINATÓW WINYLOESTROWYCH WZMOCNIONYCH WŁÓKNEM ARAMIDOWYM I SZKLANYM
 KOMPOZYTY (COMPOSITES) 3(003)7 Krystyna Imielińska 1 Politechnika Gdańska, Wydział Mechaniczny, ul. Narutowicza 11/1, 80-95 Gdańsk Rafał Wojtyra Politechnika Gdańska, Wydział Oceanotechniki i Okrętownictwa,
KOMPOZYTY (COMPOSITES) 3(003)7 Krystyna Imielińska 1 Politechnika Gdańska, Wydział Mechaniczny, ul. Narutowicza 11/1, 80-95 Gdańsk Rafał Wojtyra Politechnika Gdańska, Wydział Oceanotechniki i Okrętownictwa,
Towards Stability Analysis of Data Transport Mechanisms: a Fluid Model and an Application
 Towards Stability Analysis of Data Transport Mechanisms: a Fluid Model and an Application Gayane Vardoyan *, C. V. Hollot, Don Towsley* * College of Information and Computer Sciences, Department of Electrical
Towards Stability Analysis of Data Transport Mechanisms: a Fluid Model and an Application Gayane Vardoyan *, C. V. Hollot, Don Towsley* * College of Information and Computer Sciences, Department of Electrical
Metodyki projektowania i modelowania systemów Cyganek & Kasperek & Rajda 2013 Katedra Elektroniki AGH
 Kierunek Elektronika i Telekomunikacja, Studia II stopnia Specjalność: Systemy wbudowane Metodyki projektowania i modelowania systemów Cyganek & Kasperek & Rajda 2013 Katedra Elektroniki AGH Zagadnienia
Kierunek Elektronika i Telekomunikacja, Studia II stopnia Specjalność: Systemy wbudowane Metodyki projektowania i modelowania systemów Cyganek & Kasperek & Rajda 2013 Katedra Elektroniki AGH Zagadnienia
Tychy, plan miasta: Skala 1: (Polish Edition)
 Tychy, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000 (Polish Edition) Poland) Przedsiebiorstwo Geodezyjno-Kartograficzne (Katowice Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Tychy, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000
Tychy, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000 (Polish Edition) Poland) Przedsiebiorstwo Geodezyjno-Kartograficzne (Katowice Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Tychy, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000
Badanie wpływu poprzecznych obciążeń udarowych na właściwości wytrzymałościowe materiałów kompozytowych stosowanych w lotnictwie
 Dr inż. Andrzej Komorek Wyższa Szkoła Oficerska Sił Powietrznych ul. Dywizjonu 303 nr 12 08-521 Dęblin, Polska komman@op.pl Mgr inż. Paweł Przybyłek Wyższa Szkoła Oficerska Sił Powietrznych ul. Dywizjonu
Dr inż. Andrzej Komorek Wyższa Szkoła Oficerska Sił Powietrznych ul. Dywizjonu 303 nr 12 08-521 Dęblin, Polska komman@op.pl Mgr inż. Paweł Przybyłek Wyższa Szkoła Oficerska Sił Powietrznych ul. Dywizjonu
Akademia Morska w Szczecinie. Wydział Mechaniczny
 Akademia Morska w Szczecinie Wydział Mechaniczny ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA mgr inż. Marcin Kołodziejski Analiza metody obsługiwania zarządzanego niezawodnością pędników azymutalnych platformy pływającej Promotor:
Akademia Morska w Szczecinie Wydział Mechaniczny ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA mgr inż. Marcin Kołodziejski Analiza metody obsługiwania zarządzanego niezawodnością pędników azymutalnych platformy pływającej Promotor:
Fig 5 Spectrograms of the original signal (top) extracted shaft-related GAD components (middle) and
 Fig 4 Measured vibration signal (top). Blue original signal. Red component related to periodic excitation of resonances and noise. Green component related. Rotational speed profile used for experiment
Fig 4 Measured vibration signal (top). Blue original signal. Red component related to periodic excitation of resonances and noise. Green component related. Rotational speed profile used for experiment
Proposal of thesis topic for mgr in. (MSE) programme in Telecommunications and Computer Science
 Proposal of thesis topic for mgr in (MSE) programme 1 Topic: Monte Carlo Method used for a prognosis of a selected technological process 2 Supervisor: Dr in Małgorzata Langer 3 Auxiliary supervisor: 4
Proposal of thesis topic for mgr in (MSE) programme 1 Topic: Monte Carlo Method used for a prognosis of a selected technological process 2 Supervisor: Dr in Małgorzata Langer 3 Auxiliary supervisor: 4
EXAMPLES OF CABRI GEOMETRE II APPLICATION IN GEOMETRIC SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH
 Anna BŁACH Centre of Geometry and Engineering Graphics Silesian University of Technology in Gliwice EXAMPLES OF CABRI GEOMETRE II APPLICATION IN GEOMETRIC SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH Introduction Computer techniques
Anna BŁACH Centre of Geometry and Engineering Graphics Silesian University of Technology in Gliwice EXAMPLES OF CABRI GEOMETRE II APPLICATION IN GEOMETRIC SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH Introduction Computer techniques
4. EKSPLOATACJA UKŁADU NAPĘD ZWROTNICOWY ROZJAZD. DEFINICJA SIŁ W UKŁADZIE Siła nastawcza Siła trzymania
 3 SPIS TREŚCI Przedmowa... 11 1. WPROWADZENIE... 13 1.1. Budowa rozjazdów kolejowych... 14 1.2. Napędy zwrotnicowe... 15 1.2.1. Napęd zwrotnicowy EEA-4... 18 1.2.2. Napęd zwrotnicowy EEA-5... 20 1.3. Współpraca
3 SPIS TREŚCI Przedmowa... 11 1. WPROWADZENIE... 13 1.1. Budowa rozjazdów kolejowych... 14 1.2. Napędy zwrotnicowe... 15 1.2.1. Napęd zwrotnicowy EEA-4... 18 1.2.2. Napęd zwrotnicowy EEA-5... 20 1.3. Współpraca
Prof. dr hab. Barbara Surowska
 Raport wygenerowany z Bazy Publikacji Pracowników Politechniki Lubelskiej (01-12-2017 20:54:16) Publikacje w latach 2011-2014 dla autora: Prof. dr hab. Barbara Surowska Katedra Inżynierii Materiałowej
Raport wygenerowany z Bazy Publikacji Pracowników Politechniki Lubelskiej (01-12-2017 20:54:16) Publikacje w latach 2011-2014 dla autora: Prof. dr hab. Barbara Surowska Katedra Inżynierii Materiałowej
Lecture 18 Review for Exam 1
 Spring, 2019 ME 323 Mechanics of Materials Lecture 18 Review for Exam 1 Reading assignment: HW1-HW5 News: Ready for the exam? Instructor: Prof. Marcial Gonzalez Announcements Exam 1 - Wednesday February
Spring, 2019 ME 323 Mechanics of Materials Lecture 18 Review for Exam 1 Reading assignment: HW1-HW5 News: Ready for the exam? Instructor: Prof. Marcial Gonzalez Announcements Exam 1 - Wednesday February
OpenPoland.net API Documentation
 OpenPoland.net API Documentation Release 1.0 Michał Gryczka July 11, 2014 Contents 1 REST API tokens: 3 1.1 How to get a token............................................ 3 2 REST API : search for assets
OpenPoland.net API Documentation Release 1.0 Michał Gryczka July 11, 2014 Contents 1 REST API tokens: 3 1.1 How to get a token............................................ 3 2 REST API : search for assets
Wpływ uderzeń wielokrotnych na rozwój uszkodzenia kompozytów. polimerowych wzmacnianych włóknami
 Dr inż. Jarosław Bieniaś Prof. dr hab. Barbara Surowska Mgr inż. Patryk Jakubczak Katedra Inżynierii Materiałowej Wydział Mechaniczny Politechnika Lubelska Ul. Nadbystrzycka 36, 20-618 Lublin, Polska E-mail:
Dr inż. Jarosław Bieniaś Prof. dr hab. Barbara Surowska Mgr inż. Patryk Jakubczak Katedra Inżynierii Materiałowej Wydział Mechaniczny Politechnika Lubelska Ul. Nadbystrzycka 36, 20-618 Lublin, Polska E-mail:
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition)
 Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
Patients price acceptance SELECTED FINDINGS
 Patients price acceptance SELECTED FINDINGS October 2015 Summary With growing economy and Poles benefiting from this growth, perception of prices changes - this is also true for pharmaceuticals It may
Patients price acceptance SELECTED FINDINGS October 2015 Summary With growing economy and Poles benefiting from this growth, perception of prices changes - this is also true for pharmaceuticals It may
STATIC EXPERIMENTAL TESTING OF U-TYPE COMPOSITE SEGMENTS ENERGY ABSORPTION
 12: 3 (2012) 186-192 Paweł Gotowicki, Marian Klasztorny, Jerzy Małachowski, Daniel Nycz, Paweł Baranowski Military University of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Department of Mechanics and
12: 3 (2012) 186-192 Paweł Gotowicki, Marian Klasztorny, Jerzy Małachowski, Daniel Nycz, Paweł Baranowski Military University of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Department of Mechanics and
Zakopane, plan miasta: Skala ok. 1: = City map (Polish Edition)
 Zakopane, plan miasta: Skala ok. 1:15 000 = City map (Polish Edition) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Zakopane, plan miasta: Skala ok. 1:15 000 = City map (Polish Edition) Zakopane,
Zakopane, plan miasta: Skala ok. 1:15 000 = City map (Polish Edition) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Zakopane, plan miasta: Skala ok. 1:15 000 = City map (Polish Edition) Zakopane,
Hard-Margin Support Vector Machines
 Hard-Margin Support Vector Machines aaacaxicbzdlssnafiyn9vbjlepk3ay2gicupasvu4iblxuaw2hjmuwn7ddjjmxm1bkcg1/fjqsvt76fo9/gazqfvn8y+pjpozw5vx8zkpvtfxmlhcwl5zxyqrm2vrg5zw3vxmsoezi4ogkr6phieky5crvvjhriqvdom9l2xxftevuwcekj3lktmhghgniauiyutvrwxtvme34a77kbvg73gtygpjsrfati1+xc8c84bvraowbf+uwnipyehcvmkjrdx46vlykhkgykm3ujjdhcyzqkxy0chur6ax5cbg+1m4bbjptjcubuz4kuhvjoql93hkin5hxtav5x6yyqopnsyuneey5ni4keqrxbar5wqaxbik00icyo/iveiyqqvjo1u4fgzj/8f9x67bzmxnurjzmijtlybwfgcdjgfdtajwgcf2dwaj7ac3g1ho1n4814n7wwjgjmf/ys8fenfycuzq==
Hard-Margin Support Vector Machines aaacaxicbzdlssnafiyn9vbjlepk3ay2gicupasvu4iblxuaw2hjmuwn7ddjjmxm1bkcg1/fjqsvt76fo9/gazqfvn8y+pjpozw5vx8zkpvtfxmlhcwl5zxyqrm2vrg5zw3vxmsoezi4ogkr6phieky5crvvjhriqvdom9l2xxftevuwcekj3lktmhghgniauiyutvrwxtvme34a77kbvg73gtygpjsrfati1+xc8c84bvraowbf+uwnipyehcvmkjrdx46vlykhkgykm3ujjdhcyzqkxy0chur6ax5cbg+1m4bbjptjcubuz4kuhvjoql93hkin5hxtav5x6yyqopnsyuneey5ni4keqrxbar5wqaxbik00icyo/iveiyqqvjo1u4fgzj/8f9x67bzmxnurjzmijtlybwfgcdjgfdtajwgcf2dwaj7ac3g1ho1n4814n7wwjgjmf/ys8fenfycuzq==
WSTĘPNE MODELOWANIE ODDZIAŁYWANIA FALI CIŚNIENIA NA PÓŁSFERYCZNY ELEMENT KOMPOZYTOWY O ZMIENNEJ GRUBOŚCI
 WSTĘPNE MODELOWANIE ODDZIAŁYWANIA FALI CIŚNIENIA NA PÓŁSFERYCZNY ELEMENT KOMPOZYTOWY O ZMIENNEJ GRUBOŚCI Robert PANOWICZ Danuta MIEDZIŃSKA Tadeusz NIEZGODA Wiesław BARNAT Wojskowa Akademia Techniczna,
WSTĘPNE MODELOWANIE ODDZIAŁYWANIA FALI CIŚNIENIA NA PÓŁSFERYCZNY ELEMENT KOMPOZYTOWY O ZMIENNEJ GRUBOŚCI Robert PANOWICZ Danuta MIEDZIŃSKA Tadeusz NIEZGODA Wiesław BARNAT Wojskowa Akademia Techniczna,
FIBRE METAL LAMINATES - SOME ASPECTS OF MANUFACTURING PROCESS, STRUCTURE AND SELECTED PROPERTIES
 Kompozyty 11: 1 (2011) 39-43 Jarosław Bieniaś Lublin University of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Department of Materials Engineering, ul. Nadbystrzycka 36, 20-618 Lublin, Poland *Corresponding
Kompozyty 11: 1 (2011) 39-43 Jarosław Bieniaś Lublin University of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Department of Materials Engineering, ul. Nadbystrzycka 36, 20-618 Lublin, Poland *Corresponding
TECHNICAL CATALOGUE WHITEHEART MALLEABLE CAST IRON FITTINGS EE
 TECHNICAL CATALOGUE WHITEHEART MALLEABLE CAST IRON FITTINGS EE Poland GENERAL INFORMATION USE Whiteheart malleable cast iron fittings brand EE are used in threaded pipe joints, particularly in water, gas,
TECHNICAL CATALOGUE WHITEHEART MALLEABLE CAST IRON FITTINGS EE Poland GENERAL INFORMATION USE Whiteheart malleable cast iron fittings brand EE are used in threaded pipe joints, particularly in water, gas,
Rozpoznawanie twarzy metodą PCA Michał Bereta 1. Testowanie statystycznej istotności różnic między jakością klasyfikatorów
 Rozpoznawanie twarzy metodą PCA Michał Bereta www.michalbereta.pl 1. Testowanie statystycznej istotności różnic między jakością klasyfikatorów Wiemy, że możemy porównywad klasyfikatory np. za pomocą kroswalidacji.
Rozpoznawanie twarzy metodą PCA Michał Bereta www.michalbereta.pl 1. Testowanie statystycznej istotności różnic między jakością klasyfikatorów Wiemy, że możemy porównywad klasyfikatory np. za pomocą kroswalidacji.
ROZPRAWY NR 128. Stanis³aw Mroziñski
 UNIWERSYTET TECHNOLOGICZNO-PRZYRODNICZY IM. JANA I JÊDRZEJA ŒNIADECKICH W BYDGOSZCZY ROZPRAWY NR 128 Stanis³aw Mroziñski STABILIZACJA W ASNOŒCI CYKLICZNYCH METALI I JEJ WP YW NA TRWA OŒÆ ZMÊCZENIOW BYDGOSZCZ
UNIWERSYTET TECHNOLOGICZNO-PRZYRODNICZY IM. JANA I JÊDRZEJA ŒNIADECKICH W BYDGOSZCZY ROZPRAWY NR 128 Stanis³aw Mroziñski STABILIZACJA W ASNOŒCI CYKLICZNYCH METALI I JEJ WP YW NA TRWA OŒÆ ZMÊCZENIOW BYDGOSZCZ
A STUDY OF FAILURE ANALYSIS OF COMPOSITE PROFILE WITH OPEN CROSS-SECTION UNDER AXIAL COMPRESSION
 18: 4 (2018) 210-216 ISSN: 2084-6096 ISSN (online): 2299-128X Patryk Różyło Lublin University of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Department of Machine Design and Mechatronics, ul. Nadbystrzycka
18: 4 (2018) 210-216 ISSN: 2084-6096 ISSN (online): 2299-128X Patryk Różyło Lublin University of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Department of Machine Design and Mechatronics, ul. Nadbystrzycka
CEE 111/211 Agenda Feb 17
 CEE 111/211 Agenda Feb 17 Tuesday: SW for project work: Jetstream, MSP, Revit, Riuska, POP, SV On R: drive; takes time to install Acoustics today: \\cife server\files\classes\cee111\presentations Thursday:
CEE 111/211 Agenda Feb 17 Tuesday: SW for project work: Jetstream, MSP, Revit, Riuska, POP, SV On R: drive; takes time to install Acoustics today: \\cife server\files\classes\cee111\presentations Thursday:
QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE CHARACTERISTICS OF FINGERPRINT BIOMETRIC TEMPLATES
 ZESZYTY NAUKOWE POLITECHNIKI ŚLĄSKIEJ 2014 Seria: ORGANIZACJA I ZARZĄDZANIE z. 74 Nr kol. 1921 Adrian KAPCZYŃSKI Politechnika Śląska Instytut Ekonomii i Informatyki QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE CHARACTERISTICS
ZESZYTY NAUKOWE POLITECHNIKI ŚLĄSKIEJ 2014 Seria: ORGANIZACJA I ZARZĄDZANIE z. 74 Nr kol. 1921 Adrian KAPCZYŃSKI Politechnika Śląska Instytut Ekonomii i Informatyki QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE CHARACTERISTICS
Helena Boguta, klasa 8W, rok szkolny 2018/2019
 Poniższy zbiór zadań został wykonany w ramach projektu Mazowiecki program stypendialny dla uczniów szczególnie uzdolnionych - najlepsza inwestycja w człowieka w roku szkolnym 2018/2019. Składają się na
Poniższy zbiór zadań został wykonany w ramach projektu Mazowiecki program stypendialny dla uczniów szczególnie uzdolnionych - najlepsza inwestycja w człowieka w roku szkolnym 2018/2019. Składają się na
deep learning for NLP (5 lectures)
 TTIC 31210: Advanced Natural Language Processing Kevin Gimpel Spring 2019 Lecture 6: Finish Transformers; Sequence- to- Sequence Modeling and AJenKon 1 Roadmap intro (1 lecture) deep learning for NLP (5
TTIC 31210: Advanced Natural Language Processing Kevin Gimpel Spring 2019 Lecture 6: Finish Transformers; Sequence- to- Sequence Modeling and AJenKon 1 Roadmap intro (1 lecture) deep learning for NLP (5
WPŁYW WARUNKÓW UTWARDZANIA I GRUBOŚCI UTWARDZONEJ WARSTEWKI NA WYTRZYMAŁOŚĆ NA ROZCIĄGANIE ŻYWICY SYNTETYCZNEJ
 61/2 Archives of Foundry, Year 21, Volume 1, 1 (2/2) Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 21, Rocznik 1, Nr 1 (2/2) PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-58 WPŁYW WARUNKÓW UTWARDZANIA I GRUBOŚCI UTWARDZONEJ WARSTEWKI NA WYTRZYMAŁOŚĆ
61/2 Archives of Foundry, Year 21, Volume 1, 1 (2/2) Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 21, Rocznik 1, Nr 1 (2/2) PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-58 WPŁYW WARUNKÓW UTWARDZANIA I GRUBOŚCI UTWARDZONEJ WARSTEWKI NA WYTRZYMAŁOŚĆ
Cracow University of Economics Poland
 Cracow University of Economics Poland Sources of Real GDP per Capita Growth: Polish Regional-Macroeconomic Dimensions 2000-2005 - Keynote Speech - Presented by: Dr. David Clowes The Growth Research Unit,
Cracow University of Economics Poland Sources of Real GDP per Capita Growth: Polish Regional-Macroeconomic Dimensions 2000-2005 - Keynote Speech - Presented by: Dr. David Clowes The Growth Research Unit,
Zagadnienie odwrotne w pracach zespołu AGH. Prof. Tadeusz Uhl Katedra Robotyki i Mechatroniki Wydział InŜynierii Mechanicznej i Robotyki
 Zagadnienie odwrotne w pracach zespołu AGH Prof. Tadeusz Uhl Katedra Robotyki i Mechatroniki Wydział InŜynierii Mechanicznej i Robotyki Zagadnienia odwrotne Input Excitation Model Output Response Input
Zagadnienie odwrotne w pracach zespołu AGH Prof. Tadeusz Uhl Katedra Robotyki i Mechatroniki Wydział InŜynierii Mechanicznej i Robotyki Zagadnienia odwrotne Input Excitation Model Output Response Input
OCENA WYTRZYMAŁOŚCI RESZTKOWEJ ZSZYWANYCH LAMINATÓW ŻYWICA POLIESTROWA-WŁÓKNO SZKLANE
 KOMPOZYTY (COMPOSITES) 6(6) Mateusz Kozioł, Monika Rutecka, Józef Śleziona Politechnika Śląska, Katedra Technologii Stopów Metali i Kompozytów ul. Krasińskiego 8, 4-9 Katowice OCENA WYTRZYMAŁOŚCI RESZTKOWEJ
KOMPOZYTY (COMPOSITES) 6(6) Mateusz Kozioł, Monika Rutecka, Józef Śleziona Politechnika Śląska, Katedra Technologii Stopów Metali i Kompozytów ul. Krasińskiego 8, 4-9 Katowice OCENA WYTRZYMAŁOŚCI RESZTKOWEJ
Streszczenie pracy doktorskiej pt. Analiza zniszczenia laminatów metalowo-włóknistych w wyniku obciążenia dynamicznego z niską prędkością
 Mgr inż. Patryk Jakubczak Katedra inżynierii Materiałowej Politechnika Lubelska Lublin 19 XI 2012 Streszczenie pracy doktorskiej pt. Analiza zniszczenia laminatów metalowo-włóknistych w wyniku obciążenia
Mgr inż. Patryk Jakubczak Katedra inżynierii Materiałowej Politechnika Lubelska Lublin 19 XI 2012 Streszczenie pracy doktorskiej pt. Analiza zniszczenia laminatów metalowo-włóknistych w wyniku obciążenia
Knovel Math: Jakość produktu
 Knovel Math: Jakość produktu Knovel jest agregatorem materiałów pełnotekstowych dostępnych w formacie PDF i interaktywnym. Narzędzia interaktywne Knovel nie są stworzone wokół specjalnych algorytmów wymagających
Knovel Math: Jakość produktu Knovel jest agregatorem materiałów pełnotekstowych dostępnych w formacie PDF i interaktywnym. Narzędzia interaktywne Knovel nie są stworzone wokół specjalnych algorytmów wymagających
DEGRADACJA WŁAŚCIWOŚCI WYTRZYMAŁOŚCIOWYCH KOMPOZYTÓW POLIMEROWYCH WZMACNIANYCH WŁÓKNAMI WĘGLOWYMI POD WPŁYWEM OBCIĄŻEŃ DYNAMICZNYCH
 KOMPOZYTY (COMPOSITES) 6(26)2 Mirosław Rodzewicz 1 Politechnika Warszawska, Instytut Techniki Lotniczej i Mechaniki Stosowanej, ul. Nowowiejska 24, -665 Warszawa, e-mail: miro@meil.pw.edu.pl Anna Boczkowska
KOMPOZYTY (COMPOSITES) 6(26)2 Mirosław Rodzewicz 1 Politechnika Warszawska, Instytut Techniki Lotniczej i Mechaniki Stosowanej, ul. Nowowiejska 24, -665 Warszawa, e-mail: miro@meil.pw.edu.pl Anna Boczkowska
PROCEEDINGS OF THE INSTITUTE OF VEHICLES 2(106)/2016 (12 pt)
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE INSTITUTE OF VEHICLES 2(106)/2016 Maciej Foremny 1, Szymon Gudowski 2, Michał Malesza 3, Henryk Bąkowski 4 TRIBOLOGICAL WEAR ESTIMATION OF THE ENGINE OILS USED IN DRIFTING 1. Introduction
PROCEEDINGS OF THE INSTITUTE OF VEHICLES 2(106)/2016 Maciej Foremny 1, Szymon Gudowski 2, Michał Malesza 3, Henryk Bąkowski 4 TRIBOLOGICAL WEAR ESTIMATION OF THE ENGINE OILS USED IN DRIFTING 1. Introduction
TTIC 31210: Advanced Natural Language Processing. Kevin Gimpel Spring Lecture 9: Inference in Structured Prediction
 TTIC 31210: Advanced Natural Language Processing Kevin Gimpel Spring 2019 Lecture 9: Inference in Structured Prediction 1 intro (1 lecture) Roadmap deep learning for NLP (5 lectures) structured prediction
TTIC 31210: Advanced Natural Language Processing Kevin Gimpel Spring 2019 Lecture 9: Inference in Structured Prediction 1 intro (1 lecture) Roadmap deep learning for NLP (5 lectures) structured prediction
Auditorium classes. Lectures
 Faculty of: Mechanical and Robotics Field of study: Mechatronic with English as instruction language Study level: First-cycle studies Form and type of study: Full-time studies Annual: 2016/2017 Lecture
Faculty of: Mechanical and Robotics Field of study: Mechatronic with English as instruction language Study level: First-cycle studies Form and type of study: Full-time studies Annual: 2016/2017 Lecture
WPŁYW PROCESU TARCIA NA ZMIANĘ MIKROTWARDOŚCI WARSTWY WIERZCHNIEJ MATERIAŁÓW POLIMEROWYCH
 WOJCIECH WIELEBA WPŁYW PROCESU TARCIA NA ZMIANĘ MIKROTWARDOŚCI WARSTWY WIERZCHNIEJ MATERIAŁÓW POLIMEROWYCH THE INFLUENCE OF FRICTION PROCESS FOR CHANGE OF MICROHARDNESS OF SURFACE LAYER IN POLYMERIC MATERIALS
WOJCIECH WIELEBA WPŁYW PROCESU TARCIA NA ZMIANĘ MIKROTWARDOŚCI WARSTWY WIERZCHNIEJ MATERIAŁÓW POLIMEROWYCH THE INFLUENCE OF FRICTION PROCESS FOR CHANGE OF MICROHARDNESS OF SURFACE LAYER IN POLYMERIC MATERIALS
Efekty cieplne w procesie dynamicznego niszczenia kompozytów polimerowych
 Bi u l e t y n WAT Vo l. LX, Nr 4, 2011 Efekty cieplne w procesie dynamicznego niszczenia kompozytów polimerowych Stanisław Ochelski, Paweł Bogusz Wojskowa Akademia Techniczna, Wydział Mechaniczny, Katedra
Bi u l e t y n WAT Vo l. LX, Nr 4, 2011 Efekty cieplne w procesie dynamicznego niszczenia kompozytów polimerowych Stanisław Ochelski, Paweł Bogusz Wojskowa Akademia Techniczna, Wydział Mechaniczny, Katedra
Sargent Opens Sonairte Farmers' Market
 Sargent Opens Sonairte Farmers' Market 31 March, 2008 1V8VIZSV7EVKIRX8(1MRMWXIVSJ7XEXIEXXLI(ITEVXQIRXSJ%KVMGYPXYVI *MWLIVMIWERH*SSHTIVJSVQIHXLISJJMGMEPSTIRMRKSJXLI7SREMVXI*EVQIVW 1EVOIXMR0E]XS[R'S1IEXL
Sargent Opens Sonairte Farmers' Market 31 March, 2008 1V8VIZSV7EVKIRX8(1MRMWXIVSJ7XEXIEXXLI(ITEVXQIRXSJ%KVMGYPXYVI *MWLIVMIWERH*SSHTIVJSVQIHXLISJJMGMEPSTIRMRKSJXLI7SREMVXI*EVQIVW 1EVOIXMR0E]XS[R'S1IEXL
Raport bieżący: 44/2018 Data: g. 21:03 Skrócona nazwa emitenta: SERINUS ENERGY plc
 Raport bieżący: 44/2018 Data: 2018-05-23 g. 21:03 Skrócona nazwa emitenta: SERINUS ENERGY plc Temat: Zawiadomienie o zmianie udziału w ogólnej liczbie głosów w Serinus Energy plc Podstawa prawna: Inne
Raport bieżący: 44/2018 Data: 2018-05-23 g. 21:03 Skrócona nazwa emitenta: SERINUS ENERGY plc Temat: Zawiadomienie o zmianie udziału w ogólnej liczbie głosów w Serinus Energy plc Podstawa prawna: Inne
BADANIE PRZEBIEGU ZNISZCZENIA ZSZYWANYCH KOMPOZYTÓW POLIMER-WŁÓKNO SZKLANE PRZY ZGINANIU ZA POMOCĄ REJESTRACJI SYGNAŁU EMISJI AKUSTYCZNEJ
 KOMPOZYTY (COMPOSITES) 5(5)3 Mateusz Kozioł 1, Izabella Hyla 2 Politechnika Śląska, Wydział Inżynierii Materiałowej i Metalurgii, Katedra Technologii Stopów Metali i Kompozytów ul. Krasińskiego 8, -19
KOMPOZYTY (COMPOSITES) 5(5)3 Mateusz Kozioł 1, Izabella Hyla 2 Politechnika Śląska, Wydział Inżynierii Materiałowej i Metalurgii, Katedra Technologii Stopów Metali i Kompozytów ul. Krasińskiego 8, -19
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 11. Spectral Embedding + Clustering
 Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 11 Spectral Embedding + Clustering MOTIVATING EXAMPLE What can you say from this network? MOTIVATING EXAMPLE How about now? THOUGHT EXPERIMENT For each
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 11 Spectral Embedding + Clustering MOTIVATING EXAMPLE What can you say from this network? MOTIVATING EXAMPLE How about now? THOUGHT EXPERIMENT For each
IMPACT DAMAGE IN POLYESTER-MATRIX GLASS FIBRE-REINFORCED COMPOSITES. PART I. IMPACT DAMAGE EXTENT
 Kompozyty 11: 3 (2011) 230-234 Michał Barcikowski 1 *, Bartosz Semczyszyn 2 1 West Pomeranian University of Technology, Polymer Institute, Division of Polymer Materials Technology, ul. Pułaskiego 10, 70-322
Kompozyty 11: 3 (2011) 230-234 Michał Barcikowski 1 *, Bartosz Semczyszyn 2 1 West Pomeranian University of Technology, Polymer Institute, Division of Polymer Materials Technology, ul. Pułaskiego 10, 70-322
AKADEMIA MORSKA W SZCZECINIE WYDZIAŁ MECHANICZNY ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA. mgr inż. Piotr Smurawski
 AKADEMIA MORSKA W SZCZECINIE WYDZIAŁ MECHANICZNY ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA mgr inż. Piotr Smurawski ANALIZA CYKLU ŻYCIA SAMOCHODÓW OSOBOWYCH Z UWZGLĘDNIENIEM PROCESÓW OBSŁUGOWO-NAPRAWCZYCH Praca wykonana pod
AKADEMIA MORSKA W SZCZECINIE WYDZIAŁ MECHANICZNY ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA mgr inż. Piotr Smurawski ANALIZA CYKLU ŻYCIA SAMOCHODÓW OSOBOWYCH Z UWZGLĘDNIENIEM PROCESÓW OBSŁUGOWO-NAPRAWCZYCH Praca wykonana pod
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF CRACKING PROCESS OF POLYMER COMPOSITES ON EXAMPLE OF SENB SAMPLE
 Kompozyty 11: 4 (2011) 299-303 Dariusz Kwiatkowski 1*, Hubert Dębski 2 1 Czestochowa University of Technology, Institute of Polymer Processing and Production Management, Armii Krajowej 19c, 42-201 Częstochowa,
Kompozyty 11: 4 (2011) 299-303 Dariusz Kwiatkowski 1*, Hubert Dębski 2 1 Czestochowa University of Technology, Institute of Polymer Processing and Production Management, Armii Krajowej 19c, 42-201 Częstochowa,
MaPlan Sp. z O.O. Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically
 Mierzeja Wislana, mapa turystyczna 1:50 000: Mikoszewo, Jantar, Stegna, Sztutowo, Katy Rybackie, Przebrno, Krynica Morska, Piaski, Frombork =... = Carte touristique (Polish Edition) MaPlan Sp. z O.O Click
Mierzeja Wislana, mapa turystyczna 1:50 000: Mikoszewo, Jantar, Stegna, Sztutowo, Katy Rybackie, Przebrno, Krynica Morska, Piaski, Frombork =... = Carte touristique (Polish Edition) MaPlan Sp. z O.O Click
Weronika Mysliwiec, klasa 8W, rok szkolny 2018/2019
 Poniższy zbiór zadań został wykonany w ramach projektu Mazowiecki program stypendialny dla uczniów szczególnie uzdolnionych - najlepsza inwestycja w człowieka w roku szkolnym 2018/2019. Tresci zadań rozwiązanych
Poniższy zbiór zadań został wykonany w ramach projektu Mazowiecki program stypendialny dla uczniów szczególnie uzdolnionych - najlepsza inwestycja w człowieka w roku szkolnym 2018/2019. Tresci zadań rozwiązanych
Zarządzanie sieciami telekomunikacyjnymi
 SNMP Protocol The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an application layer protocol that facilitates the exchange of management information between network devices. It is part of the Transmission
SNMP Protocol The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an application layer protocol that facilitates the exchange of management information between network devices. It is part of the Transmission
LOAD BEARING CAPACITY OF WOODEN BEAMS REINFORCED WITH COMPOSITE SHEETS
 PAWEŁ KOSSAKOWSKI Kielce University of Technology Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering al. Tysiąclecia Państwa Polskiego 7 25-314 Kielce, Poland e-mail: kossak@tu.kielce.pl LOAD BEARING CAPACITY
PAWEŁ KOSSAKOWSKI Kielce University of Technology Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering al. Tysiąclecia Państwa Polskiego 7 25-314 Kielce, Poland e-mail: kossak@tu.kielce.pl LOAD BEARING CAPACITY
MICHAŁ BAKALARZ PAWEŁ KOSSAKOWSKI Kielce University of Technology
 Content from this work may be used under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 licence available on the site: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/pl Treści z tej pracy mogą być wykorzystywane
Content from this work may be used under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 licence available on the site: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/pl Treści z tej pracy mogą być wykorzystywane
Andrzej Katunin. Lista publikacji z dnia 31 października 2012
 Andrzej Katunin Lista publikacji z dnia 31 października 2012 I Książki i monografie: 1. Katunin A. 2012, Degradacja cieplna laminatów polimerowych, Wydawnictwo Instytutu Technologii Eksploatacji Państwowego
Andrzej Katunin Lista publikacji z dnia 31 października 2012 I Książki i monografie: 1. Katunin A. 2012, Degradacja cieplna laminatów polimerowych, Wydawnictwo Instytutu Technologii Eksploatacji Państwowego
Krytyczne czynniki sukcesu w zarządzaniu projektami
 Seweryn SPAŁEK Krytyczne czynniki sukcesu w zarządzaniu projektami MONOGRAFIA Wydawnictwo Politechniki Śląskiej Gliwice 2004 SPIS TREŚCI WPROWADZENIE 5 1. ZARZĄDZANIE PROJEKTAMI W ORGANIZACJI 13 1.1. Zarządzanie
Seweryn SPAŁEK Krytyczne czynniki sukcesu w zarządzaniu projektami MONOGRAFIA Wydawnictwo Politechniki Śląskiej Gliwice 2004 SPIS TREŚCI WPROWADZENIE 5 1. ZARZĄDZANIE PROJEKTAMI W ORGANIZACJI 13 1.1. Zarządzanie
Few-fermion thermometry
 Few-fermion thermometry Phys. Rev. A 97, 063619 (2018) Tomasz Sowiński Institute of Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences Co-authors: Marcin Płodzień Rafał Demkowicz-Dobrzański FEW-BODY PROBLEMS FewBody.ifpan.edu.pl
Few-fermion thermometry Phys. Rev. A 97, 063619 (2018) Tomasz Sowiński Institute of Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences Co-authors: Marcin Płodzień Rafał Demkowicz-Dobrzański FEW-BODY PROBLEMS FewBody.ifpan.edu.pl
Cracow University of Economics Poland. Overview. Sources of Real GDP per Capita Growth: Polish Regional-Macroeconomic Dimensions 2000-2005
 Cracow University of Economics Sources of Real GDP per Capita Growth: Polish Regional-Macroeconomic Dimensions 2000-2005 - Key Note Speech - Presented by: Dr. David Clowes The Growth Research Unit CE Europe
Cracow University of Economics Sources of Real GDP per Capita Growth: Polish Regional-Macroeconomic Dimensions 2000-2005 - Key Note Speech - Presented by: Dr. David Clowes The Growth Research Unit CE Europe
 www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
BARIERA ANTYKONDENSACYJNA
 Skład Obróbka Parametry techniczne BARIERA ANTYKONDENSACYJNA Lama "Lama" sp. z o.o. sp. k Właściwość Metoda badania Wartość Jednostka włóknina poliestrowa + klej PSA + folia polietylenowa Samoprzylepna
Skład Obróbka Parametry techniczne BARIERA ANTYKONDENSACYJNA Lama "Lama" sp. z o.o. sp. k Właściwość Metoda badania Wartość Jednostka włóknina poliestrowa + klej PSA + folia polietylenowa Samoprzylepna
WPŁYW SORPCJI I DESORPCJI NA WŁASNOŚCI CIEPLNE I MECHANICZNE LAMINATÓW
 Łukasz WIERZBICKI, Andrzej PUSZ Politechnika Śląska Instytut Materiałów Inżynierskich i Biomedycznych e-mail: lukasz.wierzbicki@polsl.pl WPŁYW SORPCJI I DESORPCJI NA WŁASNOŚCI CIEPLNE I MECHANICZNE LAMINATÓW
Łukasz WIERZBICKI, Andrzej PUSZ Politechnika Śląska Instytut Materiałów Inżynierskich i Biomedycznych e-mail: lukasz.wierzbicki@polsl.pl WPŁYW SORPCJI I DESORPCJI NA WŁASNOŚCI CIEPLNE I MECHANICZNE LAMINATÓW
SSW1.1, HFW Fry #20, Zeno #25 Benchmark: Qtr.1. Fry #65, Zeno #67. like
 SSW1.1, HFW Fry #20, Zeno #25 Benchmark: Qtr.1 I SSW1.1, HFW Fry #65, Zeno #67 Benchmark: Qtr.1 like SSW1.2, HFW Fry #47, Zeno #59 Benchmark: Qtr.1 do SSW1.2, HFW Fry #5, Zeno #4 Benchmark: Qtr.1 to SSW1.2,
SSW1.1, HFW Fry #20, Zeno #25 Benchmark: Qtr.1 I SSW1.1, HFW Fry #65, Zeno #67 Benchmark: Qtr.1 like SSW1.2, HFW Fry #47, Zeno #59 Benchmark: Qtr.1 do SSW1.2, HFW Fry #5, Zeno #4 Benchmark: Qtr.1 to SSW1.2,
IDENTYFIKACJA I ANALIZA PARAMETRÓW GEOMETRYCZNYCH I MECHANICZNYCH KOŚCI MIEDNICZNEJ CZŁOWIEKA
 POLITECHNIKA ŚLĄSKA ZESZYTY NAUKOWE Nr 1651 Antoni JOHN SUB Gottingen 7 217 780 458 2005 A 3012 IDENTYFIKACJA I ANALIZA PARAMETRÓW GEOMETRYCZNYCH I MECHANICZNYCH KOŚCI MIEDNICZNEJ CZŁOWIEKA Gliwice 2004
POLITECHNIKA ŚLĄSKA ZESZYTY NAUKOWE Nr 1651 Antoni JOHN SUB Gottingen 7 217 780 458 2005 A 3012 IDENTYFIKACJA I ANALIZA PARAMETRÓW GEOMETRYCZNYCH I MECHANICZNYCH KOŚCI MIEDNICZNEJ CZŁOWIEKA Gliwice 2004
OPBOX ver USB 2.0 Mini Ultrasonic Box with Integrated Pulser and Receiver
 OPBOX ver.0 USB.0 Mini Ultrasonic Box with Integrated Pulser and Receiver Przedsiębiorstwo BadawczoProdukcyjne OPTEL Sp. z o.o. ul. Morelowskiego 30 PL59 Wrocław phone: +8 7 39 8 53 fax.: +8 7 39 8 5 email:
OPBOX ver.0 USB.0 Mini Ultrasonic Box with Integrated Pulser and Receiver Przedsiębiorstwo BadawczoProdukcyjne OPTEL Sp. z o.o. ul. Morelowskiego 30 PL59 Wrocław phone: +8 7 39 8 53 fax.: +8 7 39 8 5 email:
PRÓBY EKSPLOATACYJNE KOMPOZYTOWYCH WSTAWEK HAMULCOWYCH TOWAROWEGO
 PRACE NAUKOWE POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ z. 112 Transport 2016 Piotr Wasilewski FRIMATRAIL Frenoplast S.A. PRÓBY EKSPLOATACYJNE KOMPOZYTOWYCH WSTAWEK HAMULCOWYCH TYPU K TOWAROWEGO : Streszczenie: Dane zbierane
PRACE NAUKOWE POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ z. 112 Transport 2016 Piotr Wasilewski FRIMATRAIL Frenoplast S.A. PRÓBY EKSPLOATACYJNE KOMPOZYTOWYCH WSTAWEK HAMULCOWYCH TYPU K TOWAROWEGO : Streszczenie: Dane zbierane
NAPRĘŻENIA W HYBRYDOWYCH KOMPOZYTACH WARSTWOWYCH TYPU FML SPOWODOWANE ZMIANĄ TEMPERATURY
 Technologia i Automatyzacja Montażu 2/2014 NAPRĘŻENIA W HYBRYDOWYCH KOMPOZYTACH WARSTWOWYCH TYPU FML SPOWODOWANE ZMIANĄ TEMPERATURY Jan GODZIMIRSKI, Agata PIETRAS Streszczenie Analiza wytężenia połączeń
Technologia i Automatyzacja Montażu 2/2014 NAPRĘŻENIA W HYBRYDOWYCH KOMPOZYTACH WARSTWOWYCH TYPU FML SPOWODOWANE ZMIANĄ TEMPERATURY Jan GODZIMIRSKI, Agata PIETRAS Streszczenie Analiza wytężenia połączeń
BIOPHYSICS. Politechnika Łódzka, ul. Żeromskiego 116, Łódź, tel. (042)
 BIOPHYSICS Prezentacja multimedialna współfinansowana przez Unię Europejską w ramach Europejskiego Funduszu Społecznego w projekcie pt. Innowacyjna dydaktyka bez ograniczeń - zintegrowany rozwój Politechniki
BIOPHYSICS Prezentacja multimedialna współfinansowana przez Unię Europejską w ramach Europejskiego Funduszu Społecznego w projekcie pt. Innowacyjna dydaktyka bez ograniczeń - zintegrowany rozwój Politechniki
Tytuł pracy w języku angielskim: Microstructural characterization of Ag/X/Ag (X = Sn, In) joints obtained as the effect of diffusion soledering.
 Dr inż. Przemysław Skrzyniarz Kierownik pracy: Prof. dr hab. inż. Paweł Zięba Tytuł pracy w języku polskim: Charakterystyka mikrostruktury spoin Ag/X/Ag (X = Sn, In) uzyskanych w wyniku niskotemperaturowego
Dr inż. Przemysław Skrzyniarz Kierownik pracy: Prof. dr hab. inż. Paweł Zięba Tytuł pracy w języku polskim: Charakterystyka mikrostruktury spoin Ag/X/Ag (X = Sn, In) uzyskanych w wyniku niskotemperaturowego
DM-ML, DM-FL. Auxiliary Equipment and Accessories. Damper Drives. Dimensions. Descritpion
 DM-ML, DM-FL Descritpion DM-ML and DM-FL actuators are designed for driving round dampers and square multi-blade dampers. Example identification Product code: DM-FL-5-2 voltage Dimensions DM-ML-6 DM-ML-8
DM-ML, DM-FL Descritpion DM-ML and DM-FL actuators are designed for driving round dampers and square multi-blade dampers. Example identification Product code: DM-FL-5-2 voltage Dimensions DM-ML-6 DM-ML-8
INFLUENCE OF POLYESTER MACROFIBERS ON SELECTED PHYSICAL AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF CEMENT COMPOSITES
 15: 4 (2015) 250-254 Agnieszka Ślosarczyk*, Wojciech Wierzbicki Poznan University of Technology, Institute of Structural Engineering, ul. Piotrowo 5, 60-965 Poznań, Poland *Corresponding author. E-mail:
15: 4 (2015) 250-254 Agnieszka Ślosarczyk*, Wojciech Wierzbicki Poznan University of Technology, Institute of Structural Engineering, ul. Piotrowo 5, 60-965 Poznań, Poland *Corresponding author. E-mail:
BADANIA WYTRZYMA OŒCI NA ŒCISKANIE PRÓBEK Z TWORZYWA ABS DRUKOWANYCH W TECHNOLOGII FDM
 dr in. Marek GOŒCIAÑSKI, dr in. Bart³omiej DUDZIAK Przemys³owy Instytut Maszyn Rolniczych, Poznañ e-mail: office@pimr.poznan.pl BADANIA WYTRZYMA OŒCI NA ŒCISKANIE PRÓBEK Z TWORZYWA ABS DRUKOWANYCH W TECHNOLOGII
dr in. Marek GOŒCIAÑSKI, dr in. Bart³omiej DUDZIAK Przemys³owy Instytut Maszyn Rolniczych, Poznañ e-mail: office@pimr.poznan.pl BADANIA WYTRZYMA OŒCI NA ŒCISKANIE PRÓBEK Z TWORZYWA ABS DRUKOWANYCH W TECHNOLOGII
IDENTYFIKACJA PARAMETRÓW CHARAKTERYZUJĄCYCH OBCIĄŻENIE SEKCJI OBUDOWY ZMECHANIZOWANEJ SPOWODOWANE DYNAMICZNYM ODDZIAŁYWANIEM GÓROTWORU
 POLITECHNIKA ŚLĄSKA ZESZYTY NAUKOWE Nr 1648 Stanisław SZWEDA STJB Gottingen 217 808 00X IDENTYFIKACJA PARAMETRÓW CHARAKTERYZUJĄCYCH OBCIĄŻENIE SEKCJI OBUDOWY ZMECHANIZOWANEJ SPOWODOWANE DYNAMICZNYM ODDZIAŁYWANIEM
POLITECHNIKA ŚLĄSKA ZESZYTY NAUKOWE Nr 1648 Stanisław SZWEDA STJB Gottingen 217 808 00X IDENTYFIKACJA PARAMETRÓW CHARAKTERYZUJĄCYCH OBCIĄŻENIE SEKCJI OBUDOWY ZMECHANIZOWANEJ SPOWODOWANE DYNAMICZNYM ODDZIAŁYWANIEM
USZKODZENIA UDAROWE W LAMINACIE WZMOCNIONYM TKANINĄ SZKLANĄ
 KOMPOZYTY (COMPOSITES) 2(2002)5 Andrzej Bełzowski 1, Zdzisław Rechul 2, Jan Stasieńko 3 Politechnika Wrocławska, Wydział Mechaniczny, ul. Smoluchowskiego 25, 50-370 Wrocław USZKODZENIA UDAROWE W LAMINACIE
KOMPOZYTY (COMPOSITES) 2(2002)5 Andrzej Bełzowski 1, Zdzisław Rechul 2, Jan Stasieńko 3 Politechnika Wrocławska, Wydział Mechaniczny, ul. Smoluchowskiego 25, 50-370 Wrocław USZKODZENIA UDAROWE W LAMINACIE
DUAL SIMILARITY OF VOLTAGE TO CURRENT AND CURRENT TO VOLTAGE TRANSFER FUNCTION OF HYBRID ACTIVE TWO- PORTS WITH CONVERSION
 ELEKTRYKA 0 Zeszyt (9) Rok LX Andrzej KUKIEŁKA Politechnika Śląska w Gliwicach DUAL SIMILARITY OF VOLTAGE TO CURRENT AND CURRENT TO VOLTAGE TRANSFER FUNCTION OF HYBRID ACTIVE TWO- PORTS WITH CONVERSION
ELEKTRYKA 0 Zeszyt (9) Rok LX Andrzej KUKIEŁKA Politechnika Śląska w Gliwicach DUAL SIMILARITY OF VOLTAGE TO CURRENT AND CURRENT TO VOLTAGE TRANSFER FUNCTION OF HYBRID ACTIVE TWO- PORTS WITH CONVERSION
PORÓWNANIE WYBRANYCH MODELI DELAMINACJI W KOMPOZYTACH WARSTWOWYCH
 MODELOWANIE INŻYNIERSKIE ISNN 1896-771X 3, s. 113-118, Gliwice 006 PORÓWNANIE WYBRANYCH MODELI DELAMINACJI W KOMPOZYTACH WARSTWOWYCH ŁUKASZ DOLIŃSKI Katedra Wysokich Napięć i Aparatów Elektrycznych, Politechnika
MODELOWANIE INŻYNIERSKIE ISNN 1896-771X 3, s. 113-118, Gliwice 006 PORÓWNANIE WYBRANYCH MODELI DELAMINACJI W KOMPOZYTACH WARSTWOWYCH ŁUKASZ DOLIŃSKI Katedra Wysokich Napięć i Aparatów Elektrycznych, Politechnika
ANALIZA NUMERYCZNA DEFORMACJI WALCOWEJ PRÓBKI W ZDERZENIOWYM TEŚCIE TAYLORA
 Michał Grązka 1) ANALIZA NUMERYCZNA DEFORMACJI WALCOWEJ PRÓBKI W ZDERZENIOWYM TEŚCIE TAYLORA Streszczenie: Przedstawiony niżej artykuł jest poświęcony komputerowym badaniom deformacji próbki osiowo symetrycznej
Michał Grązka 1) ANALIZA NUMERYCZNA DEFORMACJI WALCOWEJ PRÓBKI W ZDERZENIOWYM TEŚCIE TAYLORA Streszczenie: Przedstawiony niżej artykuł jest poświęcony komputerowym badaniom deformacji próbki osiowo symetrycznej
WPŁYW OBCIĄŻEŃ ZMĘCZENIOWYCH NA WYSTĘPOWANIE ODMIAN POLIMORFICZNYCH PA6 Z WŁÓKNEM SZKLANYM
 92/21 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 26, Rocznik 6, Nr 21(2/2) ARCHIVES OF FOUNDARY Year 26, Volume 6, Nº 21 (2/2) PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-538 WPŁYW OBCIĄŻEŃ ZMĘCZENIOWYCH NA WYSTĘPOWANIE ODMIAN POLIMORFICZNYCH
92/21 ARCHIWUM ODLEWNICTWA Rok 26, Rocznik 6, Nr 21(2/2) ARCHIVES OF FOUNDARY Year 26, Volume 6, Nº 21 (2/2) PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-538 WPŁYW OBCIĄŻEŃ ZMĘCZENIOWYCH NA WYSTĘPOWANIE ODMIAN POLIMORFICZNYCH
Network Services for Spatial Data in European Geo-Portals and their Compliance with ISO and OGC Standards
 INSPIRE Conference 2010 INSPIRE as a Framework for Cooperation Network Services for Spatial Data in European Geo-Portals and their Compliance with ISO and OGC Standards Elżbieta Bielecka Agnieszka Zwirowicz
INSPIRE Conference 2010 INSPIRE as a Framework for Cooperation Network Services for Spatial Data in European Geo-Portals and their Compliance with ISO and OGC Standards Elżbieta Bielecka Agnieszka Zwirowicz
OdPORNOść LAmiNATU WęgLOWO-EPOkSYdOWEgO NA zmęczeniowy ROzWój ROzWARSTWiEń W WARUNkACh isp
 PRACE instytutu LOTNiCTWA 221, s. 18 25, Warszawa 2011 OdPORNOść LAmiNATU WęgLOWO-EPOkSYdOWEgO NA zmęczeniowy ROzWój ROzWARSTWiEń W WARUNkACh isp KamIla CzajKoWSKa, DaNIel Szeląg, zbigniew lorenc Instytut
PRACE instytutu LOTNiCTWA 221, s. 18 25, Warszawa 2011 OdPORNOść LAmiNATU WęgLOWO-EPOkSYdOWEgO NA zmęczeniowy ROzWój ROzWARSTWiEń W WARUNkACh isp KamIla CzajKoWSKa, DaNIel Szeląg, zbigniew lorenc Instytut
SG-MICRO... SPRĘŻYNY GAZOWE P.103
 SG-MICRO... SG-MICRO 19 SG-MICRO SG-MICRO H SG-MICRO R SG-MICRO 32 SG-MICRO 32H SG-MICRO 32R SG-MICRO SG-MICRO H SG-MICRO R SG-MICRO 45 SG-MICRO SG-MICRO SG-MICRO 75 SG-MICRO 95 SG-MICRO 0 cylindra body
SG-MICRO... SG-MICRO 19 SG-MICRO SG-MICRO H SG-MICRO R SG-MICRO 32 SG-MICRO 32H SG-MICRO 32R SG-MICRO SG-MICRO H SG-MICRO R SG-MICRO 45 SG-MICRO SG-MICRO SG-MICRO 75 SG-MICRO 95 SG-MICRO 0 cylindra body
Konsorcjum Śląskich Uczelni Publicznych
 Konsorcjum Śląskich Uczelni Publicznych Dlaczego powstało? - świat przeżywa dziś rewolucję w obszarze edukacji, - naszym celem jest promocja śląskiego jako regionu opartego na wiedzy, i najnowszych technologiach,
Konsorcjum Śląskich Uczelni Publicznych Dlaczego powstało? - świat przeżywa dziś rewolucję w obszarze edukacji, - naszym celem jest promocja śląskiego jako regionu opartego na wiedzy, i najnowszych technologiach,
WYKAZ PRÓB / SUMMARY OF TESTS. mgr ing. Janusz Bandel
 Sprawozdanie z Badań Nr Strona/Page 2/24 WYKAZ PRÓB / SUMMARY OF TESTS STRONA PAGE Próba uszkodzenia przy przepięciach dorywczych TOV failure test 5 Próby wykonał / The tests were carried out by: mgr ing.
Sprawozdanie z Badań Nr Strona/Page 2/24 WYKAZ PRÓB / SUMMARY OF TESTS STRONA PAGE Próba uszkodzenia przy przepięciach dorywczych TOV failure test 5 Próby wykonał / The tests were carried out by: mgr ing.
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture11. Random Projections & Canonical Correlation Analysis
 Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture11 5 Random Projections & Canonical Correlation Analysis The Tall, THE FAT AND THE UGLY n X d The Tall, THE FAT AND THE UGLY d X > n X d n = n d d The
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture11 5 Random Projections & Canonical Correlation Analysis The Tall, THE FAT AND THE UGLY n X d The Tall, THE FAT AND THE UGLY d X > n X d n = n d d The
WŁAŚCIWOŚCI MECHANICZNE KOMPOZYTÓW AlSi13Cu2- WŁÓKNA WĘGLOWE WYTWARZANYCH METODĄ ODLEWANIA CIŚNIENIOWEGO
 31/14 Archives of Foundry, Year 2004, Volume 4, 14 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2004, Rocznik 4, Nr 14 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 WŁAŚCIWOŚCI MECHANICZNE KOMPOZYTÓW AlSi13Cu2- WŁÓKNA WĘGLOWE WYTWARZANYCH
31/14 Archives of Foundry, Year 2004, Volume 4, 14 Archiwum Odlewnictwa, Rok 2004, Rocznik 4, Nr 14 PAN Katowice PL ISSN 1642-5308 WŁAŚCIWOŚCI MECHANICZNE KOMPOZYTÓW AlSi13Cu2- WŁÓKNA WĘGLOWE WYTWARZANYCH
INFLUENCE OF SELECTED METHOD TO ESTIMATE COMPOSITE MATERIAL ELASTICITY PROPERTIES ON RESULTS OF FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
 19: 1 (2019) 34-39 ISSN: 2084-6096 ISSN (online): 2299-128X Mateusz Juzuń Silesian University of Technology, Institute of Fundamentals of Machinery Design, ul. S. Konarskiego 18A, 44-100 Gliwice, Poland
19: 1 (2019) 34-39 ISSN: 2084-6096 ISSN (online): 2299-128X Mateusz Juzuń Silesian University of Technology, Institute of Fundamentals of Machinery Design, ul. S. Konarskiego 18A, 44-100 Gliwice, Poland
Radiologiczna ocena progresji zmian próchnicowych po zastosowaniu infiltracji. żywicą o niskiej lepkości (Icon). Badania in vivo.
 Renata Zielińska Radiologiczna ocena progresji zmian próchnicowych po zastosowaniu infiltracji żywicą o niskiej lepkości (Icon). Badania in vivo. Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych Zakład Stomatologii
Renata Zielińska Radiologiczna ocena progresji zmian próchnicowych po zastosowaniu infiltracji żywicą o niskiej lepkości (Icon). Badania in vivo. Rozprawa na stopień doktora nauk medycznych Zakład Stomatologii
 www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
Wybrzeze Baltyku, mapa turystyczna 1: (Polish Edition)
 Wybrzeze Baltyku, mapa turystyczna 1:50 000 (Polish Edition) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wybrzeze Baltyku, mapa turystyczna 1:50 000 (Polish Edition) Wybrzeze Baltyku, mapa
Wybrzeze Baltyku, mapa turystyczna 1:50 000 (Polish Edition) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wybrzeze Baltyku, mapa turystyczna 1:50 000 (Polish Edition) Wybrzeze Baltyku, mapa
STATISTICAL METHODS IN BIOLOGY
 STATISTICAL METHODS IN BIOLOGY 1. Introduction 2. Populations and samples 3. Hypotheses testing and parameter estimation 4. Experimental design for biological data 5. Most widely used statistical tests
STATISTICAL METHODS IN BIOLOGY 1. Introduction 2. Populations and samples 3. Hypotheses testing and parameter estimation 4. Experimental design for biological data 5. Most widely used statistical tests
ZGŁOSZENIE WSPÓLNEGO POLSKO -. PROJEKTU NA LATA: APPLICATION FOR A JOINT POLISH -... PROJECT FOR THE YEARS:.
 ZGŁOSZENIE WSPÓLNEGO POLSKO -. PROJEKTU NA LATA: APPLICATION FOR A JOINT POLISH -... PROJECT FOR THE YEARS:. W RAMACH POROZUMIENIA O WSPÓŁPRACY NAUKOWEJ MIĘDZY POLSKĄ AKADEMIĄ NAUK I... UNDER THE AGREEMENT
ZGŁOSZENIE WSPÓLNEGO POLSKO -. PROJEKTU NA LATA: APPLICATION FOR A JOINT POLISH -... PROJECT FOR THE YEARS:. W RAMACH POROZUMIENIA O WSPÓŁPRACY NAUKOWEJ MIĘDZY POLSKĄ AKADEMIĄ NAUK I... UNDER THE AGREEMENT
THEORETICAL STUDIES ON CHEMICAL SHIFTS OF 3,6 DIIODO 9 ETHYL 9H CARBAZOLE
 THEORETICAL STUDIES ON CHEMICAL SHIFTS OF 3,6 DIIODO 9 ETHYL 9H CARBAZOLE Teobald Kupkaa, Klaudia Radula-Janika, Krzysztof Ejsmonta, Zdzisław Daszkiewicza, Stephan P. A. Sauerb a Faculty of Chemistry,
THEORETICAL STUDIES ON CHEMICAL SHIFTS OF 3,6 DIIODO 9 ETHYL 9H CARBAZOLE Teobald Kupkaa, Klaudia Radula-Janika, Krzysztof Ejsmonta, Zdzisław Daszkiewicza, Stephan P. A. Sauerb a Faculty of Chemistry,
Analysis of Movie Profitability STAT 469 IN CLASS ANALYSIS #2
 Analysis of Movie Profitability STAT 469 IN CLASS ANALYSIS #2 aaaklnictzzjb9tgfmcnadpg7oy0lxa9edva9kkapdarhyk2k7gourinlwsweyzikuyiigvyleiv/cv767fpf/5crc1xt9va5mx7w3m/ecuqw1kuztpx/rl3/70h73/w4cog9dhhn3z62d6jzy+yzj766txpoir9nzszisjynetqr+rvlfvyoozu5xbybpsxb1wahul8phczdt2v4zgchb7uecwphlyigrgkjcyiflfyci0kxnmr4z6kw0jsokvot8isntpa3gbknlcufiv/h+hh+eur4fomd417rvtfjoit5pfju6yxiab2fmwk0y/feuybobqk+axnke8xzjjhfyd8kkpl9zdoddkazd5j6bzpemjb64smjb6vb4xmehysu08lsrszopxftlzee130jcb0zjxy7r5wa2f1s2off2+dyatrughnrtpkuprlcpu55zlxpss/yqe2eamjkcf0jye8w8yas0paf6t0t2i9stmcua+inbi2rt01tz22tubbqwidypvgz6piynkpobirkxgu54ibzoti4pkw2i5ow9lnuaoabhuxfxqhvnrj6w15tb3furnbm+scyxobjhr5pmj5j/w5ix9wsa2tlwx9alpshlunzjgnrwvqbpwzjl9wes+ptyn+ypy/jgskavtl8j0hz1djdhzwtpjbbvpr1zj7jpg6ve7zxfngj75zee0vmp9qm2uvgu/9zdofq6r+g8l4xctvo+v+xdrfr8oxiwutycu0qgyf8icuyvp/sixfi9zxe11vp6mrjjovpmxm6acrtbia+wjr9bevlgjwlz5xd3rfna9g06qytaoofk8olxbxc7xby2evqjmmk6pjvvzxmpbnct6+036xp5vdbrnbdqph8brlfn/n/khnfumhf6z1v7h/80yieukkd5j0un82t9mynxzmk0s/bzn4tacdziszdhwrl8x5ako8qp1n1zn0k6w2em0km9zj1i4yt1pt3xiprw85jmc2m1ut2geum6y6es2fwx6c+wlrpykblopbuj5nnr2byygfy5opllv4+jmm7s6u+tvhywbnb0kv2lt5th4xipmiij+y1toiyo7bo0d+vzvovjkp6aoejsubhj3qrp3fjd/m23pay8h218ibvx3nicofvd1xi86+kh6nb/b+hgsjp5+qwpurzlir15np66vmdehh6tyazdm1k/5ejtuvurgcqux6yc+qw/sbsaj7lkt4x9qmtp7euk6zbdedyuzu6ptsu2eeu3rxcz06uf6g8wyuveznhkbzynajbb7r7cbmla+jbtrst0ow2v6ntkwv8svnwqnu5pa3oxfeexf93739p93chq/fv+jr8r0d9brhpcxr2w88bvqbr41j6wvrb+u5dzjpvx+veoaxwptzp/8cen+xbg==
Analysis of Movie Profitability STAT 469 IN CLASS ANALYSIS #2 aaaklnictzzjb9tgfmcnadpg7oy0lxa9edva9kkapdarhyk2k7gourinlwsweyzikuyiigvyleiv/cv767fpf/5crc1xt9va5mx7w3m/ecuqw1kuztpx/rl3/70h73/w4cog9dhhn3z62d6jzy+yzj766txpoir9nzszisjynetqr+rvlfvyoozu5xbybpsxb1wahul8phczdt2v4zgchb7uecwphlyigrgkjcyiflfyci0kxnmr4z6kw0jsokvot8isntpa3gbknlcufiv/h+hh+eur4fomd417rvtfjoit5pfju6yxiab2fmwk0y/feuybobqk+axnke8xzjjhfyd8kkpl9zdoddkazd5j6bzpemjb64smjb6vb4xmehysu08lsrszopxftlzee130jcb0zjxy7r5wa2f1s2off2+dyatrughnrtpkuprlcpu55zlxpss/yqe2eamjkcf0jye8w8yas0paf6t0t2i9stmcua+inbi2rt01tz22tubbqwidypvgz6piynkpobirkxgu54ibzoti4pkw2i5ow9lnuaoabhuxfxqhvnrj6w15tb3furnbm+scyxobjhr5pmj5j/w5ix9wsa2tlwx9alpshlunzjgnrwvqbpwzjl9wes+ptyn+ypy/jgskavtl8j0hz1djdhzwtpjbbvpr1zj7jpg6ve7zxfngj75zee0vmp9qm2uvgu/9zdofq6r+g8l4xctvo+v+xdrfr8oxiwutycu0qgyf8icuyvp/sixfi9zxe11vp6mrjjovpmxm6acrtbia+wjr9bevlgjwlz5xd3rfna9g06qytaoofk8olxbxc7xby2evqjmmk6pjvvzxmpbnct6+036xp5vdbrnbdqph8brlfn/n/khnfumhf6z1v7h/80yieukkd5j0un82t9mynxzmk0s/bzn4tacdziszdhwrl8x5ako8qp1n1zn0k6w2em0km9zj1i4yt1pt3xiprw85jmc2m1ut2geum6y6es2fwx6c+wlrpykblopbuj5nnr2byygfy5opllv4+jmm7s6u+tvhywbnb0kv2lt5th4xipmiij+y1toiyo7bo0d+vzvovjkp6aoejsubhj3qrp3fjd/m23pay8h218ibvx3nicofvd1xi86+kh6nb/b+hgsjp5+qwpurzlir15np66vmdehh6tyazdm1k/5ejtuvurgcqux6yc+qw/sbsaj7lkt4x9qmtp7euk6zbdedyuzu6ptsu2eeu3rxcz06uf6g8wyuveznhkbzynajbb7r7cbmla+jbtrst0ow2v6ntkwv8svnwqnu5pa3oxfeexf93739p93chq/fv+jr8r0d9brhpcxr2w88bvqbr41j6wvrb+u5dzjpvx+veoaxwptzp/8cen+xbg==
Arch. Min. Sci., Vol. 57 (2012), No 4, p
 Arch. Min. Sci., Vol. 57 (2012), No 4, p. 831 842 Electronic version (in color) of this paper is available: http://mining.archives.pl 831 DOI 10.2478/v10267-012-0054-x STANISŁAW WOLNY* THE INFLUENCE OF
Arch. Min. Sci., Vol. 57 (2012), No 4, p. 831 842 Electronic version (in color) of this paper is available: http://mining.archives.pl 831 DOI 10.2478/v10267-012-0054-x STANISŁAW WOLNY* THE INFLUENCE OF
TTIC 31210: Advanced Natural Language Processing. Kevin Gimpel Spring Lecture 8: Structured PredicCon 2
 TTIC 31210: Advanced Natural Language Processing Kevin Gimpel Spring 2019 Lecture 8: Structured PredicCon 2 1 Roadmap intro (1 lecture) deep learning for NLP (5 lectures) structured predic+on (4 lectures)
TTIC 31210: Advanced Natural Language Processing Kevin Gimpel Spring 2019 Lecture 8: Structured PredicCon 2 1 Roadmap intro (1 lecture) deep learning for NLP (5 lectures) structured predic+on (4 lectures)
Analiza parametrów mechaniki pękania w warunkach I modelu obciążenia betonu
 Analiza parametrów mechaniki pękania w warunkach I modelu obciążenia betonu Anna Bernatowicz 1, Andrzej Kazberuk 2 Zeszyty Naukowe Politechniki Częstochowskiej nr 24 (2018), 19 23 DOI: 10.17512/znb.2018.1.03
Analiza parametrów mechaniki pękania w warunkach I modelu obciążenia betonu Anna Bernatowicz 1, Andrzej Kazberuk 2 Zeszyty Naukowe Politechniki Częstochowskiej nr 24 (2018), 19 23 DOI: 10.17512/znb.2018.1.03
