RADA PROGRAMOWA Czesław CEMPEL Ryszard MICHALSKI Jan ADAMCZYK Wojciech MOCZULSKI Roman BARCZEWSKI Stanisław NIZIŃSKI Walter BARTELMUS Vasyl OSADCHUK
|
|
|
- Franciszek Stachowiak
- 8 lat temu
- Przeglądów:
Transkrypt
1
2 prof. dr hab. inż. Jan ADAMCZYK AGH w Krakowie dr inż. Roman BARCZEWSKI Politechnika Poznańska prof. dr hab. inż. Walter BARTELMUS Politechnika Wrocławska prof. dr hab. inż. Wojciech BATKO AGH w Krakowie prof. dr hab. inż. Lesław BĘDKOWSKI WAT Warszawa prof. dr hab. inż. Adam CHARCHALIS Akademia Morska w Gdyni prof. dr hab. inż. Wojciech CHOLEWA Politechnika Śląska prof. dr hab. inż. Zbigniew DĄBROWSKI Politechnika Warszawska prof. dr hab. inż. Marian DOBRY Politechnika Poznańska RADA PROGRAMOWA PRZEWODNICZĄCY: prof. dr hab. dr h.c. mult. Czesław CEMPEL Politechnika Poznańska REDAKTOR NACZELNY: prof. dr hab. inż. Ryszard MICHALSKI UWM w Olsztynie prof. Wiktor FRID Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm Szwecja dr inż. Tomasz GAŁKA Instytut Energetyki w Warszawie prof. dr hab. inż. Jan KICIŃSKI IMP w Gdańsku prof. dr hab. inż. Jerzy KISILOWSKI Politechnika Warszawska CZŁONKOWIE: prof. dr hab. inż. Wojciech MOCZULSKI Politechnika Śląska prof. dr hab. inż. Stanisław NIZIŃSKI UWM w Olsztynie prof. Vasyl OSADCHUK Politechnika Lwowska Ukraina prof. dr hab. inż. Stanisław RADKOWSKI Politechnika Warszawska prof. Bob RANDALL University of South Wales Australia prof. dr Raj B.K.N. RAO president COMADEM International Anglia prof. Vasily S. SHEVCHENKO BSSR Academy of Sciences Mińsk Białoruś prof. Menad SIDAHMED University of Technology Compiegne Francja prof. dr hab. inż. Tadeusz UHL AGH w Krakowie prof. Vitalijus VOLKOVAS Kaunas University - Litwa prof. dr hab. inż. Andrzej WILK Politechnika Śląska prof. Alexandr YAVLENSKY Aerospace University Sankt Petersburg Rosja prof. dr hab. inż. Bogdan ŻÓŁTOWSKI ATR w Bydgoszcz Wszystkie opublikowane prace uzyskały pozytywne recenzje wykonane przez niezależnych recenzentów. Obszar zainteresowania czasopisma to problemy diagnostyki, identyfikacji stanu technicznego i bezpieczeństwa maszyn, urządzeń, systemów i procesów w nich zachodzących. Drukujemy oryginalne prace teoretyczne, aplikacyjne, przeglądowe z badań, innowacji i kształcenia w tych zagadnieniach. WYDAWCA: Polskie Towarzystwo Diagnostyki Technicznej -98 Warszawa ul. Augustówka 5 REDAKTOR NACZELNY: prof. dr hab. inż. Ryszard MICHALSKI SEKRETARZ REDAKCJI: dr inż. Sławomir WIERZBICKI CZŁONKOWIE KOMITETU REDAKCYJNEGO: dr inż. Krzysztof LIGIER dr inż. Paweł MIKOŁAJCZAK ADRES REDAKCJI: Uniwersytet Warmińsko Mazurski w Olsztynie Katedra Budowy, Eksploatacji Pojazdów i Maszyn -736 Olsztyn, ul. Oczapowskiego tel.: , fax: diagnostyka@uwm.edu.pl KONTO PTDT: Bank Przemysłowo Handlowy S.A. II O/ Warszawa nr konta: NAKŁAD: 75 egzemplarzy
3 DIAGNOSTYKA (38)/6 Spis Treści Preface Wojciech MOCZULSKI...6 Gracjan GŁOWACKI, Krzysztof PATAN Uniwersytet Zielonogórski...7 Fault Detection In Electrical Drive By Means Of Artificial Neural Networks detekcja uszkodzeń w silniku elektrycznym przy pomocy sztucznych sieci neuronowych Rafał SZKLARCZYK e-lan s.c.... CLP Solution For New Variant Of VRP Rozwiązanie nowego wariantu problemu marszrutyzacji pojazdów metodą CLP Józef RYBCZYŃSKI IMP PAN w Gdańsku...7 Acquisition Of Some Relations Concerning Bearing Misalignment Defects Applicable In Technical Diagnostics Pozyskiwanie pewnych relacji związanych z defektem rozosiowania łożysk mających zastosowanie w diagnostyce technicznej Przemysław WESOŁEK, Marek KUBIAK Politechnika Poznańska... Multiobjective Fuzzy Approach To The Vehicle Routing Problem With Time Windows Wielokryterialny problem planowania tras z oknami czasowymi w wersji rozmytej Wojciech SKARKA, Łukasz ZAJĄC Politechnika Śląska...5 Comparing Methods For Implementing VBA In Catia For Elaborating KBE Package Porównanie metod programowych z zastosowaniem VBA w systemie Catia na etapie tworzenie pakietu systemu KBE Piotr PRZYSTAŁKA Politechnika Śląska...3 Heuristic Modeling Of Objects And Processes Using Dynamic Neural Networks Heurystyczne modelowanie obiektów i procesów przy pomocy dynamicznych sieci neuronowych Wojciech SKARKA Politechnika Śląska...37 Constructing Model Of Knowledge Base According To MOKA Methodology Budowanie modelu bazy wiedzy zgodnego z metodologią MOKA Dominik WACHLA Politechnika Śląska...4 Identification Of Submersible Pump Temperature Changes Model Using KDD Methods Identyfikacja modelu zmian temperatury pompy głębinowej z zastosowaniem metod odkrywania wiedzy w bazach danych Krzysztof CIUPKE Politechnika Śląska...45 Cost-Sensitive Feature Selection Selekcja cech z uwzględnieniem kosztu ich pozyskania Bogdan WYSOGLĄD, Ryszard WYCZÓŁKOWSKI Politechnika Śląska...49 An Optimization Of Heuristic Model Of Water Supply System With Genetic Algorithm Optymalizacja modelu heurystycznego sieci wodociągowej z zastosowaniem algorytmu genetycznego Eugeniusz ZIENIUK, Andrzej KUŻELEWSKI, Wiesław GABREL Uniwersytet w Białymstoku...53 Artificial Intelligence Algorithms Combined With The Pies In Identification Of Polygonal Boundary Geometry Algorytmy sztucznej inteligencji połączone z PURC w identyfikacji kształtu wielokątnej geometrii brzegu Grzegorz URBANEK Politechnika Śląska...57 Application Of Evolutionary Algorithms To Identification Of Diagnostic Inverse Models Zastosowanie algorytmów ewolucyjnych w identyfikacji odwrotnych modeli diagnostycznych
4 DIAGNOSTYKA (38)/6 SPIS TREŚCI Agnieszka KIMACZYŃSKA, Sebastian KIMACZYŃSKI, Ryszard ROHATYŃSKI Uniwersytet Zielonogórski...6 The Influence Of Some Controlling Parameters On The Efficiency Of An Immune Algorithm Wpływ parametrów sterujących na efektywność algorytmu immunologicznego Anna BZYMEK Politechnika Śląska...65 Application Of Equivalent Source Method To Identification Of Models Of Noise Sources In Automotive Air Conditioning Systems Zastosowanie metody ekwiwalentnych źródeł w celu identyfikacji modeli źródeł hałasu w układzie klimatyzacji samochodowej Krzysztof MENDROK AGH Kraków...69 Zastosowanie analizy modalnej do detekcji uszkodzenia wiaduktu Damage Detection Of The Viaduct With Use Of The Modal Analysis Jan KICIŃSKI Instytut Maszyn Przepływowych PAN w Gdańsku...75 Wpływ wymiany ciepła w węzłach łożyskowych na symptomy diagnostyczne maszyn wirnikowych The Influence Of Heat Transfer In Bearings Knots On Diagnostics Symptoms Of Rotor Machines Stanisław RADKOWSKI Politechnika Warszawska...85 Wykorzystanie informacji diagnostycznej w zorientowanej na bezpieczeństwo eksploatacji maszyn Presuming Of Diagnostic Information In Safety Oriented Use Of Machinery Jan Maciej KOŚCIELNY, Bolesław DZIEMBOWSKI Politechnika Warszawska...93 Rozróżnialność uszkodzeń w układach liniowych Fault Distinguishabilty For Linear Systems Stanisław NIZIŃSKI, Sławomir WIERZBICKI UWM Olsztyn... Inteligentny pojazd mechaniczny jako mechatroniczny obiekt diagnozowania Intelligent Motor Vehicle As A Mechatronic Object Of Diagnosis Lesław BĘDKOWSKI WAT Warszawa...9 Diagnozowanie z dwupoziomową komparacją niepewnych symptomów i syndromu stanu obiektu Diagnosing With Double-Level Comparison Of Uncertain Symptoms And Syndrome Of An Object State Tadeusz DĄBROWSKI WAT Warszawa...5 Badanie symulacyjne skuteczności diagnozowania komparacyjnego na przykładzie systemu alarmowego Efficiency Of Comparative Diagnosing For An Alarm System Simulation Results Wojciech CHOLEWA Politechnika Śląska... Sieci stwierdzeń w diagnostyce technicznej Statement Networks In Technical Diagnostics Eliza JARYSZ-KAMIŃSKA Politechnika Szczecińska...9 Nadzór nad sprzętem pomiarowo-kontrolnym - unormowania i przepisy prawne Supervising Of Measuring-Control Equipment Krzysztof KOŁOWROCKI Akademia Morska w Gdyni...35 Wielostanowe podejście do analizy bezpieczeństwa systemów Multi-State Approach To System Safety Analysis Adam ROSIŃSKI Politechnika Warszawska...43 Metoda optymalizacji przeglądów okresowych transportowych systemów nadzoru Exploitation Strategies Of Monitoring Transport Systems Jerzy GIRTLER Politechnika Gdańska...5 Zastosowanie diagnostyki do decyzyjnego sterowania procesem eksploatacji urządzeń Application Of Diagnostics For Decision Control Over The Process Of Systems Operation
5 DIAGNOSTYKA (38)/6 SPIS TREŚCI Jerzy JAŹWIŃSKI, Sławomir KLIMASZEWSKI Instytut Techniczny Wojsk Lotniczych Warszawa...59 Identyfikacja stanu zdatności systemu Identification Of The Ability State Of The System Wiktor OLCHOWIK WAT Warszawa...67 Metrologiczne aspekty diagnozowania Metrological Aspects Of Diagnosing Janusz MINDYKOWSKI, Tomasz TARASIUK, Edward SZMIT, Daniel CZARKOWSKI Akademia Morska w Gdyni...7 Diagnostyka izolowanego systemu elektroenergetycznego na przykładzie jednostki pływającej Diagnostics Of Isolated Electrical Power System On Example Of The Ship Mariusz BOGDAN, Józef BŁACHNIO Politechnika Białostocka...77 Analiza sygnału świetlnego odbitego od powierzchni w diagnostyce obiektów technicznych Analysis Of Light Signal Reflected Of A Surface In Technical System Diagnostics Janusz GARDULSKI Politechnika Śląska...87 Badania diagnostyczne amortyzatorów Diagnostic Of Shock Absorbers Piotr KRZYWORZEKA, Witold CIOCH AGH Kraków...99 PLD we wspomaganiu demodulacji drgań maszyn PLD Aided Demodulation Of Machine Vibrations Henryk KAŹMIERCZAK Przemysłowy Instytut Maszyn Rolniczych w Poznaniu... Energetyczne charakterystyki degradacji systemu The Energetics Characteristics Of Machine s Degradation Marek DZIDA Politechnika Gdańska, Andrzej ADAMKIEWICZ Akademia Morska w Szczecinie...7 Zagadnienie bilansowania obiegu cieplnego z zastosowaniem rachunku wyrównawczego w diagnostyce okrętowych turbinowych silników spalinowych A Problem Of Balancing Thermal Cycle Using Reconciliation Calculations In The Diagnostics Of Marine Gas Turbine Engines WARTO PRZECZYTAĆ Zeszyty Naukowe Katedry Podstaw Konstrukcji Maszyn, Politechniki Śląskiej...5
6 6 DIAGNOSTYKA (38)/6 Słowo wstępne PREFACE Technical diagnostics is aimed at estimating technical condition of the object of diagnosis, given evidence collected about this object, and diagnostic knowledge and skill attributable to the subject of diagnosis. As an object of diagnosis one can understand either a machine or a piece of equipment, or a useful process the machine/equipment is intended to carry out. The subject of diagnosis has been since many years a human operator or diagnostician. Nowadays, automated or computerized systems are ever more and more often used for this purpose. For many years, the main area of interests of scientists involved in the development of foundations of technical diagnostics (including the author itself) has been how to measure signals, and then how to select optimal signal features, and subsequently how to arrive at conclusions when countable set of the values of features was given. However, in case of modern technical diagnostics, where ever more and more attention is paid to model-based technical diagnostics of objects and processes, several scientific groups switched their interests to gathering knowledge that could be used in diagnostic reasoning. For this reason, methodology of identifying models of objects and processes attracted the diagnostic society. At the very beginning, physical and input-output models were most frequently used. They were easy to apply in case of quite uncomplicated objects and processes. Unfortunately, quite a few of objects and processes are too complex to allow us to create models efficient enough for applications in modelbased diagnostics. Hence, this approach became infeasible. To overcome these difficulties, soft (or heuristic) models of objects and processes were introduced. Heuristic models take advantage of achievements of Artificial Intelligence, since they may be represented by such prominent methods and means, as Artificial Neural Networks, Fuzzy Logic Systems, Bayesian Networks, rulesets, qualitative models, and many others. Nowadays there are ever more and more applications of usage of these models. Bearing this in mind, the editor invited groups active in the area of heuristic modeling to share results of their work with diagnostic society in the country. In the following the Reader can find several descriptions of work done in the framework of heuristic modeling of objects and processes. Individual papers represent all the stages of development of the methodology of heuristic modeling of objects and processes, starting from rough concepts and ideas, and finishing with short reports about verification of methods and software tools. It is worth stressing that the prevailing part of papers has been prepared by young Colleagues. It is our hope that the Readers of Diagnostyka will find here some interesting issues. Finally, special thanks should be expressed to the Editor and the Secretary of Editorial Staff for their kind approval for including this Section Heuristic Modeling of Objects and Processes into the current issue, and for their patient assistance by editing. Wojciech Moczulski Guest Editor
7 DIAGNOSTYKA (38)/6 GŁOWACKI, PATAN, Fault Detection In Electrical Drive By Means Of Artificial Neural Networks 7 FAULT DETECTION IN ELECTRICAL DRIVE BY MEANS OF ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORKS * Gracjan GŁOWACKI, Krzysztof PATAN Institute of Control and Computation Engineering, University of Zielona Góra ul. Podgórna 5, Zielona Góra, Poland, {g.glowacki, k.patan}@issi.uz.zgora.pl Summry The paper deals with problem model-based of fault detection electrical drive by using neural networks. The multilayer perceptron with tapped delay lines has been applied to model the diagnosed process at the nominal operation conditions. In turn, decision about faults has been performed using simple MultiLayer Feedforward Network (MFN). The electrical drive under consideration (AMIRA DR3) works in the closed loop and is controlled by PID controller. This laboratory electrical drive renders it positive to simulate a several faulty scenarios. In this way the proposed fault detection scheme can be tested on a number of faulty conditions. Keywords: fault detection, neural network, neural classifier, modelling, electrical drive. DETEKCJA USZKODZEŃ W SILNIKU ELEKTRYCZNYM PRZY POMOCY SZTUCZNYCH SIECI NEURONOWYCH Streszczenie Artykuł przedstawia problem detekcji uszkodzeń w silniku elektrycznym przy pomocy sieci neuronowych. Do zamodelowania diagnozowanego obiektu pracującego w warunkach normalnych użyto sieci jednokierunkowych z liniami opóźniającymi. Następnie, jako blok decyzyjny o wystąpieniu uszkodzeń zastosowano zwykłe jednokierunkowe sieci wielowarstwowe. Do przeprowadzenia badań wykorzystano silnik prądu stałego firmy AMIRA (DR3). Silnik pracuje w układzie zamkniętym z regulatorem PID i umożliwia symulację pewnych scenariuszy uszkodzeń. Dzięki temu możliwe jest przetestowanie zaproponowanego schematu detekcji uszkodzeń na przykładzie wadliwych warunków pracy obiektu. Słowa kluczowe: detekcja uszkodzeń, sieci neuronowe, klasyfikator neuronowy, modelowanie, silnik elektryczny. INTRODUCTION Electrical Direct Current (DC) and Alternating Current (AC) engines are very often used in many industrial applications [7]. The changing conditions of operation and intensive exploitation result in systematic wearing off of individual parts of engines. This phenomenon can be interpreted as an incipient fault, which in the final phase changes to an abrupt fault and causes large damages in an engine. It is very important in this case to detect faults at an early stage and apply a special procedure to avoid them so that the worn off elements can be replaced. The faults considered manifest themselves at an early stage by a decreased efficiency, but finally, if the fault is not detected, some parts of the engine can be damaged. Thus, it is important to develop a reliable fault detection algorithm which should detect even small changes in the system behaviour. The traditional methods of monitoring engines require a direct inspection, so the whole process must be stopped for the time of the inspection. Such approaches are usually timeconsuming and causes financial loses for the company. Another methods use online identification of engine parameters. Fault detection in this case is done by monitoring the values of the parameters. Unfortunately, these methods require a detailed mathematical model of an engine and the expert who interprets the results should have a deep knowledge about an engine and experience in evaluating its behaviour. An interesting alternative solution can be obtained using artificial intelligence. Artificial * The work was supported by the Integrated Regional Operational Programme (Measure.6: Regional innovation strategies and the transfer of knowledge) co-financed from the European Social Fund.
8 8 DIAGNOSTYKA (38)/6 GŁOWACKI, PATAN, Fault Detection In Electrical Drive By Means Of Artificial Neural Networks neural networks seem to be particularly very attractive when designing fault detection diagnosis schemes. Artificial neural networks can be effectively applied to both the modelling of the plant operating conditions and decision making [,, 3].. FAULT DETECTION SCHEME In order to design fault diagnosis system for the considered-electrical engine, a neural network is used to model the process at normal operation conditions. First, the network has to be trained for this task. Process modelling in closed loop control and is controlled by PID controller. The model is designed applying the multilayer perceptron with tapped delay lines. Two neural models are designed model of tachometer y T = f NN (u), where y T is tachometer measurement and u is control signal, and model of motor drive y D = f NN (u), where y D is motor drive measurement. Fig.. The FD scheme based on neural network. ELECTRICAL ENGINE The effectiveness of the fault detection scheme has been examined using laboratory stand of the Institute of Control and Computation Engineering of the University of Zielona Góra AMIRA (DR3). The laboratory stand shown in Fig. can be used to control the rotation speed of a DC engine with a changing load. Fig.. Laboratory stand with a DC engine Laboratory object considered consists of five main elements: DC engine M, DC engine M, two engine-speed indicators, clutch K. The input signal for the engine M is an armature current. Its value is determined by a cascade control loop. The servo-amplifier of the current controller works in four modes, thus the current direction can be chosen appropriately according to the demanded direction of rotation. The output of the object is the rotational speed of the engine. The rotational speed can be measured using two sensors: a tachometer on optical sensor, which generates impulses that correspond to the rotations of the engine. The shaft of the engine M is connected with the identical engine M by the clutch K. The engine M works in the generator mode and the generated current is controlled by another controller. The basic technical data concerning the laboratory system are shown in Table. Table. Laboratory system technical date Variable Value Engine rated voltage 4 V rated current A rated power 3 W rated speed 3 rpm rated moment.96 Nm moment of inertia Kgm Resistance 3.3 Ω Tachometer output voltage moment of interia 5 mv/prm.6-6 Kgm Clutch Moment of inertia 33-6 Kgm The engine M is controlled using the servoamplifier, where the control signal has the form of the voltage from range -V to V with amplification.4 A/V. The engine M is also controlled using the servo-amplifier, where the control signal has the form of the voltage from the range -V to V with the amplification.37 A/V. The tachometer serves to measure indirectly the rotational speed of the engine M. The output range of the tachometer is -V to V [6]. A set of potential faulty scenarios defined for the engine considered. The faults were simulated artificially using the elements of the laboratory system. It was impossible to generate real faults in the laboratory environment. The faults are divided into two groups: tachometer faults and mechanical faults of the engine M, which manifest themselves as a decreasing efficiency of the engine. Tachometer T f faults were simulated by increasing tachometer T T measure by 5% (fault f ), % (fault f ), 5% T (fault f 3 ) and decreasing tachometer measure by T T T 5% (fault f 4 ), % (fault f 5 ), 5% (fault f 6 ). In order to generate the mechanical faults, the engine M connected with the engine M via the clutch K was used to simulate an additional faulty load. It was assumed that faults can be abrupt. Mechanical D faults f were simulated by setting load values to D D D.5A (fault f ), A (fault f ),.5A (fault f 3 ), - D D D.5A (fault f 4 ), -A (fault f 5 ), -.5A (fault f 6 ). The effectiveness of the designed fault detection
9 DIAGNOSTYKA (38)/6 GŁOWACKI, PATAN, Fault Detection In Electrical Drive By Means Of Artificial Neural Networks 9 system was tested using data generated during fault simulations. Faulty data were prepared for all designed scenarios. Some results of fault detection are presented in the next section. 3. EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS 3.. Process Modelling Due to the complex nature of the fault detection problem, the electrical engine was modeled by the multilayer perceptron with tapped delay lines. The considered neural network belongs to the class N,, ( processing layer, input layer, hidden layer with neurons and linear output unit). Each neuron in hidden layer possesses hyperbolic tangent transfer function. Number of past outputs used for determining the prediction was equal to 3, number of past inputs was equal to 3. Marquardt method. The learning set contains 3 samples for nominal condition, and for each faulty scenario a set of test samples has been generated. Analysis of the considered working conditions show that it is extremely difficult to differentiate between particular faulty scenarios. This situation is presented in Fig. 5. Even normal operation conditions are not clearly separated from faulty ones. Fig. 5. Distribution of residuals patterns (normal T T T conditions - *, f - o, f - x, f 3 - Fig. 3. Output of the motor drive and neural model In Fig. 3. one can observe that the neural model of the motor drive approximate the modelled object precisely. Moreover, in the Fig. 4. the residual signal for normal condition of the object is presented. Fig. 4. Residuals for normal conditions 3.. Tachometer faults Decision about faults has been performed using simple MultiLayer Feedforward Network (MFN). The neural classifier structure of the neural network was N,5,. Each neuron has sigmoid activation function. The parameters of the network were adjusted by using the well-known Levenberg- Taking into account that all tachometer faults are hardly distinguishable one from another, let us consider two classes of system behaviour. First class represented by represents normal operation conditions, and second class represented by represents generalized tachometer fault. The sensitivity of the proposed fault diagnosis system is checked using the so-called false detection rate [4] defined as follows: where r fd from i fd t i = () t t i t fd is the period of ith false fault detection, t on is the benchmark start up time, t from is the period of time from the begin of fault start-up. The fault detection quality is evaluated using true detection rate [4] defined as follows: r td hor i t i td on = () t t from i where t rd is the period of ith true fault detection, t hor is the benchmark time horizon. In the case of tachometers fault patterns related to the nominal condition overlap patterns collected for faulty scenarios, (Fig.5) what results in high false detection rate at the nominal condition r fd =.5. Table. True detection rate T f T T T f f f 3 T f 4 T f 5 T f 6 r td,83,8,8,87,88,87
10 DIAGNOSTYKA (38)/6 GŁOWACKI, PATAN, Fault Detection In Electrical Drive By Means Of Artificial Neural Networks 3.3. Mechanical fault of the engine In this case problem of distinction between nominal and faulty conditions less complicated. One can see in the Fig. 6 that patterns associated with the nominal state are located in the separated area from the faulty space. Thus, the false detection rate at the nominal condition is much better than in the previous case and r =. 7. fd Fig. 6. Distribution of residuals patterns (normal D D D conditions - *, f - o, f - x, f 3 - f D Table 3. True detection rate D D D D f f f 3 f 4 D f 5 D f 6 r td,93,94,78,9,94,95 4. SUMMARY The paper deals with application of neural networks to model-based fault detection systems. On the basis of the experimental results presented in the paper, the multilayer perceptron with tapped delay lines has appeared to be applicable to the system modelling during designing the FD systems. All experimental simulations were carry out with real object, electrical engine. On the basis of simulation experiments it to turned out that particular faults are not distinguish and an attempt of their isolation by means of simple MultiLayer Feedforward Network ended in failure. In both cases faults can be isolated as a group of faults. REFERENCES [] Korbicz J., Kościelny J. M., Kowalczuk Z., Cholewa W. (Eds.): Fault Diagnosis: Models, Artificial Intelligence, Applications. Springer- Verlag, Berlin, 4. [] Duch W., Korbicz J., Rutkowski L., Tadeusiewicz R. (Eds.): Neural Network Vol. 6. Akademicka Oficyna Wydawnicza EXIT, Warszawa,. (in polish) [3] Gupta M. M., Jin L., Homma N.: Static and Dynamic Neural Networks. John Wiley & Sons, New Jersey, 3. [4] Patan K., Parsini T.: Identification of neural dynamic models for fault detection and isolation : the case of real sugar evaporation process. Journal of Process Control,Vol. 5, pp [5] Korbicz J., Patan K., Obuchowicz A.: Dynamic neural networks for process modelling in fault detection and isolation systems. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Comuter Science, Vol. 9, No. 3, pp [6] Kowal M.: Optimization of Neuro-Fuzzy Structures in Technical Diagnostics Systems. University of Zielona Góra Press, Zielona Góra, 5. [7] Leonhard W.: Control of Electrical Drives. Springer, Berlin, 996. [8] Witczak M.: Advances in Model-Based Fault Diagnosis with Evolutionary Algorithms and Neural Network. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Comuter Science, Vol. 6, No., pp [9] Basseville M., Nikiforov I. V.: Detection of Abrupt Changes: Theory and Application. Prentice-Hall, Englewood, 993. [] Janczak A.: Identification of Nonlinear Systems Using Neural Networks and Polynominal Models. Springer, Berlin, 5. Gracjan GŁOWACKI received the M.Sc. degree in software engineering from Technical University of Zielona Góra, Poland in 5. He is first-year doctoral student in Computer Science as well as Electrical Engineering. Since 4 he has been with the Institute of Control and Computation Engineering. His current research include fault detection and diagnosis, neural networks and their applications. Krzysztof PATAN received the M.Sc. degree in electrical engineering from Technical University of Zielona Góra, Poland in 996 and Ph.D. degree in machine design and exploitation from Warsaw University of Technology Poland in. Since 996 he has been with the Institute of Control and Computation Engineering, University of Zielona Góra. His research interests include dynamic neural networks, fault diagnosis, optimisation methods.
11 DIAGNOSTYKA (38)/6 SZKLARCZYK, CLP Solution For New Variant Of VRP CLP SOLUTION FOR NEW VARIANT OF VRP Rafał SZKLARCZYK e-lan s.c. Piłsudskiego Street 4/, 43-3 Bielsko-Biała, Poland, Summary In the paper a mathematical model of MDMGVRP is presented. The two CLP programs solving above are described and discussed. The new variant of VRP consider certain number of commodities (goods) transported. In classic VRP there is only one commodity. The second main difference to classic problem is limited stock in depots. This two aspects cause the problem more complicated and prevent from direct applying of common known algorithms for solving the MDMGVRP. Two CLP solver tools were used to formulate CLP programs. The first was Cosytec CHIP the other was GNU-Prolog. Finally a demonstration problem is presented and solution is discussed. Keywords: vehicle routing problem, VRP, MDMGVRP, CLP, CHIP, GNU-Prolog. ROZWIĄZANIE NOWEGO WARIANTU PROBLEMU MARSZRUTYZACJI POJAZDÓW METODĄ CLP Streszczenie W artykule przedstawiono nowy wariant problemu marszrutyzacji pojazdów MDMGVRP, czyli problem marszrutyzacji pojazdów z wieloma magazynami i wieloma asortymentami. Zagadnienie zostało opisane modelem matematycznym a następnie rozwiązane metodą CLP. Opisano dwa programy wykonane przy użyciu narzędzi CLP: Cosytec CHIP i GNU-Prolog. Na koniec przedstawiono przykładowe dane oraz rozwiązanie uzyskane przy pomocy opisanych programów. Słowa kluczowe: problem marszrutyzacji pojazdów, VRP, MDMGVRP, CLP, CHIP, GNU-Prolog. INTRODUCTION In nowadays world of high level of competition there is extremely important to hold a strict regime of cost control. Especially parts of cost that do not bring any added value to a products shall be most reduced. A transportation cost is one of the kind. Control of logistic processes is one of main matters of concern of operational research. The CLP is a method that help to perfect us dealing with the problem.. MDMGVRP VS VRP You face Vehicle Routing Problem every time when you need to determine routes for certain fleet of vehicles which have limited capacity and are located in one or more depots. The vehicles must distribute goods to a clients. Every client has a demand for a certain number of goods. The distances between client locations and depot locations are given. Usually the aim is to minimize sum of total distance traveled by all cars. About fifty years have elapsed since Dantzig and Ramser [] introduced VRP but in the last decade VRP was a matter of interest for operational research. Good overview of the problem was presented by Toth and Vigo []. A classification of VRP was introduced by Garn [3]. He also proposed quite wide set of bibliography [4] Sometimes TSP with multiple salesmen is classified as VRP [5], but in fact it is much less complicated and is particular instance of VRP. There is quite a lot of VRP variants, all focused on different problem restrictions. Every day life comes with various situations, that is why we need to formulate new mathematical models and find a new solution methods. MDMGVRP is for Multiple Depots Multiple Goods Vehicle Routing Problem. In this case demands are determined for certain set of commodities. The additional constraint is that a stores of goods and a vehicles can be located in a certain number of depots. Every depot has limited stock of goods. This are reasons that make new variant of VRP more complicated.. MATHEMATICAL MODEL Let M be a number of cities, V a number of vehicles and A number of commodities (types of goods). We assume that commodities are packed with the same kind of wrapping, so their number is
12 determined in same units, which are packages of commodity. The distances between cities are given with matrix O: DIAGNOSTYKA (38)/6 SZKLARCZYK, CLP Solution For New Variant Of VRP It also have to be less than a capacity of the vehicle: The matrix of unload is defined in the same way: where i means start city, j means end city. There are depots in some cities. In depots a limited number of commodities is stored: where a is means commodity, m the city where s a,m packages of commodity a is stored. There are some clients located in the cities. Each client has certain demand: where a is means commodity, m the city where d a,m packages of commodity a is required. There can not be a depot and a client located in the same city: where r v a,m is the number of packages with commodity a unloaded from vehicle v in city m. All demands shall be fulfilled. It means that number of commodities unloaded in a particular city is equal to demand in the city: In MDMGVRP (apart from SDVRP) one client need to be served by a single vehicle: Each vehicle loads in total the same number of commodities as total number of unloaded commodities during its journey: Each vehicle has certain capacity l v that is determined with package of commodity unit: and each vehicle has exploitation cost c v, which is determined as a cost of travel of one distance unit by the vehicle v: Each vehicle starts from specified depot: where p v means the city of start of vehicle v. Let us define: where X v is the matrix of travel of vehicle v, that is determined in following way: Particular vehicle can visit particular city at most once, so: That is also known that particular vehicle leaves particular city at most once: If particular vehicle takes part in fulfilling the demands, it would leave its start depot. Otherwise it stays at start depot and all its travel matrix elements are equal to : Let Z v be a matrix of load, defined in following way: where z v a,m is the number of packages with commodity a loaded to vehicle v in city m. The total number of units loaded in a particular city can not be greater than a stock in the city (depot): A vehicle must visit a city to unload or load commodities. The model must define such constraint, so vehicle must travel in or out the city if number of loaded or unloaded commodities is greater than. In this model vehicles do not have to return to their start depots. So there is: Each vehicle can not be overloaded and underloaded in any visited city. This means that a load of vehicle, which is equal to sum of load state in previous city and change of load (load or unload) in current city, must be less than or equal to vehicle capacity and greater than or equal to zero: where: and in the start depot of vehicle v: You need to remember that vehicle shall visit a city to perform load or unload there. You can describe this relation in following way: Total cost depends on total distance traveled by all vehicles and their exploitation costs, so:
13 To solve the problem means to find such X v, Z v and R v, that keep all relations defined above. The goal of optimization is to find the solution with minimum value of objective function F. 3. CLP PROGRAMS Constraint Logic Programing is still not very popular approach however it is flexible and effective. Two CLP tools have been used to formulate the programs: Cosytec CHIP and GNU Prolog. Both are Prolog descendant with constraint over finite domains functions. They are similar but there are some differences. The syntaxes are slightly different but more important differences are in functionality. CHIP offers more build-in predicates [6] that help a lot to solve even very complicated problems. GNU Prolog has less predicates but offers a possibility of extending features with function libraries written in C. It also accepts nonlinear constraints [7] that was useful to solve MDMGVRP. Another advantage of GNU-Prolog is that the program is distributed freely under GPL license. The MDMGVRP programs consist of 4 main sections:. Entry data and constraints,. Main (computing) part, 3. Additional predicates, 4. Distance matrix definition. First vehicle parameters are defined: L=5, C=3, MS=4, L means capacity, C exploitation cost, MS start depot. The digits following letters are indexes. The mean number of vehicle. When there are more than one index of variable in the program, the rule of order is that the first index means vehicle, second is for commodity kind, third is for city. There are stocks determined forth: S=[S,S,S3,S4], SA=[SA,SA,SA3,SA4], SA=[SA,SA,SA3,SA4], [...] S#=SASASA3SA4SA5SA6, S#=SASASA3SA4SA5SA6, [...] SA=[,,,7], SA=[,,4,], S, S... mean total stocks of all commodities in the cities. SA means stock of commodities in city. The demands are defined in the same way: D=[D,D,D3,D4], DA=[DA,DA,DA3,DA4], DA=[DA,DA,DA3,DA4], In the last section of program a distances between the cities are defined. It is done with predicate odl: odl(_,,). odl(,,). odl(,,). odl(,3,3). [...] Predicate odl has three arguments: first is source city, second is destination city and third the distance DIAGNOSTYKA (38)/6 SZKLARCZYK, CLP Solution For New Variant Of VRP between them. The first row is used to calculate objective function value in case when vehicle do not travel from some city. Next line means that the distance from city to city one is distance units. It is obvious. Third line means that distance from city to city is. Back to the first row it means that distance from any city to dummy city number, which really means that a vehicle stops, is equal to distance units. When a vehicle stops it do not affect with growth of objective function. It is more understandable after definition of travel matrix. The definitions in first section of the program are mixed with constraints like: ZA3#=<SA3, This example means that loading of vehicle with commodity in city 3 shall be less or equal appropriate stock in the city. One of most important constraints is: R*D#=R*R It holds when total unload of vehicle in city is equal to demand in the city or when is equal to. It is useful to define relation which says that single customer shall be served by single vehicle. However it is possible to use above only in GNU Prolog. In CHIP, because there are no nonlinear constraints, you need to write it in a different way: if (R#\=D) then (R#=), The travel matrix X v in program is replaced with vector T v, which size is equal to number of cities. The index of element means a source city, the value of an element means destination city. If the value is equal to, it means that vehicle stops, it does not leave the city. For example matrix X: is replaced with a vector T: After definitions and constraints the main section of program is located: statistics(real_time,[czas_s,_]), fd_minimize(( fd_labeling(ra), fd_labeling(ra), fd_labeling(ra), fd_labeling(ra), fd_labeling(za), fd_labeling(za), fd_labeling(za), fd_labeling(za), niezaladowane_stoja(z,t), niezaladowane_stoja(z,t), jedz_gdzie_trzeba(z,r,t,ms), jedz_gdzie_trzeba(z,r,t,ms), fd_labeling(t), fd_labeling(t), sprawdz_przeladowanie(ms,t,z,r,,l), bilans(ms,t,za,ra,), bilans(ms,t,za,ra,), sprawdz_przeladowanie(ms,t,z,r,,l), bilans(ms,t,za,ra,), bilans(ms,t,za,ra,), 3
14 4 dlugosc_trasy(t,,dt), dlugosc_trasy(t,,dt), CEL is (DT*C)(DT*C), DIAGNOSTYKA (38)/6 SZKLARCZYK, CLP Solution For New Variant Of VRP statistics(real_time,[czas_l,_]), write('cel'),nl, write(cel),nl, write('eureka!'),nl, write('zaladunki'),nl, write('z='),write(z),nl, write('za='),write(za),nl, write('za='),write(za),nl, write('z='),write(z),nl, write('za='),write(za),nl, write('za='),write(za),nl, write('rozladunki'),nl, write('r='),write(r),nl, write('ra='),write(ra),nl, write('ra='),write(ra),nl, write('r='),write(r),nl, write('ra='),write(ra),nl, write('ra='),write(ra),nl, write('trasy'),nl, write('t='),write(t),nl, write('t='),write(t),nl, write(''),nl, Czas is Czas_l-Czas_s, write('czas liczenia='), write(czas),write(' ms'),nl, write(''),nl ), CEL ), In GNP Prolog the main role plays predicate fd_minimize. It runs a code given as first parameter until the second parameter (in this case variable CEL) achieves minimum value. The first part of code inside fd_mnimize is labeling of loads and unloads. Then there are some additional constrains in predicates niezaladowane_stoja and jedz_gdzie_trzeba. They provide that every vehicle that do not fulfill any demand stays in start depot and that every city where loads or unloads are performed is visited by the appropriate vehicle. Then there is labeling of vectors Tv and predicates sprawdz_przeladowanie and bilans. The predicates provide that all vehicle routes are continuous. Vector that contain two routes like T=[,,,5,4] are forbidden. The predicates also provide balance checking for routs. It means that any vehicle can not be over or underload all route long. 4. DEMONSTRATIONAL PROBLEM Consider MDMGVRP with given vehicles, commodity kinds and 6 cities. There are two depots and four customers. Below stock values are defined: SA=[,,,7,,], SA=[,,,4,,], and demand values: DA=[,4,,,,], DA=[,,,,,], Vehicle parameters are following: L=, C=3, MS=6, L=6, C=, MS=6, The distance matrix: GNU Prolog that is running on machine with Intel processor (Celeron.4GHz, 56MB RAM, OS MS Windows XP Home) solves the problem above in time of 3397 milliseconds and shows the solution: Cel 5 EUREKA! Rozwiazanie ostateczne: Zaladunki Z=[,,,8,,] ZA=[,,,5,,] ZA=[,,,3,,] Z=[,,,,,] ZA=[,,,,,] ZA=[,,,,,] Rozladunki R=[3,6,,,,] RA=[,4,,,,] RA=[,,,,,] R=[,,,,,] RA=[,,,,,] RA=[,,,,,] Trasy T=[,,,3,4,5] T=[,,,,,] Czas liczenia=3397 ms It also signalize that there are more optimal solutions (with the same objective function value). It is possible to view them all. CHIP needs time of 3855 milliseconds for completing the task and shows only the first solution found. 5. SUMMARY CLP is useful method to solve MDMGVRP a new variant of VRP and quite complicated one. MDMGVRP is still an issue of research as there is a need to determine maximal size of the problem that can be solved with CHIP and GNU- Prolog. The CLP solution should be compared with some other methods and maybe performance should improved by using heuristic methods or other means. REFERENCES [] Dantzig G. B., Ramser R. H. The Truck Dispatching Problem. Management Science, 959, Vol. 6, pp [] Toth P., Vigo D. The Vehicle Routing Problem. SIAM Monographs on Discrete Mathematics and Applications,, pp. 5. [3] Garn W.: VehicleRouting/vehicle_routing.html. Internet pucation, Wien,. [4] Garn W.: VehicleRouting/neo/biblio.html. Internet pucation, Wien,.
15 DIAGNOSTYKA (38)/6 SZKLARCZYK, CLP Solution For New Variant Of VRP [5] Jadczak R., Trzaskalik T.: Algorytmy genetyczne, ewolucyjne i metaheurystyki. Informatyka w badaniach operacyjnych, Prace naukowe AE, Katowice, 5, pp [6] COSYTEC SA.: CHIP System documentation. Orsay Cedex, 997. [7] Diaz D.: GNU Prolog documentation, Paris,. 5 Rafał SZKLARCZYK is a graduate of Academy of Computer Science and Management in Bielsko-Biała (computer science engineer) and Academy of Mining and Metallurgy in Cracow (master of management). Now he is running a software engineering company with success for over five years. He is also a PhD student at Silesian University of Technology with special interest on operational research and CPL methods.
16
17 DIAGNOSTYKA (38)/6 RYBCZYŃSKI, Acquisition Of Some Relations Concerning Bearing Misalignment Defects 7 ACQUISITION OF SOME RELATIONS CONCERNING BEARING MISALIGNMENT DEFECTS APPLICABLE IN TECHNICAL DIAGNOSTICS Józef RYBCZYŃSKI Institute of Fluid-Flow Machinery, Polish Academy of Sciences 8-95 Gdańsk, ul. Fiszera 4, tel.: (48) , fax: (48) ryb@imp.gda.pl Summary The investigations aimed at determining the tolerable misalignment areas of two neuralgic bearings in the turbine set, taking into account criteria of permissible load of the bearings. The areas have been evaluated by numerical analysis of the discrete model of the machine with the aid of a package of MESWIR computer codes. The ranges of tolerable misalignments of the bearings to any direction are presented in the graphs as the envelopes of maximum permissible bearing load. Basing on the method it is possible to correct the location of particular bearings to optimize tolerable bearing misalignment areas. The research will make possible to formulate a system of diagnostic relations connected with the bearing misalignment defects. Keywords: technical diagnostics, rotating machine, slider bearing. POZYSKIWANIE PEWNYCH RELACJI ZWIĄZANYCH Z DEFEKTEM ROZOSIOWANIA ŁOŻYSK MAJĄCYCH ZASTOSOWANIE W DIAGNOSTYCE TECHNICZNEJ Streszczenie Badania miały na celu wyznaczenie obszarów bezpiecznych rozosiowań dwóch newralgicznych łożysk turbozespołu z punktu widzenia kryterium dopuszczalnego obciążenia łożysk. Obszary te zostały wyznaczone w drodze numerycznej analizy dyskretnego modelu maszyny przy użyciu pakietu oprogramowania MESWIR. Zakresy bezpiecznych rozosiowań łożysk w dowolnym kierunku są prezentowane na wykresach jako miejsce geometryczne maksymalnych dopuszczalnych obciążeń łożysk. Bazując na zastosowanej metodzie możliwa jest korekta położenia poszczególnych łożysk maszyny w celu optymalizacji obszarów dopuszczalnych rozosiowań łożysk. Praca umożliwi sformułowanie systemu relacji diagnostycznych związanych z defektem rozosiowania łożysk. Słowa kluczowe: diagnostyka techniczna, maszyna wirnikowa, łożysko ślizgowe.. INTRODUCTION Large-power turbine sets consist of a number of rotors linked together by couplings and supported in a number of slider bearings. For such a machine, the bearings have to be set in a precisely defined manner with respect to each other, namely shafts should create a catenary line [,, 3]. Deviations of bearing locations with respect to their design location change operating conditions in this one bearing and also in other bearings. The static load of the shafts and bearings as well as the shaft line shape is changed [, 4, 5]. Exceeding the tolerable bearing misalignments makes further operation of a machine at least dangerous [, 5]. Relations between bearing misalignments and the machine bearing loads, make in fact a set of relations linking the defects and their symptoms. Therefore matching like bearing displacement bearing load characteristics can be considered as diagnostic relations and included to the diagnostic knowledge basis for the examined machine. Such a knowledge basis is necessary for automatic diagnostic systems. The motivations for examining the effect of bearing misalignment defect on bearing load characteristics originated from the earlier research activities in the subject, which resulted in determining tolerable displacements of bearings in the 3K5 turbine set in two directions only: horizontally to the left and to the right and vertically upward and downward [6, 7].. APPLICATION OF THE DIAGNOSTIC RELATIONS IN DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS For their operation, automatic diagnostic and advisory systems need the information, based on which they can formulate diagnoses, suggest, or even make decisions in certain situations of object s behaviour. This information should be delivered to the diagnostic system in such a form that the inherence algorithms, implemented in the system in the form of rules bearing the names of diagnostic relations, could make use of it. Preferably, this
18 8 DIAGNOSTYKA (38)/6 RYBCZYŃSKI, Acquisition Of Some Relations Concerning Bearing Misalignment Defects information should have a form of sets of already formulated rules, but advanced diagnostic systems can formulate these rules themselves. The diagnostic relations are the cause-effect relations linking the type of defect with its symptoms [3, 9]. If the set of diagnostic relations is based on discrete values assumed for defect simulations, these relations can be given a form of simple logical sentences of the following type: if (cause) then (effect), (P S). Sets of relations of P S type are usually obtained using of the simulation method. The method consists in assuming a defect in the machine model and finding a response to the defect simulated in this way. A direction in which diagnostic and expert systems are developed is artificial intelligence. This name is given to systems capable of simulating the way of inference characteristic of human beings. A similar method of formulating conclusions in computer science is referred to as heuristics. The heuristic inherence allows finding an approximate solution to the examined problem, without guarantee of its correctness. However, this solution is frequently the optimal and only possible one in a certain situation, for instance when an exact solution algorithm or sufficient database are missing. The investigations presented in this article aimed at creating sets of diagnostic relations describing bearing misalignment defect in a multisupport rotating machine, a large-power turboset. In the examined the causes were the locations and scales of rotor misalignment defect, described by numerical values of displacements of particular bearings. Each individual cause P i can be defined by a set of three numerical values: P i = [bearing_number, Δ x, Δ y ], where: Δ x horizontal bearing displacement, Δ y vertical bearing displacement. A displacement of the bearing to any direction may be presented as a vector sum of the Δ x and Δ y.the effect of the defect, describing the resultant static and dynamic state of the machine, is expressed by a set of values of quantities selected taking into account certain requirements of the diagnostic system. Generally, the set of values describing the effect is larger, and its size depends on the number of parameters considered significant for diagnostic purposes. If the state of bearing loads is of some interest from the diagnostic point of view, this set may include average pressures on bush surfaces in bearings in horizontal and vertical projections. If of certain interest is the dynamic state of the machine, this set can be composed of values characterising the intensity of absolute and relative vibrations, horizontal and vertical, of all bearings. From the point of view of practical applications in automatic diagnostic systems of high importance are the relations, which allow indicating a defect from the set of its symptoms, i.e.: S P. These are inverse relations to those directly obtained using simulation methods. A way to find the relations of S P type is inverting the P S type relations obtained using simulation methods. An expected result of this operation is a set of mutually unique relations. This task can be done in an exact and unambiguous way only when certain assumptions concerning the sets of causes and effects are made. In practice it is not unambiguous due to the physical nature of the object of examination and the resultant nature of phenomena treated as symptoms, as well as the nature of the simulation procedure applied for obtaining these relations. The set of simulation results is limited in size and does not include all possible effects of the assumed defects. Moreover the results of simulations are burdened with errors, therefore obtaining sets of inverse diagnostic relations is only possible using the mentioned above heuristic methods. These methods were successfully applied by a research team of the Silesian University of Technology for examining bearing misalignment defect in a turboset [8, 9]. They inversed the diagnostic relations, which had been obtained from simulation calculations in IF-FM, and then used these relations in the developed experimental diagnostic system making use of heuristic procedures [8]. This system is capable of indicating, with certain probability, the type of defect from given symptoms. The experimental diagnostic system was trained on sets of simulation-based diagnostic relations describing the bearing misalignment defect in the 3K5 turboset in horizontal and vertical direction [6, 7]. These data included relations between maximum permissible displacement of bearings 5 and 6 in four directions: right, left, up and down, and the vibration state of the turboset resulting from those displacements. The same material was used for verifying the operation of the system. In this article presented are the results of investigations being the continuation and extension of the above investigations. Determined were ranges of permissible displacements of the two turboset bearings in arbitrary direction from the point of view of the permissible bearing load criterion and the permissible vibration criterion. Discrete maximum states of permissible bearing displacements were linked with the parameters characterising the machine state, such as loads and vibrations of all bearings. This way sets of diagnostic relations were created in the form: P i [bearing number, Δ x, Δ y ] S i [bearing number, Q x, Q y ], P i [bearing number, Δ x, Δ y ] S i [bearing number, A x, A y, V x, V y ]. All these sets of diagnostic relations can be used in the experimental diagnostic system developed at the Silesian University of Technology. The article presents part of this work, which is the results of investigations of permissible displacements of bearings 5 and 6 in the 3K5 turboset, and related diagnostic relations from the point of view of bearing load criterion. The diagnostic relations
Proposal of thesis topic for mgr in. (MSE) programme in Telecommunications and Computer Science
 Proposal of thesis topic for mgr in (MSE) programme 1 Topic: Monte Carlo Method used for a prognosis of a selected technological process 2 Supervisor: Dr in Małgorzata Langer 3 Auxiliary supervisor: 4
Proposal of thesis topic for mgr in (MSE) programme 1 Topic: Monte Carlo Method used for a prognosis of a selected technological process 2 Supervisor: Dr in Małgorzata Langer 3 Auxiliary supervisor: 4
Hard-Margin Support Vector Machines
 Hard-Margin Support Vector Machines aaacaxicbzdlssnafiyn9vbjlepk3ay2gicupasvu4iblxuaw2hjmuwn7ddjjmxm1bkcg1/fjqsvt76fo9/gazqfvn8y+pjpozw5vx8zkpvtfxmlhcwl5zxyqrm2vrg5zw3vxmsoezi4ogkr6phieky5crvvjhriqvdom9l2xxftevuwcekj3lktmhghgniauiyutvrwxtvme34a77kbvg73gtygpjsrfati1+xc8c84bvraowbf+uwnipyehcvmkjrdx46vlykhkgykm3ujjdhcyzqkxy0chur6ax5cbg+1m4bbjptjcubuz4kuhvjoql93hkin5hxtav5x6yyqopnsyuneey5ni4keqrxbar5wqaxbik00icyo/iveiyqqvjo1u4fgzj/8f9x67bzmxnurjzmijtlybwfgcdjgfdtajwgcf2dwaj7ac3g1ho1n4814n7wwjgjmf/ys8fenfycuzq==
Hard-Margin Support Vector Machines aaacaxicbzdlssnafiyn9vbjlepk3ay2gicupasvu4iblxuaw2hjmuwn7ddjjmxm1bkcg1/fjqsvt76fo9/gazqfvn8y+pjpozw5vx8zkpvtfxmlhcwl5zxyqrm2vrg5zw3vxmsoezi4ogkr6phieky5crvvjhriqvdom9l2xxftevuwcekj3lktmhghgniauiyutvrwxtvme34a77kbvg73gtygpjsrfati1+xc8c84bvraowbf+uwnipyehcvmkjrdx46vlykhkgykm3ujjdhcyzqkxy0chur6ax5cbg+1m4bbjptjcubuz4kuhvjoql93hkin5hxtav5x6yyqopnsyuneey5ni4keqrxbar5wqaxbik00icyo/iveiyqqvjo1u4fgzj/8f9x67bzmxnurjzmijtlybwfgcdjgfdtajwgcf2dwaj7ac3g1ho1n4814n7wwjgjmf/ys8fenfycuzq==
Fig 5 Spectrograms of the original signal (top) extracted shaft-related GAD components (middle) and
 Fig 4 Measured vibration signal (top). Blue original signal. Red component related to periodic excitation of resonances and noise. Green component related. Rotational speed profile used for experiment
Fig 4 Measured vibration signal (top). Blue original signal. Red component related to periodic excitation of resonances and noise. Green component related. Rotational speed profile used for experiment
Zakopane, plan miasta: Skala ok. 1: = City map (Polish Edition)
 Zakopane, plan miasta: Skala ok. 1:15 000 = City map (Polish Edition) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Zakopane, plan miasta: Skala ok. 1:15 000 = City map (Polish Edition) Zakopane,
Zakopane, plan miasta: Skala ok. 1:15 000 = City map (Polish Edition) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Zakopane, plan miasta: Skala ok. 1:15 000 = City map (Polish Edition) Zakopane,
Rozpoznawanie twarzy metodą PCA Michał Bereta 1. Testowanie statystycznej istotności różnic między jakością klasyfikatorów
 Rozpoznawanie twarzy metodą PCA Michał Bereta www.michalbereta.pl 1. Testowanie statystycznej istotności różnic między jakością klasyfikatorów Wiemy, że możemy porównywad klasyfikatory np. za pomocą kroswalidacji.
Rozpoznawanie twarzy metodą PCA Michał Bereta www.michalbereta.pl 1. Testowanie statystycznej istotności różnic między jakością klasyfikatorów Wiemy, że możemy porównywad klasyfikatory np. za pomocą kroswalidacji.
 www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
Karpacz, plan miasta 1:10 000: Panorama Karkonoszy, mapa szlakow turystycznych (Polish Edition)
 Karpacz, plan miasta 1:10 000: Panorama Karkonoszy, mapa szlakow turystycznych (Polish Edition) J Krupski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Karpacz, plan miasta 1:10 000: Panorama
Karpacz, plan miasta 1:10 000: Panorama Karkonoszy, mapa szlakow turystycznych (Polish Edition) J Krupski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Karpacz, plan miasta 1:10 000: Panorama
Katowice, plan miasta: Skala 1: = City map = Stadtplan (Polish Edition)
 Katowice, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000 = City map = Stadtplan (Polish Edition) Polskie Przedsiebiorstwo Wydawnictw Kartograficznych im. Eugeniusza Romera Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically
Katowice, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000 = City map = Stadtplan (Polish Edition) Polskie Przedsiebiorstwo Wydawnictw Kartograficznych im. Eugeniusza Romera Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically
 www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
Akademia Morska w Szczecinie. Wydział Mechaniczny
 Akademia Morska w Szczecinie Wydział Mechaniczny ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA mgr inż. Marcin Kołodziejski Analiza metody obsługiwania zarządzanego niezawodnością pędników azymutalnych platformy pływającej Promotor:
Akademia Morska w Szczecinie Wydział Mechaniczny ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA mgr inż. Marcin Kołodziejski Analiza metody obsługiwania zarządzanego niezawodnością pędników azymutalnych platformy pływającej Promotor:
P R A C A D Y P L O M O W A
 POLITECHNIKA POZNAŃSKA Wydział Maszyn Roboczych i Transportu P R A C A D Y P L O M O W A Autor: inż. METODA Ε-CONSTRAINTS I PRZEGLĄDU FRONTU PARETO W ZASTOSOWANIU DO ROZWIĄZYWANIA PROBLEMU OPTYMALIZACJI
POLITECHNIKA POZNAŃSKA Wydział Maszyn Roboczych i Transportu P R A C A D Y P L O M O W A Autor: inż. METODA Ε-CONSTRAINTS I PRZEGLĄDU FRONTU PARETO W ZASTOSOWANIU DO ROZWIĄZYWANIA PROBLEMU OPTYMALIZACJI
Helena Boguta, klasa 8W, rok szkolny 2018/2019
 Poniższy zbiór zadań został wykonany w ramach projektu Mazowiecki program stypendialny dla uczniów szczególnie uzdolnionych - najlepsza inwestycja w człowieka w roku szkolnym 2018/2019. Składają się na
Poniższy zbiór zadań został wykonany w ramach projektu Mazowiecki program stypendialny dla uczniów szczególnie uzdolnionych - najlepsza inwestycja w człowieka w roku szkolnym 2018/2019. Składają się na
Tychy, plan miasta: Skala 1: (Polish Edition)
 Tychy, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000 (Polish Edition) Poland) Przedsiebiorstwo Geodezyjno-Kartograficzne (Katowice Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Tychy, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000
Tychy, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000 (Polish Edition) Poland) Przedsiebiorstwo Geodezyjno-Kartograficzne (Katowice Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Tychy, plan miasta: Skala 1:20 000
SSW1.1, HFW Fry #20, Zeno #25 Benchmark: Qtr.1. Fry #65, Zeno #67. like
 SSW1.1, HFW Fry #20, Zeno #25 Benchmark: Qtr.1 I SSW1.1, HFW Fry #65, Zeno #67 Benchmark: Qtr.1 like SSW1.2, HFW Fry #47, Zeno #59 Benchmark: Qtr.1 do SSW1.2, HFW Fry #5, Zeno #4 Benchmark: Qtr.1 to SSW1.2,
SSW1.1, HFW Fry #20, Zeno #25 Benchmark: Qtr.1 I SSW1.1, HFW Fry #65, Zeno #67 Benchmark: Qtr.1 like SSW1.2, HFW Fry #47, Zeno #59 Benchmark: Qtr.1 do SSW1.2, HFW Fry #5, Zeno #4 Benchmark: Qtr.1 to SSW1.2,
SYNTEZA SCENARIUSZY EKSPLOATACJI I STEROWANIA
 POLITECHNIKA POZNAŃSKA WYDZIAŁ BUDOWNICTWA I INŻYNIERII ŚRODOWISKA INSTYTUT INŻYNIERII ŚRODOWISKA ZAKŁAD ZAOPATRZENIA W WODĘ I OCHRONY ŚRODOWISKA mgr inż. Rafał BRODZIAK SYNTEZA SCENARIUSZY EKSPLOATACJI
POLITECHNIKA POZNAŃSKA WYDZIAŁ BUDOWNICTWA I INŻYNIERII ŚRODOWISKA INSTYTUT INŻYNIERII ŚRODOWISKA ZAKŁAD ZAOPATRZENIA W WODĘ I OCHRONY ŚRODOWISKA mgr inż. Rafał BRODZIAK SYNTEZA SCENARIUSZY EKSPLOATACJI
MaPlan Sp. z O.O. Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically
 Mierzeja Wislana, mapa turystyczna 1:50 000: Mikoszewo, Jantar, Stegna, Sztutowo, Katy Rybackie, Przebrno, Krynica Morska, Piaski, Frombork =... = Carte touristique (Polish Edition) MaPlan Sp. z O.O Click
Mierzeja Wislana, mapa turystyczna 1:50 000: Mikoszewo, Jantar, Stegna, Sztutowo, Katy Rybackie, Przebrno, Krynica Morska, Piaski, Frombork =... = Carte touristique (Polish Edition) MaPlan Sp. z O.O Click
EXAMPLES OF CABRI GEOMETRE II APPLICATION IN GEOMETRIC SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH
 Anna BŁACH Centre of Geometry and Engineering Graphics Silesian University of Technology in Gliwice EXAMPLES OF CABRI GEOMETRE II APPLICATION IN GEOMETRIC SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH Introduction Computer techniques
Anna BŁACH Centre of Geometry and Engineering Graphics Silesian University of Technology in Gliwice EXAMPLES OF CABRI GEOMETRE II APPLICATION IN GEOMETRIC SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH Introduction Computer techniques
ARNOLD. EDUKACJA KULTURYSTY (POLSKA WERSJA JEZYKOWA) BY DOUGLAS KENT HALL
 Read Online and Download Ebook ARNOLD. EDUKACJA KULTURYSTY (POLSKA WERSJA JEZYKOWA) BY DOUGLAS KENT HALL DOWNLOAD EBOOK : ARNOLD. EDUKACJA KULTURYSTY (POLSKA WERSJA Click link bellow and free register
Read Online and Download Ebook ARNOLD. EDUKACJA KULTURYSTY (POLSKA WERSJA JEZYKOWA) BY DOUGLAS KENT HALL DOWNLOAD EBOOK : ARNOLD. EDUKACJA KULTURYSTY (POLSKA WERSJA Click link bellow and free register
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture11. Random Projections & Canonical Correlation Analysis
 Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture11 5 Random Projections & Canonical Correlation Analysis The Tall, THE FAT AND THE UGLY n X d The Tall, THE FAT AND THE UGLY d X > n X d n = n d d The
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture11 5 Random Projections & Canonical Correlation Analysis The Tall, THE FAT AND THE UGLY n X d The Tall, THE FAT AND THE UGLY d X > n X d n = n d d The
XXIII Konferencja Naukowa POJAZDY SZYNOWE 2018
 XXIII Konferencja Naukowa POJAZDY SZYNOWE 2018 Abstract Application of longitudinal dynamics of the train in the simulator of catenary maintenance vehicles - experimental and numerical tests Robert Konowrocki
XXIII Konferencja Naukowa POJAZDY SZYNOWE 2018 Abstract Application of longitudinal dynamics of the train in the simulator of catenary maintenance vehicles - experimental and numerical tests Robert Konowrocki
OPTYMALIZACJA PUBLICZNEGO TRANSPORTU ZBIOROWEGO W GMINIE ŚRODA WIELKOPOLSKA
 Politechnika Poznańska Wydział Maszyn Roboczych i Transportu Inż. NATALIA LEMTIS OPTYMALIZACJA PUBLICZNEGO TRANSPORTU ZBIOROWEGO W GMINIE ŚRODA WIELKOPOLSKA Promotor: DR INŻ. MARCIN KICIŃSKI Poznań, 2016
Politechnika Poznańska Wydział Maszyn Roboczych i Transportu Inż. NATALIA LEMTIS OPTYMALIZACJA PUBLICZNEGO TRANSPORTU ZBIOROWEGO W GMINIE ŚRODA WIELKOPOLSKA Promotor: DR INŻ. MARCIN KICIŃSKI Poznań, 2016
Linear Classification and Logistic Regression. Pascal Fua IC-CVLab
 Linear Classification and Logistic Regression Pascal Fua IC-CVLab 1 aaagcxicbdtdbtmwfafwdgxlhk8orha31ibqycvkdgpshdqxtwotng2pxtvqujmok1qlky5xllzrnobbediegwcap4votk2kqkf+/y/tnphdschtadu/giv3vtea99cfma8fpx7ytlxx7ckns4sylo3doom7jguhj1hxchmy/irhrlgh67lxb5x3blis8jjqynmedqujiu5zsqqagrx+yjcfpcrydusshmzeluzsg7tttiew5khhcuzm5rv0gn1unw6zl3gbzlpr3liwncyr6aaqinx4wnc/rpg6ix5szd86agoftuu0g/krjxdarph62enthdey3zn/+mi5zknou2ap+tclvhob9sxhwvhaqketnde7geqjp21zvjsfrcnkfhtejoz23vq97elxjlpbtmxpl6qxtl1sgfv1ptpy/yq9mgacrzkgje0hjj2rq7vtywnishnnkzsqekucnlblrarlh8x8szxolrrxkb8n6o4kmo/e7siisnozcfvsedlol60a/j8nmul/gby8mmssrfr2it8lkyxr9dirxxngzthtbaejv
Linear Classification and Logistic Regression Pascal Fua IC-CVLab 1 aaagcxicbdtdbtmwfafwdgxlhk8orha31ibqycvkdgpshdqxtwotng2pxtvqujmok1qlky5xllzrnobbediegwcap4votk2kqkf+/y/tnphdschtadu/giv3vtea99cfma8fpx7ytlxx7ckns4sylo3doom7jguhj1hxchmy/irhrlgh67lxb5x3blis8jjqynmedqujiu5zsqqagrx+yjcfpcrydusshmzeluzsg7tttiew5khhcuzm5rv0gn1unw6zl3gbzlpr3liwncyr6aaqinx4wnc/rpg6ix5szd86agoftuu0g/krjxdarph62enthdey3zn/+mi5zknou2ap+tclvhob9sxhwvhaqketnde7geqjp21zvjsfrcnkfhtejoz23vq97elxjlpbtmxpl6qxtl1sgfv1ptpy/yq9mgacrzkgje0hjj2rq7vtywnishnnkzsqekucnlblrarlh8x8szxolrrxkb8n6o4kmo/e7siisnozcfvsedlol60a/j8nmul/gby8mmssrfr2it8lkyxr9dirxxngzthtbaejv
Metodyki projektowania i modelowania systemów Cyganek & Kasperek & Rajda 2013 Katedra Elektroniki AGH
 Kierunek Elektronika i Telekomunikacja, Studia II stopnia Specjalność: Systemy wbudowane Metodyki projektowania i modelowania systemów Cyganek & Kasperek & Rajda 2013 Katedra Elektroniki AGH Zagadnienia
Kierunek Elektronika i Telekomunikacja, Studia II stopnia Specjalność: Systemy wbudowane Metodyki projektowania i modelowania systemów Cyganek & Kasperek & Rajda 2013 Katedra Elektroniki AGH Zagadnienia
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition)
 Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
DUAL SIMILARITY OF VOLTAGE TO CURRENT AND CURRENT TO VOLTAGE TRANSFER FUNCTION OF HYBRID ACTIVE TWO- PORTS WITH CONVERSION
 ELEKTRYKA 0 Zeszyt (9) Rok LX Andrzej KUKIEŁKA Politechnika Śląska w Gliwicach DUAL SIMILARITY OF VOLTAGE TO CURRENT AND CURRENT TO VOLTAGE TRANSFER FUNCTION OF HYBRID ACTIVE TWO- PORTS WITH CONVERSION
ELEKTRYKA 0 Zeszyt (9) Rok LX Andrzej KUKIEŁKA Politechnika Śląska w Gliwicach DUAL SIMILARITY OF VOLTAGE TO CURRENT AND CURRENT TO VOLTAGE TRANSFER FUNCTION OF HYBRID ACTIVE TWO- PORTS WITH CONVERSION
INSPECTION METHODS FOR QUALITY CONTROL OF FIBRE METAL LAMINATES IN AEROSPACE COMPONENTS
 Kompozyty 11: 2 (2011) 130-135 Krzysztof Dragan 1 * Jarosław Bieniaś 2, Michał Sałaciński 1, Piotr Synaszko 1 1 Air Force Institute of Technology, Non Destructive Testing Lab., ul. ks. Bolesława 6, 01-494
Kompozyty 11: 2 (2011) 130-135 Krzysztof Dragan 1 * Jarosław Bieniaś 2, Michał Sałaciński 1, Piotr Synaszko 1 1 Air Force Institute of Technology, Non Destructive Testing Lab., ul. ks. Bolesława 6, 01-494
Stargard Szczecinski i okolice (Polish Edition)
 Stargard Szczecinski i okolice (Polish Edition) Janusz Leszek Jurkiewicz Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Stargard Szczecinski i okolice (Polish Edition) Janusz Leszek Jurkiewicz
Stargard Szczecinski i okolice (Polish Edition) Janusz Leszek Jurkiewicz Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Stargard Szczecinski i okolice (Polish Edition) Janusz Leszek Jurkiewicz
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 11. Spectral Embedding + Clustering
 Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 11 Spectral Embedding + Clustering MOTIVATING EXAMPLE What can you say from this network? MOTIVATING EXAMPLE How about now? THOUGHT EXPERIMENT For each
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 11 Spectral Embedding + Clustering MOTIVATING EXAMPLE What can you say from this network? MOTIVATING EXAMPLE How about now? THOUGHT EXPERIMENT For each
Zarządzanie sieciami telekomunikacyjnymi
 SNMP Protocol The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an application layer protocol that facilitates the exchange of management information between network devices. It is part of the Transmission
SNMP Protocol The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an application layer protocol that facilitates the exchange of management information between network devices. It is part of the Transmission
DOI: / /32/37
 . 2015. 4 (32) 1:18 DOI: 10.17223/1998863 /32/37 -,,. - -. :,,,,., -, -.,.-.,.,.,. -., -,.,,., -, 70 80. (.,.,. ),, -,.,, -,, (1886 1980).,.,, (.,.,..), -, -,,,, ; -, - 346, -,.. :, -, -,,,,,.,,, -,,,
. 2015. 4 (32) 1:18 DOI: 10.17223/1998863 /32/37 -,,. - -. :,,,,., -, -.,.-.,.,.,. -., -,.,,., -, 70 80. (.,.,. ),, -,.,, -,, (1886 1980).,.,, (.,.,..), -, -,,,, ; -, - 346, -,.. :, -, -,,,,,.,,, -,,,
TTIC 31210: Advanced Natural Language Processing. Kevin Gimpel Spring Lecture 9: Inference in Structured Prediction
 TTIC 31210: Advanced Natural Language Processing Kevin Gimpel Spring 2019 Lecture 9: Inference in Structured Prediction 1 intro (1 lecture) Roadmap deep learning for NLP (5 lectures) structured prediction
TTIC 31210: Advanced Natural Language Processing Kevin Gimpel Spring 2019 Lecture 9: Inference in Structured Prediction 1 intro (1 lecture) Roadmap deep learning for NLP (5 lectures) structured prediction
 www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
ERASMUS + : Trail of extinct and active volcanoes, earthquakes through Europe. SURVEY TO STUDENTS.
 ERASMUS + : Trail of extinct and active volcanoes, earthquakes through Europe. SURVEY TO STUDENTS. Strona 1 1. Please give one answer. I am: Students involved in project 69% 18 Student not involved in
ERASMUS + : Trail of extinct and active volcanoes, earthquakes through Europe. SURVEY TO STUDENTS. Strona 1 1. Please give one answer. I am: Students involved in project 69% 18 Student not involved in
Realizacja systemów wbudowanych (embeded systems) w strukturach PSoC (Programmable System on Chip)
 Realizacja systemów wbudowanych (embeded systems) w strukturach PSoC (Programmable System on Chip) Embeded systems Architektura układów PSoC (Cypress) Możliwości bloków cyfrowych i analogowych Narzędzia
Realizacja systemów wbudowanych (embeded systems) w strukturach PSoC (Programmable System on Chip) Embeded systems Architektura układów PSoC (Cypress) Możliwości bloków cyfrowych i analogowych Narzędzia
Patients price acceptance SELECTED FINDINGS
 Patients price acceptance SELECTED FINDINGS October 2015 Summary With growing economy and Poles benefiting from this growth, perception of prices changes - this is also true for pharmaceuticals It may
Patients price acceptance SELECTED FINDINGS October 2015 Summary With growing economy and Poles benefiting from this growth, perception of prices changes - this is also true for pharmaceuticals It may
 !850016! www.irs.gov/form8879eo. e-file www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C,
!850016! www.irs.gov/form8879eo. e-file www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C,
Selection of controller parameters Strojenie regulatorów
 Division of Metrology and Power Processes Automation Selection of controller parameters Strojenie regulatorów A-9 Automatics laboratory Laboratorium automatyki Developed by//opracował: mgr inż. Wojciech
Division of Metrology and Power Processes Automation Selection of controller parameters Strojenie regulatorów A-9 Automatics laboratory Laboratorium automatyki Developed by//opracował: mgr inż. Wojciech
Miedzy legenda a historia: Szlakiem piastowskim z Poznania do Gniezna (Biblioteka Kroniki Wielkopolski) (Polish Edition)
 Miedzy legenda a historia: Szlakiem piastowskim z Poznania do Gniezna (Biblioteka Kroniki Wielkopolski) (Polish Edition) Piotr Maluskiewicz Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Miedzy
Miedzy legenda a historia: Szlakiem piastowskim z Poznania do Gniezna (Biblioteka Kroniki Wielkopolski) (Polish Edition) Piotr Maluskiewicz Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Miedzy
 aforementioned device she also has to estimate the time when the patients need the infusion to be replaced and/or disconnected. Meanwhile, however, she must cope with many other tasks. If the department
aforementioned device she also has to estimate the time when the patients need the infusion to be replaced and/or disconnected. Meanwhile, however, she must cope with many other tasks. If the department
Weronika Mysliwiec, klasa 8W, rok szkolny 2018/2019
 Poniższy zbiór zadań został wykonany w ramach projektu Mazowiecki program stypendialny dla uczniów szczególnie uzdolnionych - najlepsza inwestycja w człowieka w roku szkolnym 2018/2019. Tresci zadań rozwiązanych
Poniższy zbiór zadań został wykonany w ramach projektu Mazowiecki program stypendialny dla uczniów szczególnie uzdolnionych - najlepsza inwestycja w człowieka w roku szkolnym 2018/2019. Tresci zadań rozwiązanych
Wydział Fizyki, Astronomii i Informatyki Stosowanej Uniwersytet Mikołaja Kopernika w Toruniu
 IONS-14 / OPTO Meeting For Young Researchers 2013 Khet Tournament On 3-6 July 2013 at the Faculty of Physics, Astronomy and Informatics of Nicolaus Copernicus University in Torun (Poland) there were two
IONS-14 / OPTO Meeting For Young Researchers 2013 Khet Tournament On 3-6 July 2013 at the Faculty of Physics, Astronomy and Informatics of Nicolaus Copernicus University in Torun (Poland) there were two
No matter how much you have, it matters how much you need
 CSR STRATEGY KANCELARIA FINANSOWA TRITUM GROUP SP. Z O.O. No matter how much you have, it matters how much you need Kancelaria Finansowa Tritum Group Sp. z o.o. was established in 2007 we build trust among
CSR STRATEGY KANCELARIA FINANSOWA TRITUM GROUP SP. Z O.O. No matter how much you have, it matters how much you need Kancelaria Finansowa Tritum Group Sp. z o.o. was established in 2007 we build trust among
QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE CHARACTERISTICS OF FINGERPRINT BIOMETRIC TEMPLATES
 ZESZYTY NAUKOWE POLITECHNIKI ŚLĄSKIEJ 2014 Seria: ORGANIZACJA I ZARZĄDZANIE z. 74 Nr kol. 1921 Adrian KAPCZYŃSKI Politechnika Śląska Instytut Ekonomii i Informatyki QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE CHARACTERISTICS
ZESZYTY NAUKOWE POLITECHNIKI ŚLĄSKIEJ 2014 Seria: ORGANIZACJA I ZARZĄDZANIE z. 74 Nr kol. 1921 Adrian KAPCZYŃSKI Politechnika Śląska Instytut Ekonomii i Informatyki QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE CHARACTERISTICS
 www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
Pielgrzymka do Ojczyzny: Przemowienia i homilie Ojca Swietego Jana Pawla II (Jan Pawel II-- pierwszy Polak na Stolicy Piotrowej) (Polish Edition)
 Pielgrzymka do Ojczyzny: Przemowienia i homilie Ojca Swietego Jana Pawla II (Jan Pawel II-- pierwszy Polak na Stolicy Piotrowej) (Polish Edition) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically
Pielgrzymka do Ojczyzny: Przemowienia i homilie Ojca Swietego Jana Pawla II (Jan Pawel II-- pierwszy Polak na Stolicy Piotrowej) (Polish Edition) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically
Domy inaczej pomyślane A different type of housing CEZARY SANKOWSKI
 Domy inaczej pomyślane A different type of housing CEZARY SANKOWSKI O tym, dlaczego warto budować pasywnie, komu budownictwo pasywne się opłaca, a kto się go boi, z architektem, Cezarym Sankowskim, rozmawia
Domy inaczej pomyślane A different type of housing CEZARY SANKOWSKI O tym, dlaczego warto budować pasywnie, komu budownictwo pasywne się opłaca, a kto się go boi, z architektem, Cezarym Sankowskim, rozmawia
F-16 VIRTUAL COCKPIT PROJECT OF COMPUTER-AIDED LEARNING APPLICATION WEAPON SYSTEM POWER ON PROCEDURE
 GRZESIK Norbert 1 Virtual cockpit, computer-aided learning application, maintenance procedures F-16 VIRTUAL COCKPIT PROJECT OF COMPUTER-AIDED LEARNING APPLICATION WEAPON SYSTEM POWER ON PROCEDURE Author,
GRZESIK Norbert 1 Virtual cockpit, computer-aided learning application, maintenance procedures F-16 VIRTUAL COCKPIT PROJECT OF COMPUTER-AIDED LEARNING APPLICATION WEAPON SYSTEM POWER ON PROCEDURE Author,
Auditorium classes. Lectures
 Faculty of: Mechanical and Robotics Field of study: Mechatronic with English as instruction language Study level: First-cycle studies Form and type of study: Full-time studies Annual: 2016/2017 Lecture
Faculty of: Mechanical and Robotics Field of study: Mechatronic with English as instruction language Study level: First-cycle studies Form and type of study: Full-time studies Annual: 2016/2017 Lecture
Latent Dirichlet Allocation Models and their Evaluation IT for Practice 2016
 Latent Dirichlet Allocation Models and their Evaluation IT for Practice 2016 Paweł Lula Cracow University of Economics, Poland pawel.lula@uek.krakow.pl Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) Documents Latent
Latent Dirichlet Allocation Models and their Evaluation IT for Practice 2016 Paweł Lula Cracow University of Economics, Poland pawel.lula@uek.krakow.pl Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) Documents Latent
Dolny Slask 1: , mapa turystycznosamochodowa: Plan Wroclawia (Polish Edition)
 Dolny Slask 1:300 000, mapa turystycznosamochodowa: Plan Wroclawia (Polish Edition) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Dolny Slask 1:300 000, mapa turystyczno-samochodowa: Plan Wroclawia
Dolny Slask 1:300 000, mapa turystycznosamochodowa: Plan Wroclawia (Polish Edition) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Dolny Slask 1:300 000, mapa turystyczno-samochodowa: Plan Wroclawia
Krytyczne czynniki sukcesu w zarządzaniu projektami
 Seweryn SPAŁEK Krytyczne czynniki sukcesu w zarządzaniu projektami MONOGRAFIA Wydawnictwo Politechniki Śląskiej Gliwice 2004 SPIS TREŚCI WPROWADZENIE 5 1. ZARZĄDZANIE PROJEKTAMI W ORGANIZACJI 13 1.1. Zarządzanie
Seweryn SPAŁEK Krytyczne czynniki sukcesu w zarządzaniu projektami MONOGRAFIA Wydawnictwo Politechniki Śląskiej Gliwice 2004 SPIS TREŚCI WPROWADZENIE 5 1. ZARZĄDZANIE PROJEKTAMI W ORGANIZACJI 13 1.1. Zarządzanie
Wybrzeze Baltyku, mapa turystyczna 1: (Polish Edition)
 Wybrzeze Baltyku, mapa turystyczna 1:50 000 (Polish Edition) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wybrzeze Baltyku, mapa turystyczna 1:50 000 (Polish Edition) Wybrzeze Baltyku, mapa
Wybrzeze Baltyku, mapa turystyczna 1:50 000 (Polish Edition) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wybrzeze Baltyku, mapa turystyczna 1:50 000 (Polish Edition) Wybrzeze Baltyku, mapa
Network Services for Spatial Data in European Geo-Portals and their Compliance with ISO and OGC Standards
 INSPIRE Conference 2010 INSPIRE as a Framework for Cooperation Network Services for Spatial Data in European Geo-Portals and their Compliance with ISO and OGC Standards Elżbieta Bielecka Agnieszka Zwirowicz
INSPIRE Conference 2010 INSPIRE as a Framework for Cooperation Network Services for Spatial Data in European Geo-Portals and their Compliance with ISO and OGC Standards Elżbieta Bielecka Agnieszka Zwirowicz
Emilka szuka swojej gwiazdy / Emily Climbs (Emily, #2)
 Emilka szuka swojej gwiazdy / Emily Climbs (Emily, #2) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Emilka szuka swojej gwiazdy / Emily Climbs (Emily, #2) Emilka szuka swojej gwiazdy / Emily
Emilka szuka swojej gwiazdy / Emily Climbs (Emily, #2) Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Emilka szuka swojej gwiazdy / Emily Climbs (Emily, #2) Emilka szuka swojej gwiazdy / Emily
A n g i e l s k i. Phrasal Verbs in Situations. Podręcznik z ćwiczeniami. Dorota Guzik Joanna Bruska FRAGMENT
 A n g i e l s k i Phrasal Verbs in Situations Podręcznik z ćwiczeniami FRAGMENT Dorota Guzik Joanna Bruska Autorzy: Dorota Guzik, Joanna Bruska Konsultacja językowa: Tadeusz Z. Wolański Lektorzy: Maybe
A n g i e l s k i Phrasal Verbs in Situations Podręcznik z ćwiczeniami FRAGMENT Dorota Guzik Joanna Bruska Autorzy: Dorota Guzik, Joanna Bruska Konsultacja językowa: Tadeusz Z. Wolański Lektorzy: Maybe
Knovel Math: Jakość produktu
 Knovel Math: Jakość produktu Knovel jest agregatorem materiałów pełnotekstowych dostępnych w formacie PDF i interaktywnym. Narzędzia interaktywne Knovel nie są stworzone wokół specjalnych algorytmów wymagających
Knovel Math: Jakość produktu Knovel jest agregatorem materiałów pełnotekstowych dostępnych w formacie PDF i interaktywnym. Narzędzia interaktywne Knovel nie są stworzone wokół specjalnych algorytmów wymagających
Podstawy automatyki. Energetics 1 st degree (1st degree / 2nd degree) General (general / practical) Full-time (full-time / part-time)
 MODULE DESCRIPTION Module code Module name Podstawy automatyki Module name in English The Fundamentals of Automatic Control Valid from academic year 2012/2013 MODULE PLACEMENT IN THE SYLLABUS Subject Level
MODULE DESCRIPTION Module code Module name Podstawy automatyki Module name in English The Fundamentals of Automatic Control Valid from academic year 2012/2013 MODULE PLACEMENT IN THE SYLLABUS Subject Level
Revenue Maximization. Sept. 25, 2018
 Revenue Maximization Sept. 25, 2018 Goal So Far: Ideal Auctions Dominant-Strategy Incentive Compatible (DSIC) b i = v i is a dominant strategy u i 0 x is welfare-maximizing x and p run in polynomial time
Revenue Maximization Sept. 25, 2018 Goal So Far: Ideal Auctions Dominant-Strategy Incentive Compatible (DSIC) b i = v i is a dominant strategy u i 0 x is welfare-maximizing x and p run in polynomial time
PORTS AS LOGISTICS CENTERS FOR CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION OF THE OFFSHORE WIND FARMS - CASE OF SASSNITZ
 Part-financed by EU South Baltic Programme w w w. p t m e w. p l PROSPECTS OF THE OFFSHORE WIND ENERGY DEVELOPMENT IN POLAND - OFFSHORE WIND INDUSTRY IN THE COASTAL CITIES AND PORT AREAS PORTS AS LOGISTICS
Part-financed by EU South Baltic Programme w w w. p t m e w. p l PROSPECTS OF THE OFFSHORE WIND ENERGY DEVELOPMENT IN POLAND - OFFSHORE WIND INDUSTRY IN THE COASTAL CITIES AND PORT AREAS PORTS AS LOGISTICS
The Overview of Civilian Applications of Airborne SAR Systems
 The Overview of Civilian Applications of Airborne SAR Systems Maciej Smolarczyk, Piotr Samczyński Andrzej Gadoś, Maj Mordzonek Research and Development Department of PIT S.A. PART I WHAT DOES SAR MEAN?
The Overview of Civilian Applications of Airborne SAR Systems Maciej Smolarczyk, Piotr Samczyński Andrzej Gadoś, Maj Mordzonek Research and Development Department of PIT S.A. PART I WHAT DOES SAR MEAN?
SCIENTIFIC PROBLEMS OF MACHINES OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE
 POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES COMMITTEE OF MACHINE ENGINEERING SCIENTIFIC PROBLEMS OF MACHINES OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE ZAGADNIENIA EKSPLOATACJI MASZYN TRIBOLOGY RELIABILITY TEROTECHNOLOGY DIAGNOSTICS SAFETY
POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES COMMITTEE OF MACHINE ENGINEERING SCIENTIFIC PROBLEMS OF MACHINES OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE ZAGADNIENIA EKSPLOATACJI MASZYN TRIBOLOGY RELIABILITY TEROTECHNOLOGY DIAGNOSTICS SAFETY
TTIC 31210: Advanced Natural Language Processing. Kevin Gimpel Spring Lecture 8: Structured PredicCon 2
 TTIC 31210: Advanced Natural Language Processing Kevin Gimpel Spring 2019 Lecture 8: Structured PredicCon 2 1 Roadmap intro (1 lecture) deep learning for NLP (5 lectures) structured predic+on (4 lectures)
TTIC 31210: Advanced Natural Language Processing Kevin Gimpel Spring 2019 Lecture 8: Structured PredicCon 2 1 Roadmap intro (1 lecture) deep learning for NLP (5 lectures) structured predic+on (4 lectures)
2014-3-30. Urbanek J., Jabłoński A., Barszcz T ssswedfsdfurbanek J., Jabłoński A., Barszcz T., Wykonanie pomiarów
 Wykonanie pomiarów sygnałów wibroakustycznych przy stałych oraz zmiennych warunkach eksploatacyjnych na stanowisku testowym. Część II: Analiza poprawności pomiarów. Autorzy: Urbanek J., Jabłoński A., Barszcz
Wykonanie pomiarów sygnałów wibroakustycznych przy stałych oraz zmiennych warunkach eksploatacyjnych na stanowisku testowym. Część II: Analiza poprawności pomiarów. Autorzy: Urbanek J., Jabłoński A., Barszcz
POLITECHNIKA WARSZAWSKA. Wydział Zarządzania ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA. mgr Marcin Chrząścik
 POLITECHNIKA WARSZAWSKA Wydział Zarządzania ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA mgr Marcin Chrząścik Model strategii promocji w zarządzaniu wizerunkiem regionu Warmii i Mazur Promotor dr hab. Jarosław S. Kardas, prof.
POLITECHNIKA WARSZAWSKA Wydział Zarządzania ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA mgr Marcin Chrząścik Model strategii promocji w zarządzaniu wizerunkiem regionu Warmii i Mazur Promotor dr hab. Jarosław S. Kardas, prof.
Ankiety Nowe funkcje! Pomoc magda.szewczyk@slo-wroc.pl. magda.szewczyk@slo-wroc.pl. Twoje konto Wyloguj. BIODIVERSITY OF RIVERS: Survey to students
 Ankiety Nowe funkcje! Pomoc magda.szewczyk@slo-wroc.pl Back Twoje konto Wyloguj magda.szewczyk@slo-wroc.pl BIODIVERSITY OF RIVERS: Survey to students Tworzenie ankiety Udostępnianie Analiza (55) Wyniki
Ankiety Nowe funkcje! Pomoc magda.szewczyk@slo-wroc.pl Back Twoje konto Wyloguj magda.szewczyk@slo-wroc.pl BIODIVERSITY OF RIVERS: Survey to students Tworzenie ankiety Udostępnianie Analiza (55) Wyniki
PROCEEDINGS OF THE INSTITUTE OF VEHICLES 2(106)/2016 (12 pt)
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE INSTITUTE OF VEHICLES 2(106)/2016 Maciej Foremny 1, Szymon Gudowski 2, Michał Malesza 3, Henryk Bąkowski 4 TRIBOLOGICAL WEAR ESTIMATION OF THE ENGINE OILS USED IN DRIFTING 1. Introduction
PROCEEDINGS OF THE INSTITUTE OF VEHICLES 2(106)/2016 Maciej Foremny 1, Szymon Gudowski 2, Michał Malesza 3, Henryk Bąkowski 4 TRIBOLOGICAL WEAR ESTIMATION OF THE ENGINE OILS USED IN DRIFTING 1. Introduction
Analysis of Movie Profitability STAT 469 IN CLASS ANALYSIS #2
 Analysis of Movie Profitability STAT 469 IN CLASS ANALYSIS #2 aaaklnictzzjb9tgfmcnadpg7oy0lxa9edva9kkapdarhyk2k7gourinlwsweyzikuyiigvyleiv/cv767fpf/5crc1xt9va5mx7w3m/ecuqw1kuztpx/rl3/70h73/w4cog9dhhn3z62d6jzy+yzj766txpoir9nzszisjynetqr+rvlfvyoozu5xbybpsxb1wahul8phczdt2v4zgchb7uecwphlyigrgkjcyiflfyci0kxnmr4z6kw0jsokvot8isntpa3gbknlcufiv/h+hh+eur4fomd417rvtfjoit5pfju6yxiab2fmwk0y/feuybobqk+axnke8xzjjhfyd8kkpl9zdoddkazd5j6bzpemjb64smjb6vb4xmehysu08lsrszopxftlzee130jcb0zjxy7r5wa2f1s2off2+dyatrughnrtpkuprlcpu55zlxpss/yqe2eamjkcf0jye8w8yas0paf6t0t2i9stmcua+inbi2rt01tz22tubbqwidypvgz6piynkpobirkxgu54ibzoti4pkw2i5ow9lnuaoabhuxfxqhvnrj6w15tb3furnbm+scyxobjhr5pmj5j/w5ix9wsa2tlwx9alpshlunzjgnrwvqbpwzjl9wes+ptyn+ypy/jgskavtl8j0hz1djdhzwtpjbbvpr1zj7jpg6ve7zxfngj75zee0vmp9qm2uvgu/9zdofq6r+g8l4xctvo+v+xdrfr8oxiwutycu0qgyf8icuyvp/sixfi9zxe11vp6mrjjovpmxm6acrtbia+wjr9bevlgjwlz5xd3rfna9g06qytaoofk8olxbxc7xby2evqjmmk6pjvvzxmpbnct6+036xp5vdbrnbdqph8brlfn/n/khnfumhf6z1v7h/80yieukkd5j0un82t9mynxzmk0s/bzn4tacdziszdhwrl8x5ako8qp1n1zn0k6w2em0km9zj1i4yt1pt3xiprw85jmc2m1ut2geum6y6es2fwx6c+wlrpykblopbuj5nnr2byygfy5opllv4+jmm7s6u+tvhywbnb0kv2lt5th4xipmiij+y1toiyo7bo0d+vzvovjkp6aoejsubhj3qrp3fjd/m23pay8h218ibvx3nicofvd1xi86+kh6nb/b+hgsjp5+qwpurzlir15np66vmdehh6tyazdm1k/5ejtuvurgcqux6yc+qw/sbsaj7lkt4x9qmtp7euk6zbdedyuzu6ptsu2eeu3rxcz06uf6g8wyuveznhkbzynajbb7r7cbmla+jbtrst0ow2v6ntkwv8svnwqnu5pa3oxfeexf93739p93chq/fv+jr8r0d9brhpcxr2w88bvqbr41j6wvrb+u5dzjpvx+veoaxwptzp/8cen+xbg==
Analysis of Movie Profitability STAT 469 IN CLASS ANALYSIS #2 aaaklnictzzjb9tgfmcnadpg7oy0lxa9edva9kkapdarhyk2k7gourinlwsweyzikuyiigvyleiv/cv767fpf/5crc1xt9va5mx7w3m/ecuqw1kuztpx/rl3/70h73/w4cog9dhhn3z62d6jzy+yzj766txpoir9nzszisjynetqr+rvlfvyoozu5xbybpsxb1wahul8phczdt2v4zgchb7uecwphlyigrgkjcyiflfyci0kxnmr4z6kw0jsokvot8isntpa3gbknlcufiv/h+hh+eur4fomd417rvtfjoit5pfju6yxiab2fmwk0y/feuybobqk+axnke8xzjjhfyd8kkpl9zdoddkazd5j6bzpemjb64smjb6vb4xmehysu08lsrszopxftlzee130jcb0zjxy7r5wa2f1s2off2+dyatrughnrtpkuprlcpu55zlxpss/yqe2eamjkcf0jye8w8yas0paf6t0t2i9stmcua+inbi2rt01tz22tubbqwidypvgz6piynkpobirkxgu54ibzoti4pkw2i5ow9lnuaoabhuxfxqhvnrj6w15tb3furnbm+scyxobjhr5pmj5j/w5ix9wsa2tlwx9alpshlunzjgnrwvqbpwzjl9wes+ptyn+ypy/jgskavtl8j0hz1djdhzwtpjbbvpr1zj7jpg6ve7zxfngj75zee0vmp9qm2uvgu/9zdofq6r+g8l4xctvo+v+xdrfr8oxiwutycu0qgyf8icuyvp/sixfi9zxe11vp6mrjjovpmxm6acrtbia+wjr9bevlgjwlz5xd3rfna9g06qytaoofk8olxbxc7xby2evqjmmk6pjvvzxmpbnct6+036xp5vdbrnbdqph8brlfn/n/khnfumhf6z1v7h/80yieukkd5j0un82t9mynxzmk0s/bzn4tacdziszdhwrl8x5ako8qp1n1zn0k6w2em0km9zj1i4yt1pt3xiprw85jmc2m1ut2geum6y6es2fwx6c+wlrpykblopbuj5nnr2byygfy5opllv4+jmm7s6u+tvhywbnb0kv2lt5th4xipmiij+y1toiyo7bo0d+vzvovjkp6aoejsubhj3qrp3fjd/m23pay8h218ibvx3nicofvd1xi86+kh6nb/b+hgsjp5+qwpurzlir15np66vmdehh6tyazdm1k/5ejtuvurgcqux6yc+qw/sbsaj7lkt4x9qmtp7euk6zbdedyuzu6ptsu2eeu3rxcz06uf6g8wyuveznhkbzynajbb7r7cbmla+jbtrst0ow2v6ntkwv8svnwqnu5pa3oxfeexf93739p93chq/fv+jr8r0d9brhpcxr2w88bvqbr41j6wvrb+u5dzjpvx+veoaxwptzp/8cen+xbg==
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition)
 Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
WYDZIAŁ NAUK EKONOMICZNYCH. Studia II stopnia niestacjonarne Kierunek Międzynarodowe Stosunki Gospodarcze Specjalność INERNATIONAL LOGISTICS
 Studia II stopnia niestacjonarne Kierunek Międzynarodowe Stosunki Gospodarcze Specjalność INERNATIONAL LOGISTICS Description Master Studies in International Logistics is the four-semesters studies, dedicate
Studia II stopnia niestacjonarne Kierunek Międzynarodowe Stosunki Gospodarcze Specjalność INERNATIONAL LOGISTICS Description Master Studies in International Logistics is the four-semesters studies, dedicate
AKADEMIA MORSKA W SZCZECINIE WYDZIAŁ MECHANICZNY ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA. mgr inż. Piotr Smurawski
 AKADEMIA MORSKA W SZCZECINIE WYDZIAŁ MECHANICZNY ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA mgr inż. Piotr Smurawski ANALIZA CYKLU ŻYCIA SAMOCHODÓW OSOBOWYCH Z UWZGLĘDNIENIEM PROCESÓW OBSŁUGOWO-NAPRAWCZYCH Praca wykonana pod
AKADEMIA MORSKA W SZCZECINIE WYDZIAŁ MECHANICZNY ROZPRAWA DOKTORSKA mgr inż. Piotr Smurawski ANALIZA CYKLU ŻYCIA SAMOCHODÓW OSOBOWYCH Z UWZGLĘDNIENIEM PROCESÓW OBSŁUGOWO-NAPRAWCZYCH Praca wykonana pod
European Crime Prevention Award (ECPA) Annex I - new version 2014
 European Crime Prevention Award (ECPA) Annex I - new version 2014 Załącznik nr 1 General information (Informacje ogólne) 1. Please specify your country. (Kraj pochodzenia:) 2. Is this your country s ECPA
European Crime Prevention Award (ECPA) Annex I - new version 2014 Załącznik nr 1 General information (Informacje ogólne) 1. Please specify your country. (Kraj pochodzenia:) 2. Is this your country s ECPA
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition)
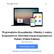 Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie: Obiekty i walory krajoznawcze (Inwentaryzacja krajoznawcza Polski) (Polish Edition) Robert Respondowski Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Wojewodztwo Koszalinskie:
PROJECT. Syllabus for course Negotiations. on the study program: Management
 Poznań, 2012, September 20th Doctor Anna Scheibe adiunct in the Department of Economic Sciences PROJECT Syllabus for course Negotiations on the study program: Management I. General information 1. Name
Poznań, 2012, September 20th Doctor Anna Scheibe adiunct in the Department of Economic Sciences PROJECT Syllabus for course Negotiations on the study program: Management I. General information 1. Name
WYBRANE PROBLEMY BADAWCZE EKOLOGII, ORGANIZACJI I INFRASTRUKTURY TRANSPORTU
 POLITECHNIKA WARSZAWSKA ISSN 1230 9265 PRACE NAUKOWE TRANSPORT z. 106 WYBRANE PROBLEMY BADAWCZE EKOLOGII, ORGANIZACJI I INFRASTRUKTURY TRANSPORTU OFICYNA WYDAWNICZA POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ WARSZAWA 2015
POLITECHNIKA WARSZAWSKA ISSN 1230 9265 PRACE NAUKOWE TRANSPORT z. 106 WYBRANE PROBLEMY BADAWCZE EKOLOGII, ORGANIZACJI I INFRASTRUKTURY TRANSPORTU OFICYNA WYDAWNICZA POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ WARSZAWA 2015
OpenPoland.net API Documentation
 OpenPoland.net API Documentation Release 1.0 Michał Gryczka July 11, 2014 Contents 1 REST API tokens: 3 1.1 How to get a token............................................ 3 2 REST API : search for assets
OpenPoland.net API Documentation Release 1.0 Michał Gryczka July 11, 2014 Contents 1 REST API tokens: 3 1.1 How to get a token............................................ 3 2 REST API : search for assets
DM-ML, DM-FL. Auxiliary Equipment and Accessories. Damper Drives. Dimensions. Descritpion
 DM-ML, DM-FL Descritpion DM-ML and DM-FL actuators are designed for driving round dampers and square multi-blade dampers. Example identification Product code: DM-FL-5-2 voltage Dimensions DM-ML-6 DM-ML-8
DM-ML, DM-FL Descritpion DM-ML and DM-FL actuators are designed for driving round dampers and square multi-blade dampers. Example identification Product code: DM-FL-5-2 voltage Dimensions DM-ML-6 DM-ML-8
Few-fermion thermometry
 Few-fermion thermometry Phys. Rev. A 97, 063619 (2018) Tomasz Sowiński Institute of Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences Co-authors: Marcin Płodzień Rafał Demkowicz-Dobrzański FEW-BODY PROBLEMS FewBody.ifpan.edu.pl
Few-fermion thermometry Phys. Rev. A 97, 063619 (2018) Tomasz Sowiński Institute of Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences Co-authors: Marcin Płodzień Rafał Demkowicz-Dobrzański FEW-BODY PROBLEMS FewBody.ifpan.edu.pl
Financial support for start-uppres. Where to get money? - Equity. - Credit. - Local Labor Office - Six times the national average wage (22000 zł)
 Financial support for start-uppres Where to get money? - Equity - Credit - Local Labor Office - Six times the national average wage (22000 zł) - only for unymployed people - the company must operate minimum
Financial support for start-uppres Where to get money? - Equity - Credit - Local Labor Office - Six times the national average wage (22000 zł) - only for unymployed people - the company must operate minimum
PRACA DYPLOMOWA Magisterska
 POLITECHNIKA WARSZAWSKA Wydział Samochodów i Maszyn Roboczych PRACA DYPLOMOWA Magisterska Studia stacjonarne dzienne Semiaktywne tłumienie drgań w wymuszonych kinematycznie układach drgających z uwzględnieniem
POLITECHNIKA WARSZAWSKA Wydział Samochodów i Maszyn Roboczych PRACA DYPLOMOWA Magisterska Studia stacjonarne dzienne Semiaktywne tłumienie drgań w wymuszonych kinematycznie układach drgających z uwzględnieniem
 www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
www.irs.gov/form990. If "Yes," complete Schedule A Schedule B, Schedule of Contributors If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part I If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part II If "Yes," complete Schedule C, Part
KONSPEKT DO LEKCJI MATEMATYKI W KLASIE 3 POLO/ A LAYER FOR CLASS 3 POLO MATHEMATICS
 KONSPEKT DO LEKCJI MATEMATYKI W KLASIE 3 POLO/ A LAYER FOR CLASS 3 POLO MATHEMATICS Temat: Funkcja logarytmiczna (i wykładnicza)/ Logarithmic (and exponential) function Typ lekcji: Lekcja ćwiczeniowa/training
KONSPEKT DO LEKCJI MATEMATYKI W KLASIE 3 POLO/ A LAYER FOR CLASS 3 POLO MATHEMATICS Temat: Funkcja logarytmiczna (i wykładnicza)/ Logarithmic (and exponential) function Typ lekcji: Lekcja ćwiczeniowa/training
PRZEWODNIK PO PRZEDMIOCIE. Negotiation techniques. Management. Stationary. II degree
 Politechnika Częstochowska, Wydział Zarządzania PRZEWODNIK PO PRZEDMIOCIE Nazwa przedmiotu Kierunek Forma studiów Poziom kwalifikacji Rok Semestr Jednostka prowadząca Osoba sporządzająca Profil Rodzaj
Politechnika Częstochowska, Wydział Zarządzania PRZEWODNIK PO PRZEDMIOCIE Nazwa przedmiotu Kierunek Forma studiów Poziom kwalifikacji Rok Semestr Jednostka prowadząca Osoba sporządzająca Profil Rodzaj
Wprowadzenie do programu RapidMiner, część 2 Michał Bereta 1. Wykorzystanie wykresu ROC do porównania modeli klasyfikatorów
 Wprowadzenie do programu RapidMiner, część 2 Michał Bereta www.michalbereta.pl 1. Wykorzystanie wykresu ROC do porównania modeli klasyfikatorów Zaimportuj dane pima-indians-diabetes.csv. (Baza danych poświęcona
Wprowadzenie do programu RapidMiner, część 2 Michał Bereta www.michalbereta.pl 1. Wykorzystanie wykresu ROC do porównania modeli klasyfikatorów Zaimportuj dane pima-indians-diabetes.csv. (Baza danych poświęcona
How much does SMARTech system cost?
 1. How much does an intelligent home system cost? With over six years of experience in construction of Intelligent Home Systems we have done a value analysis of systems and services usually purchased by
1. How much does an intelligent home system cost? With over six years of experience in construction of Intelligent Home Systems we have done a value analysis of systems and services usually purchased by
Installation of EuroCert software for qualified electronic signature
 Installation of EuroCert software for qualified electronic signature for Microsoft Windows systems Warsaw 28.08.2019 Content 1. Downloading and running the software for the e-signature... 3 a) Installer
Installation of EuroCert software for qualified electronic signature for Microsoft Windows systems Warsaw 28.08.2019 Content 1. Downloading and running the software for the e-signature... 3 a) Installer
Politechnika Krakowska im. Tadeusza Kościuszki. Karta przedmiotu. obowiązuje studentów rozpoczynających studia w roku akademickim 2014/2015
 Politechnika Krakowska im. Tadeusza Kościuszki Karta przedmiotu Wydział Inżynierii Środowiska obowiązuje studentów rozpoczynających studia w roku akademickim 014/015 Kierunek studiów: Inżynieria Środowiska
Politechnika Krakowska im. Tadeusza Kościuszki Karta przedmiotu Wydział Inżynierii Środowiska obowiązuje studentów rozpoczynających studia w roku akademickim 014/015 Kierunek studiów: Inżynieria Środowiska
Strona główna > Produkty > Systemy regulacji > System regulacji EASYLAB - LABCONTROL > Program konfiguracyjny > Typ EasyConnect.
 Typ EasyConnect FOR THE COMMISSIONING AND DIAGNOSIS OF EASYLAB COMPONENTS, FSE, AND FMS Software for the configuration and diagnosis of controllers Type TCU3, adapter modules TAM, automatic sash device
Typ EasyConnect FOR THE COMMISSIONING AND DIAGNOSIS OF EASYLAB COMPONENTS, FSE, AND FMS Software for the configuration and diagnosis of controllers Type TCU3, adapter modules TAM, automatic sash device
Cracow University of Economics Poland. Overview. Sources of Real GDP per Capita Growth: Polish Regional-Macroeconomic Dimensions 2000-2005
 Cracow University of Economics Sources of Real GDP per Capita Growth: Polish Regional-Macroeconomic Dimensions 2000-2005 - Key Note Speech - Presented by: Dr. David Clowes The Growth Research Unit CE Europe
Cracow University of Economics Sources of Real GDP per Capita Growth: Polish Regional-Macroeconomic Dimensions 2000-2005 - Key Note Speech - Presented by: Dr. David Clowes The Growth Research Unit CE Europe
Convolution semigroups with linear Jacobi parameters
 Convolution semigroups with linear Jacobi parameters Michael Anshelevich; Wojciech Młotkowski Texas A&M University; University of Wrocław February 14, 2011 Jacobi parameters. µ = measure with finite moments,
Convolution semigroups with linear Jacobi parameters Michael Anshelevich; Wojciech Młotkowski Texas A&M University; University of Wrocław February 14, 2011 Jacobi parameters. µ = measure with finite moments,
TACHOGRAPH SIMULATOR DTCOSIM
 TACHOGRAPH SIMULATOR DTCOSIM Service Manual USB-KSIM interface General description The simulator is a device that is used as a replacement for tachograph in the vehicle where the tachograph is not mandatory,
TACHOGRAPH SIMULATOR DTCOSIM Service Manual USB-KSIM interface General description The simulator is a device that is used as a replacement for tachograph in the vehicle where the tachograph is not mandatory,
REHABILITATION OF MEDIUM-HEAD HYDROPOWER PLANTS WITH EXPLOITED TWIN-FRANCIS TURBINES.
 ZRE Gdańsk S.A. ul. Litewska 14A 80-719 Gdańsk REHABILITATION OF MEDIUM-HEAD HYDROPOWER PLANTS WITH EXPLOITED TWIN-FRANCIS TURBINES. Maciej Kaniecki, PhD Andrzej Łojek, PhD Marusz Hajdarowicz, M.Sc.Eng
ZRE Gdańsk S.A. ul. Litewska 14A 80-719 Gdańsk REHABILITATION OF MEDIUM-HEAD HYDROPOWER PLANTS WITH EXPLOITED TWIN-FRANCIS TURBINES. Maciej Kaniecki, PhD Andrzej Łojek, PhD Marusz Hajdarowicz, M.Sc.Eng
Raport bieżący: 44/2018 Data: g. 21:03 Skrócona nazwa emitenta: SERINUS ENERGY plc
 Raport bieżący: 44/2018 Data: 2018-05-23 g. 21:03 Skrócona nazwa emitenta: SERINUS ENERGY plc Temat: Zawiadomienie o zmianie udziału w ogólnej liczbie głosów w Serinus Energy plc Podstawa prawna: Inne
Raport bieżący: 44/2018 Data: 2018-05-23 g. 21:03 Skrócona nazwa emitenta: SERINUS ENERGY plc Temat: Zawiadomienie o zmianie udziału w ogólnej liczbie głosów w Serinus Energy plc Podstawa prawna: Inne
Effective Governance of Education at the Local Level
 Effective Governance of Education at the Local Level Opening presentation at joint Polish Ministry OECD conference April 16, 2012, Warsaw Mirosław Sielatycki Ministry of National Education Doskonalenie
Effective Governance of Education at the Local Level Opening presentation at joint Polish Ministry OECD conference April 16, 2012, Warsaw Mirosław Sielatycki Ministry of National Education Doskonalenie
archivist: Managing Data Analysis Results
 archivist: Managing Data Analysis Results https://github.com/pbiecek/archivist Marcin Kosiński 1,2, Przemysław Biecek 2 1 IT Research and Development Grupa Wirtualna Polska 2 Faculty of Mathematics, Informatics
archivist: Managing Data Analysis Results https://github.com/pbiecek/archivist Marcin Kosiński 1,2, Przemysław Biecek 2 1 IT Research and Development Grupa Wirtualna Polska 2 Faculty of Mathematics, Informatics
photo graphic Jan Witkowski Project for exhibition compositions typography colors : +48 506 780 943 : janwi@janwi.com
 Jan Witkowski : +48 506 780 943 : janwi@janwi.com Project for exhibition photo graphic compositions typography colors Berlin London Paris Barcelona Vienna Prague Krakow Zakopane Jan Witkowski ARTIST FROM
Jan Witkowski : +48 506 780 943 : janwi@janwi.com Project for exhibition photo graphic compositions typography colors Berlin London Paris Barcelona Vienna Prague Krakow Zakopane Jan Witkowski ARTIST FROM
STATISTICAL METHODS IN BIOLOGY
 STATISTICAL METHODS IN BIOLOGY 1. Introduction 2. Populations and samples 3. Hypotheses testing and parameter estimation 4. Experimental design for biological data 5. Most widely used statistical tests
STATISTICAL METHODS IN BIOLOGY 1. Introduction 2. Populations and samples 3. Hypotheses testing and parameter estimation 4. Experimental design for biological data 5. Most widely used statistical tests
Presented by. Dr. Morten Middelfart, CTO
 Meeting Big Data challenges in Leadership with Human-Computer Synergy. Presented by Dr. Morten Middelfart, CTO Big Data Data that exists in such large amounts or in such unstructured form that it is difficult
Meeting Big Data challenges in Leadership with Human-Computer Synergy. Presented by Dr. Morten Middelfart, CTO Big Data Data that exists in such large amounts or in such unstructured form that it is difficult
Towards Stability Analysis of Data Transport Mechanisms: a Fluid Model and an Application
 Towards Stability Analysis of Data Transport Mechanisms: a Fluid Model and an Application Gayane Vardoyan *, C. V. Hollot, Don Towsley* * College of Information and Computer Sciences, Department of Electrical
Towards Stability Analysis of Data Transport Mechanisms: a Fluid Model and an Application Gayane Vardoyan *, C. V. Hollot, Don Towsley* * College of Information and Computer Sciences, Department of Electrical
Edukacja matematyczna w przedszkolu
 Edukacja matematyczna w przedszkolu Krystyna Żuchelkowska Edukacja matematyczna w przedszkolu Toruń 2019 Recenzenci dr hab. Marzenna Magda-Adamowicz, prof. Uniwersytetu Zielonogórskiego dr hab. Andrzej
Edukacja matematyczna w przedszkolu Krystyna Żuchelkowska Edukacja matematyczna w przedszkolu Toruń 2019 Recenzenci dr hab. Marzenna Magda-Adamowicz, prof. Uniwersytetu Zielonogórskiego dr hab. Andrzej
